What is nominal current in electrical engineering
Academician Ozhegov's Explanatory Dictionary of the Russian Language explains the meaning of the word "nominal", as designated, named, but not fulfilling its duties, appointment, that is, fictitious.
This definition quite accurately explains the electrical terms of rated voltage, current, and power. They seem to be there, defined and defined, but really only serve as guidelines for electricians. The actual numerical expressions of these parameters actually differ from the set values.
For example, we are all familiar with an alternating single-phase network with a voltage of 220 volts, which is considered nominal. In fact, its value according to GOST can only reach the upper limit of 252 volts. This is how the state standard works.
The same picture can be seen with the rated current.
Principle of determining the nominal current
As a basis for choosing its value, the maximum possible thermal heating of electrical wires, including their insulation, which must work reliably under load for an unlimited time, was taken.
At rated current, a thermal balance is maintained between:
-
heating of wires from the temperature effect of electric charges, described by the action of the Joule-Lenz law;
-
cooling due to removal of part of the heat to the environment.
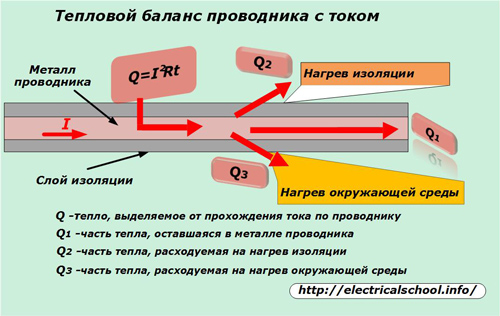
In this case, the heat Q1 should not affect the mechanical and strength characteristics of the metal, and Q2 — on the change in the chemical and dielectric properties of the insulating layer.
Even if the current rating is slightly exceeded, after a certain period of time it will be necessary to remove the voltage from the electrical equipment in order to cool the metal of the current conductor and the insulation. Otherwise, their electrical properties will be impaired and a breakdown of the dielectric layer or deformation of the metal will occur.
Any electrical equipment (including current sources, its consumers, connecting wires and systems, protective devices) is calculated, designed and manufactured to operate at a certain rated current.
Its value is indicated not only in the technical factory documentation, but also on the housing or nameplates of the electrical equipment.

The photo above clearly shows the current ratings of 2.5 and 10 amps which are made by stamping in the manufacture of the electrical plug.
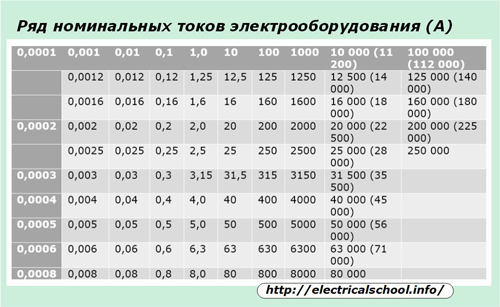
In order to standardize the equipment, GOST 6827-76 introduces a number of rated currents at which almost all electrical installations must operate.
How to select the protective device for rated current
Since the rated current determines the possibility of long-term operation of electrical equipment without any damage, then all current protection devices are configured to work when it is exceeded.
In practice, there are often situations when, for a short period of time, an overload occurs in the power circuit for various reasons. In this case, the temperature of the metal of the conductor and the insulating layer does not have time to reach the limit when their electrical properties are violated.
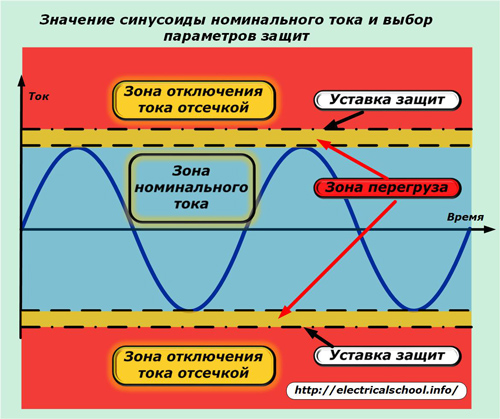
For these reasons, the overload zone is divided into a separate zone, which is limited not only by the size, but also by the duration of the action. When the critical temperature values of the insulation layer and the metal of the conductor are reached, the voltage from the electrical installation must be removed to cool it down.
These functions are performed by thermal overload protections:
-
circuit breakers;
-
thermal releases.
They perceive the heat load and adjust to turn off with a certain time. The setting of protections that perform «momentary» interruption of the load is slightly higher than the overload current. The term "instantaneous" actually defines the action in the shortest possible period of time. For today's fastest overcurrent protections, interruption takes place in just under 0.02 seconds.
The operating current in normal power mode is usually less than the nominal value.
In the given example, the case is analyzed for AC circuits. In DC voltage circuits, there is no fundamental difference in the relationship between the operating, rated current and the choice of settings for the protective operation.
How the circuit breaker is configured to operate at rated current
In the protection of industrial devices and household electrical networks, the most common are automatic switches, which combine in their design:
-
thermally delayed releases;
-
current interruption, very fast shutdown of the emergency mode.
In this case, circuit breakers are manufactured for rated voltage and current. Protective devices are selected according to their size to work in the specific conditions of a certain circuit.
For this purpose, the standards define 4 types of current-time characteristics for different machine designs. They are marked with Latin letters A, B, C, D and are designed for guaranteed disconnection of faults with a multiple of the rated current from 1.3 to 14.
The time-current circuit breaker, taking into account the ambient temperature, is selected for a certain type of load, for example:
-
semiconductor devices;
-
lighting systems;
-
circuits with mixed loads and moderate inrush currents;
-
circuits with high overload capacity.
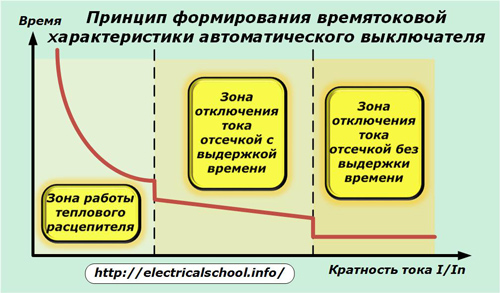
The current-time characteristic can consist of three zones of action, as shown in the picture, or two (without the middle).
The designation of the rated current can be found on the machine housing. The picture shows a switch that is labeled with a 100 amp rating.
This means that it will work (turn off) not from the rated current (100 A), but from its excess. Suppose that if the interrupter of the machine is set to a multiple of 3.5, then a current of 100×3.5 = 350 amps or more will be stopped by it without time delay.
When the thermal release is set to a multiple of 1.25, then when a value of 100×1.25 = 125 amps is reached, the trip will occur after some time, for example one hour. In this case, the circuit will operate with overload during this period.
It should be borne in mind that other factors related to the maintenance of the protection temperature regime also affect the machine shutdown time:
-
environmental conditions;
-
the degree of filling of the switchboard with equipment;
-
the possibility of heating or cooling from external sources.
How are the wiring and circuit breaker rated?
To determine the main electrical parameters of protections and conductors, the load applied to them must be taken into account. To do this, it is calculated according to the nominal power of the devices related to the work, taking into account the coefficient of their employment.
For example, a dishwasher, a multicooker, an electric oven and a microwave oven are connected to the output group located in the kitchen, which consumes a total power in normal mode of 5660 watts (taking into account the switching frequency).
The nominal voltage of the household network is 220 volts. Determine the load current that will flow through the conductors and protective devices by dividing the power by the voltage. I = 5660/220 = 25.7 A.
Next, we look at a table with a number of rated currents for electrical equipment. It does not have a circuit breaker for such a current. But manufacturers produce machines for 25 amps. Its value is closest to our goals. Therefore, we choose it as the basis for a protective device for wiring consumers of the output group.
Next, we need to decide on the material of the wires and the cross-section. Let's take copper as a base, since aluminum wiring, even for household purposes, is no longer popular due to its characteristics.
Electrician's manuals contain tables for selecting conductors of various materials for current loading. Let's take our case, taking into account the fact that the wiring is done with a separate PE-insulated cable hidden in the wall gutter. Temperature limits are assumed to correspond to room conditions.
The table will provide us with information that the minimum permissible cross-section of a standard copper wire for our case is 4 mm square. You cannot take less, but it is better to increase it.
Sometimes there is a problem with choosing a degree of protection for already working wiring. In this case, it is fully justified to determine the load current of the consumer network with an electrical measuring instrument and compare it with that calculated by the above theoretical method.
Thus, the term "rated current" helps electricians navigate the technical characteristics of electrical equipment.
