Types of electrical capacitors
 Structurally, each capacitor can be represented by two conductive areas (usually plates), on which electric charges of opposite signs accumulate and a dielectric zone between them. The materials used for them and the sizes of the plates with different properties of the insulating layer affect the electrical characteristics of the structure and its area of application. They also define classification possibilities.
Structurally, each capacitor can be represented by two conductive areas (usually plates), on which electric charges of opposite signs accumulate and a dielectric zone between them. The materials used for them and the sizes of the plates with different properties of the insulating layer affect the electrical characteristics of the structure and its area of application. They also define classification possibilities.
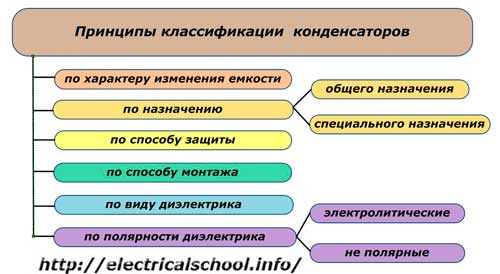
Principles of systematization
General purpose capacitors widely distributed, used in many fields, especially in electronics. They have no special requirements for working conditions. But special-purpose models must work reliably at a certain value of voltage, frequency, current pulses, large electromagnetic disturbances or increased currents when starting motors and other special factors.
Classification principles for capacity regulation
The main criterion for a capacitor is its capacity. The nature of its change determines the mechanical design.
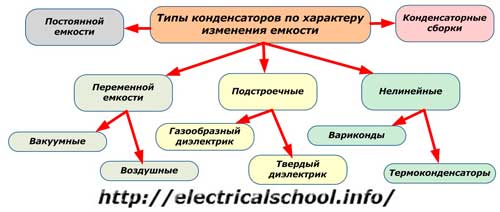
Constant capacity models cannot change it during operation, this is done by specially designed products with variable capacity and different management methods:
-
mechanical adjustment of the mutual position of the plates;
-
supply voltage deviation;
-
heating or cooling.
Trimmer capacitors are not designed for long-term, constant operation in a circuit with on-line capacitance regulation. Their purpose is the initial adjustment and periodic adjustment of the parameters of electric circuits with a small range of capacity adjustment.
Non-linear capacitors change the capacitance depending on the value of the applied voltage or the temperature of the working environment, but not in a straight line. Varikondami are called structures in which the capacitance depends on the potential difference. attached to the plates and thermal capacitors — from heating or cooling.

Principles of classification by installation methods and protection from external influences
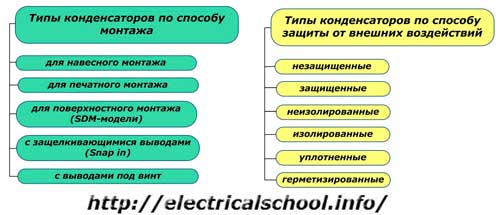
Surface mount capacitors feature a wide variety of implemented conclusions that can be generated:
-
made of soft or hard alloy;
-
with axial or radial arrangement;
-
round profile;
-
rectangular strip;
-
with supporting screw;
-
under the threaded pin;
-
with fastening using a screw or bolt.
Capacitors designed for printed wiring are available with non-elastic round leads for easy placement on electronic component boards.
Surface mount devices are usually denoted by the index «SDM». Their peculiarity lies in the fact that parts of the body serve as conductors of the plates.
Including capacitors (Snap in) belong to the latest modern developments. They are equipped with cables, which, when installed in the holes of the board, are firmly connected to it. This is done for convenience of soldering.
Models with screw terminals have a thread for connection to the circuit. they are used in power circuits and power supplies operating at high currents. These cables are easy to attach to heatsinks to reduce thermal stress.
Unprotected capacitors are designed to work in normal conditions, and protected - in high humidity.
Non-insulated capacitors They differ from insulated ones in the dielectric properties of the case and the possibility of touching the chassis of the device or the current-carrying parts of the circuit.
I have compacted models, the body is filled with organic materials.
Sealed capacitors equipped with a housing that isolates the internal working space from the influence of the environment.
Principles of dielectric classification
The qualitative properties of the dielectric in the capacitor affect the value of the insulation resistance between the plates and, therefore, the stability of capacity maintenance, allowable losses and other electrical characteristics.
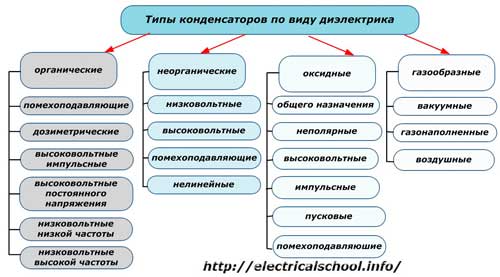
Organic dielectric products made on the basis of various brands of capacitor paper, films and their combinations.
Interference suppression structures reduce electromagnetic field interference, have low inductance.
Dosimetric models are designed to perceive a low level of current loads, have a small self-discharge and significant insulation resistance.
Separation by high voltage and low voltage capacitors a little conditional.As a critical value for determining their limits, a voltage of the order of 1600 volts is taken.
I have pulse products with high voltage. The dielectric is paper or combined materials, and for structures with constant voltage, polystyrene, paper, polytetrafluoroethylene and their combinations are chosen.
The value 104 ... 105 ... 107 Hz is taken as the definition of the frequency limit for the operation of low-voltage capacitors.
Low-frequency dielectric capacitors use polar or slightly polar organic films with a dielectric loss tangent depending on the frequency of the transmitted signal, and high-frequency films based on polystyrene and fluoroplastic films have characteristics that are not affected by the frequency of the transmitted signal.
Inorganic dielectric models use mica, glass, ceramics, glass enamel and glass ceramics. They have a thin layer of metal in the form of a foil over the dielectric or it is deposited.
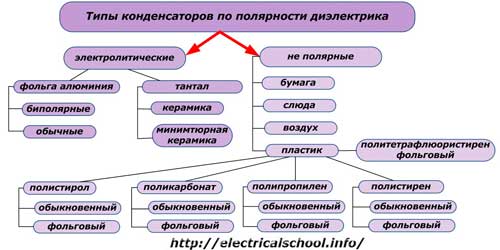
Oxide capacitors also have a second name — electrolytic... They have a dielectric of an oxide layer created electrochemically on a metal anode: aluminum, tantalum or niobium. Their cathode is a liquid electrolyte that fills a fabric or paper gasket in aluminum or tantalum structures. In oxide-semiconductor models based on manganese dioxide, the electrolyte can be a gel or a liquid.
Gas, air or vacuum based dielectric capacitors can be created with constant or adjustable capacitance. They have the lowest dissipation factor and the most stable electrical parameters. Therefore, they are used in high voltage and high frequency equipment.
Vacuum capacitors differ in the simplicity of the device, less loss, better temperature stability, vibration resistance.
Also, capacitors are classified according to the shape of the plates. They are created:
-
apartment;
-
cylindrical;
-
spherical.