Selsyns: purpose, device, principle of action
 Selsyns are a special type of alternating current electrical machine with power from a few watts to several hundred watts (less than a kilowatt). Serves selsyn to remotely transmit the mechanical angle of rotation electrically between devices that have no mechanical connection to each other.
Selsyns are a special type of alternating current electrical machine with power from a few watts to several hundred watts (less than a kilowatt). Serves selsyn to remotely transmit the mechanical angle of rotation electrically between devices that have no mechanical connection to each other.
Each selsin has a stator and a rotor on which the alternating current windings are located. There are coils with a single winding on the stator and a winding with three windings on the rotor, and vice versa, with a winding of three windings on the stator and a winding with one winding on the rotor, and finally, with a winding with three windings on the stator and with the same winding on the rotor.
According to their purpose in autoregulation schemes, selsyns are divided into:
- selsyn sensors,
- selsyn receivers
- differential.
To understand the operation of selsyn, consider Fig. 1, a.
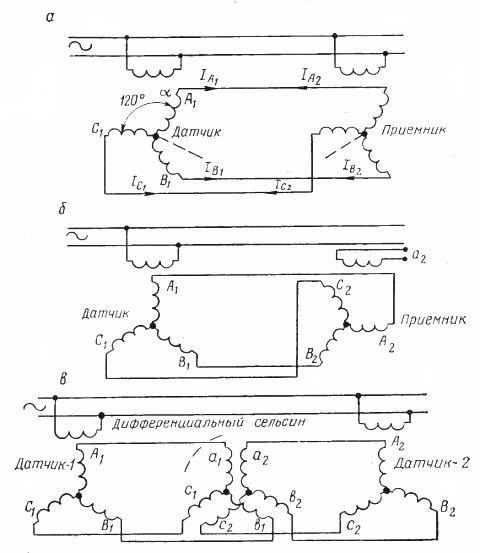
Rice. 1. Schemes for turning on selsin: a — according to the system sensor — receiver; b — transformer receiver in transformer mode; c — differential
The selsyn-sensor and the selsyn-receiver with their single-winding stator windings are connected to the same AC network, and the three-winding rotor windings are connected to each other. If you now rotate the sensor rotor to any angle, then the receiver rotor will rotate to the same angle. If the sensor rotor rotates continuously at a random speed, then the receiver rotor will rotate at the same speed.
The action of the Selsin connection is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, which is as follows. The alternating current in the single-winding stator winding induces currents in the three-winding rotor winding, the values of which depend on the relative position of the rotor and stator windings.
If the rotors of the two selsins are equally spaced with respect to their stators, the currents in the connecting wires of the rotors are equal and opposite to each other, and therefore the current in each coil is zero. As a result, the shaft torque of both selsyn is zero.
If you now manually or otherwise turn the rotor of the selsin sensor to a certain angle, then the balance of currents between the rotors will be disturbed, and a torque will appear on the shaft of the selsin receiver, due to which its rotor will rotate, while the imbalance of the currents disappear. That is, until this rotor takes the same position as the synchrosensor.

In autoregulation systems, the selsyn receiver often operates in transformer mode (Fig. 1, b). In this case, the rotor of the receiver is fixed stationary, and its stator winding is disconnected from the network. In this coil e is induced. etc. v. on the side of the rotor, through the windings of which currents flow due to the position of the rotor of the selsyn sensor.This means that the value of e. etc. with the terminals, the rotor of the receiver is proportional to the angle of rotation of the sensor.
In the initial position, the rotors are displaced by 90 ° relative to each other, and in this case e. etc. s. is zero. Now that the rotor sensor is rotated, e will be induced on the receiver rotor. etc. with Ep, proportional to the angle of divergence of the rotors
Epr = Emax x sinθ
The differential selsyn is used in cases where it is necessary to control the difference in the rotation angles of two axes, i.e. their discrepancy. In this case, two selsin sensors are located on two shafts, the speeds of which are compared with each other. The rotors of these selsins are connected by three-winding windings to the three-winding windings of the stator and the rotor of the third selsin, which is differential (Fig. 1 , in). The rotation angle of the selsyn differential rotor is equal to the difference between the rotation angles of the selsyn sensors.
