Differential protection of transformers
 Differential protection is used as the main protection of transformers in case of damage to their windings, inputs and busbars. Due to its relative complexity, differential protection is installed only on single-operating transformers of 6300 kVA and above, on transformers operating in parallel with a capacity of 4000 kVA and above, and on transformers with a capacity of 1000 kVA and above, if the breaking current does not provide a protective effect, and the overcurrent protection has a time delay of more than 1 s.
Differential protection is used as the main protection of transformers in case of damage to their windings, inputs and busbars. Due to its relative complexity, differential protection is installed only on single-operating transformers of 6300 kVA and above, on transformers operating in parallel with a capacity of 4000 kVA and above, and on transformers with a capacity of 1000 kVA and above, if the breaking current does not provide a protective effect, and the overcurrent protection has a time delay of more than 1 s.
Differential protection is based on the principle of comparing the values of the currents at the beginning and at the end of the protected zone, for example, the beginning and end of the windings of a power transformer, generator, etc. In particular, the area between current transformers mounted on the upper and lower sides of the power transformer is considered a protected area.
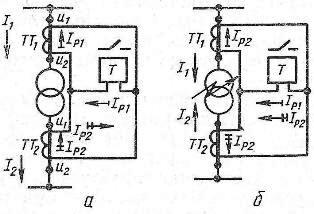
The operation of differential protection is illustrated in fig. Current transformers TT1 and TT2 are installed on both sides of the transformer, the secondary windings of which are connected in series. A current relay T is connected in parallel to them.If the characteristics of the current transformers are the same, then in normal mode, as well as in case of an external short circuit, the currents in the secondary windings of the current transformers will be equal, their difference will be zero, the current will not flow through the winding of the current relay T, therefore the protection it will not work.
In case of a short circuit in the transformer and at any point in the protected area, for example in the winding of the transformer, a current will flow through the winding of the relay T and if its value is equal to or greater than the operating current of the relay, then the relay will operate and through the appropriate auxiliary devices will turn off the damaged section. This system will operate phase-to-phase and turn-to-turn.
Rice. 1. Differential protection of the transformer: a — current distribution during normal operation, b — the same with a short circuit in the transformer
Differential protection has high sensitivity and is fast-acting, since it does not require a time delay, it can be carried out with an instantaneous action, which is its main positive property. However, it does not provide protection against external short circuits and can cause false breaks if there is an open circuit in the secondary bonding wires.
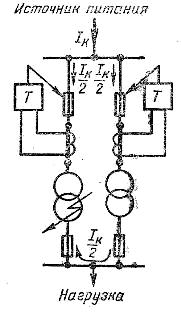
Rice. 2. Differential protection of two transformers operating in parallel