Electrostatic filters — device, principle of operation, areas of application
The ability to breathe fresh air is our physiological need, a guarantee of health and longevity. However, powerful modern industrial enterprises pollute the environment and atmosphere with industrial emissions that are dangerous for humans.
Ensuring air purity during technological processes in enterprises and removing harmful impurities from it in everyday life - these are the tasks that electrostatic filters perform.
The first such design was registered in US patent No. 895729 in 1907. Its author, Frederick Cottrell, was engaged in researching methods for separating suspended particles from gaseous media.
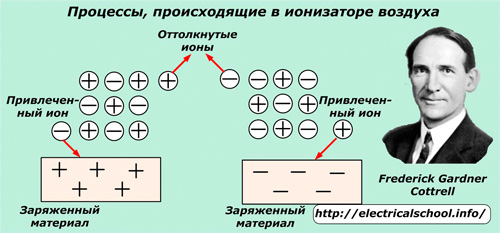
For this, he used the action of the basic laws of the electrostatic field, passing gaseous mixtures with fine solid impurities through electrodes with positive and negative potentials. Oppositely charged ions with dust particles are attracted to the electrodes, settle on them, and the ions of the same name are repelled.
This development served as a prototype for the creation of modern electrostatic filters.
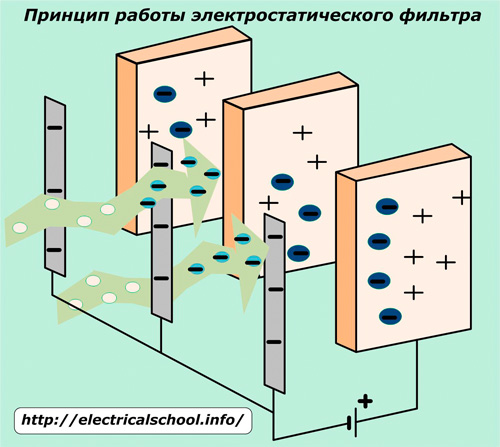
Potentials of opposite signs from a direct current source are applied to lamellar sheet electrodes (commonly referred to by the term «precipitation») assembled in separate sections and placed between them metal filament-grids.
The magnitude of the voltage between the network and the plates in household appliances is several kilovolts. For filters operating in industrial facilities, it can be increased by an order of magnitude.
Through these electrodes, fans pass through special ducts a flow of air or gases containing mechanical impurities and bacteria.
Under the influence of high voltage, a strong electric field is formed and the surface corona discharge flows from the filaments (corona electrodes). This leads to ionization of the air adjacent to the electrodes with the release of anions (+) and cations (-), an ionic current is created.
Ions with a negative charge under the action of an electrostatic field move to the collecting electrodes, simultaneously charging the impurity counters. These charges are acted upon by electrostatic forces that create a buildup of dust on the collecting electrodes. In this way, the air driven through the filter is purified.
When the filter is working, the dust layer on its electrodes is constantly increasing. Periodically it should be removed. For household structures, this operation is performed manually. In powerful production plants, the settling electrodes and the corona are mechanically shaken to direct the pollutants into a special hopper, from where they are removed for disposal.
Industrial electrostatic precipitator design features
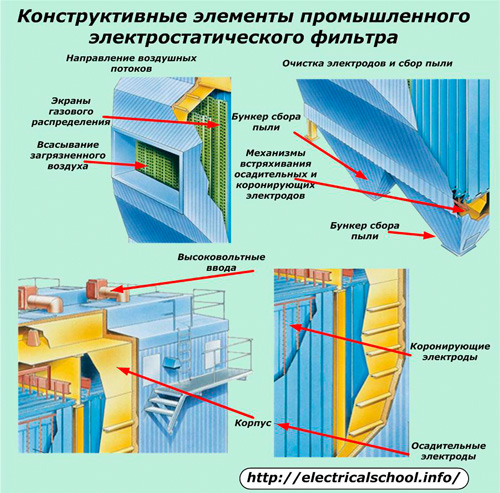
The details of its body can be made from concrete blocks or metal structures.
Gas distribution screens are installed at the inlet of the polluted air and at the outlet of the purified air, which optimally direct the air masses between the electrodes.
Dust collection takes place in silos, which are usually flat-bottomed and equipped with a scraper conveyor. Dust collectors are produced in the form of:
-
trays;
-
inverted pyramid;
-
truncated cone.
Electrode shaking mechanisms work on the principle of a falling hammer. They can be located below or above the plates. The operation of these devices significantly speeds up the cleaning of the electrodes. Best results are achieved with designs where each hammer acts on a different electrode.
To create a high-voltage corona discharge, standard transformers with rectifiers operating from an industrial frequency network or special high-frequency devices of several tens of kilohertz are used. Microprocessor control systems are involved in their work.
Among the different types of discharge electrodes, stainless steel spirals work best for optimal filament tension. They are less polluted than all other models.
The constructions of the collecting electrodes in the form of plates with a special profile are combined in sections created for uniform distribution of surface charges.
Industrial filters for capturing highly toxic aerosols
An example of one of the schemes of operation of such devices is shown in the photo.
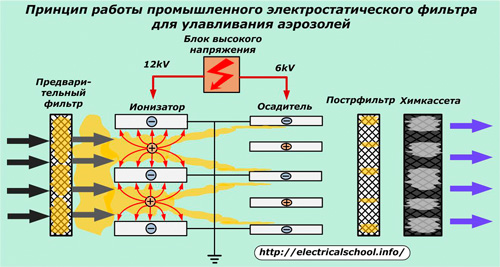
These structures use a two-stage air purification zone contaminated with solid impurities or aerosol vapors.The largest particles are deposited on the pre-filter.
The flux is then directed to an ionizer with a corona wire and ground plates. About 12 kilovolts are supplied from the high voltage unit to the electrodes.
As a result, a corona discharge occurs and the impurity particles become charged. The blown air mixture passes through a precipitator, in which harmful substances are concentrated on grounded plates.
A postfilter located after the precipitator captures the remaining unsettled particles. The chemical cartridge additionally cleans the air from the remaining impurities of carbon dioxide and other gases.
Aerosols applied to the plates simply flow down the shaft under the influence of gravity.
Applications of industrial electrostatic precipitators
Purification of polluted air is used in:
-
coal-fired power plants;
-
sites for the production of fuel oil;
-
waste incineration plants;
-
industrial boilers for chemical recovery;
-
industrial limestone kilns;
-
technological boilers for burning biomass;
-
ferrous metallurgy enterprises;
-
production of non-ferrous metals;
-
sites of the cement industry;
-
agricultural enterprises and other industries.
Possibilities for cleaning a contaminated environment
The diagrams of operation of powerful industrial electrostatic filters with various harmful substances are shown in the diagram.
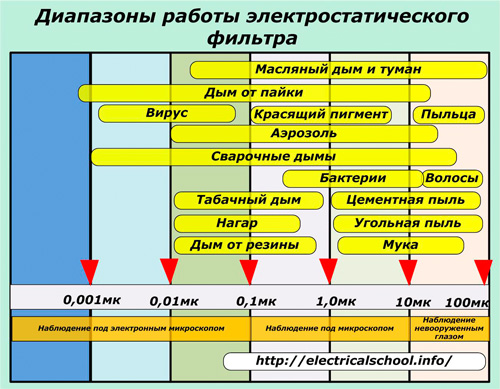
Characteristics of filter structures in household appliances
Air purification in residential premises is carried out:
-
air conditioners;
-
ionizers.
The principle of operation of the air conditioner is shown in the photo.
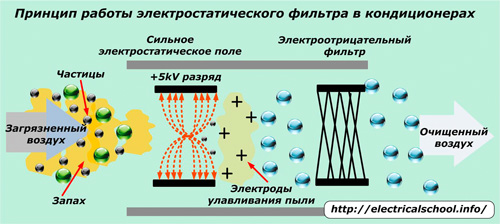
Contaminated air is driven by the fans through the electrodes with a voltage of about 5 kilovolts applied to them. Microbes, mites, viruses, bacteria in the air stream die and impurity particles, being charged, fly to the dust collection electrodes and settle on them.
At the same time, the air is ionized and ozone is released. Since it belongs to the category of the strongest natural oxidizers, all living organisms in the air conditioner are destroyed.
Exceeding the normative concentration of ozone in the air is inadmissible according to sanitary and hygienic standards. This indicator is closely monitored by the supervisory authorities of air conditioner manufacturers.
Characteristics of a household ionizer
The prototype of modern ionizers is the development of the Soviet scientist Alexander Leonidovich Chizhevsky, which he created to restore the health of people exhausted in prison from the heaviest hard labor and poor conditions of detention.
Due to the application of high voltage voltage to the electrodes of a source suspended from the ceiling instead of the lighting chandelier, ionization occurs in the air with the release of healthy cations. They were called "air ions" or "air vitamins".
Cations give vital energy to the weakened body, and the released ozone kills disease-causing microbes and bacteria.
Modern ionizers are devoid of many shortcomings that were in the first designs. In particular, the concentration of ozone is now strictly limited, measures are taken to reduce the effect of a high-voltage electromagnetic field, and bipolar ionization devices are used.
It is worth noting, however, that many people still confuse the purpose of ionizers and ozonators (production of ozone in the maximum amount), using the latter for other purposes that greatly harm their health.
According to the principle of their operation, ionizers do not perform all the functions of air conditioners and do not purify the air from dust.

