Types of asynchronous motors, varieties, what are the motors
AC motors, which use the rotating magnetic field of the stator for their operation, are currently very common electrical machines. Those of them in which the speed of the rotor differs from the frequency of rotation of the magnetic field of the stator are called asynchronous motors.

Due to the large capacity of energy systems and the long length of electrical networks, the energy supply to consumers is always carried out on alternating current. Therefore, it is natural to strive for maximum use of AC electric motors. This, it seems, frees you from the need for multiple energy conversions.
Unfortunately, AC motors are significantly inferior to DC motors in terms of their properties and especially controllability, which is why they are mainly used in installations where speed control is not required.
Relatively recently controlled AC systems with connecting AC motors through frequency converters.
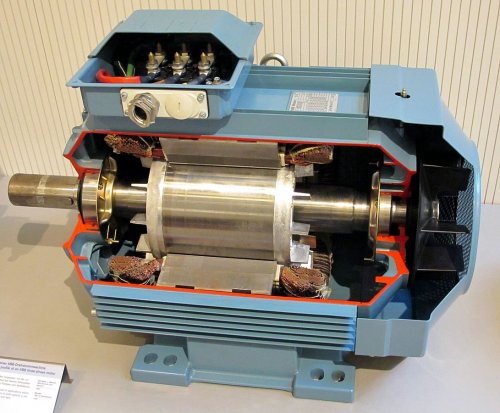
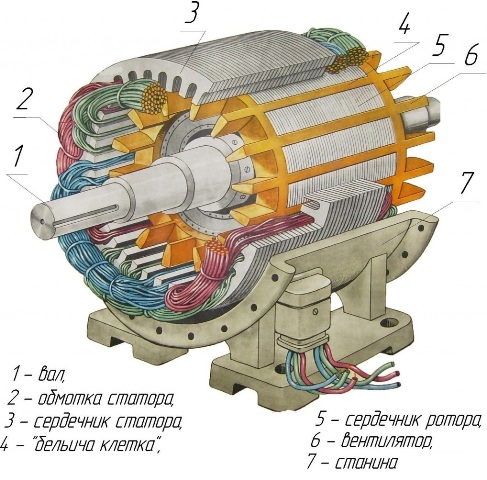
A squirrel cage induction motor is a rotating transformer whose primary winding is the stator and the secondary winding is the rotor. There is an air gap between the stator and the rotor. As in any real transformer, each coil also has its own resistance.
When the motor is connected to the electrical network, a magnetic field arises in the stator, which rotates synchronously with the frequency of the power network. Due to the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction under the action of the stator magnetic field in the electrically closed rotor windings, electricity.
The induced electric current in the rotor will create its own magnetic field which interacts with the rotating magnetic field of the stator. As a result, the rotor begins to rotate and a mechanical moment proportional to the stator current appears on the motor shaft.
Sectional model of a three-phase induction motor
A characteristic feature of an asynchronous motor is that due to the interaction of the fields of the stator and the rotor, the speed of rotation of the motor shaft is slightly less than the frequency of the supply network. The difference between the frequency of the mains and the speed of rotation is called slipping.
Asynchronous motors are widely used in various sectors of the economy and production due to their simplicity of manufacture and high reliability. Meanwhile, there are four main types of induction motors:
-
single-phase asynchronous squirrel-cage motor;
-
two-phase squirrel-cage induction motor;
-
three-phase squirrel-cage asynchronous motor;
-
three-phase wound-rotor asynchronous motor.

A single-phase induction motor contains only one working stator winding to which alternating current is supplied while the motor is running.But to start the motor, there is an additional winding on its stator, which is briefly connected to the network through a capacitor or inductance, or it is short-circuited. This is necessary to create an initial phase shift so that the rotor starts spinning, otherwise the pulsating stator magnetic field would not push the rotor into place.
The rotor of such a motor, like any squirrel-rotor induction motor, is a cylindrical core with molded aluminum channels, with co-molded ventilation fins. Such a squirrel cage rotor is called a squirrel cage rotor. Single-phase motors are used in low power applications such as room fans or small pumps.

Two-phase induction motors are most efficient when operating on a single-phase AC network. They contain two working stator windings located perpendicularly, and one of the windings is connected directly to the alternating current network, and the second through a phase-shifting capacitor, so a rotating magnetic field is obtained, and without a capacitor, the rotor itself will not move.
These motors also have a squirrel-cage rotor and their application is much wider than that of single-phase. There are now washing machines and various machines. Two-phase motors for supply from single-phase networks are called capacitor motors, because the phase-shifting capacitor is often an integral part of them.

A three-phase induction motor contains three stator windings offset relative to each other, so that when connected to a three-phase network, their magnetic fields are displaced in space relative to each other by 120 degrees.When a three-phase motor is connected to a three-phase AC network, a rotating magnetic field is produced that drives the cage rotor.
The stator windings of a three-phase motor can be connected in star or delta connection, and a higher voltage is required to supply the motor in star connection than in delta connection, and therefore two voltages are specified on the motor for example: 127 /220 or 220/380. Three-phase motors are indispensable for driving various metal-cutting machines, winches, circular saws, cranes, etc.

A three-phase asynchronous motor with a phase rotor has a stator similar to the types of motors described above, a laminated magnetic circuit with three windings placed in its channels, but the aluminum rods are not cast into the phase rotor, and the complete -phase three-phase winding is already laid star connection… The star ends of the phase rotor winding are led to three slip rings mounted on the rotor shaft and electrically isolated from it.
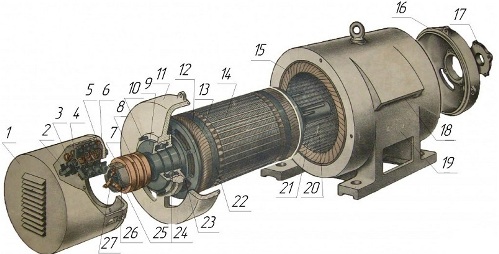
1 — housing with grids, 2 — brushes, 3 — brush stroke with brush holders, 4 — brush fixing pin, 5 — cable brushes, 6 — block, 7 — insulating sleeve, 8 — slip rings, 9 — outer bearing cover, 10 — stud for fastening the box and bearing caps, 11 — rear end shield, 12 — rotor coil, 13 — coil holder, 14 — rotor core, 15 — rotor coil, 16 — shield on the front end, 7 — outer bearing cover, 18 — vents, 19 — frame, 20 — stator core, 21 — inner bearing cover studs, 22 — bandage, 23 — inner bearing cover, 21 — bearing, 25 — shaft, 26 — sliding rings, 27 — rotor windings
A three-phase AC voltage is supplied to the rings through brushes, and the connection can be made both directly and through rheostats. Of course, motors with rotary engines are more expensive, but theirs Starting torque under load is significantly higher than that of squirrel-cage engine types. Due to the increased power and high starting torque, this type of motor has found application in elevator and crane drives, that is, where the device is started under load, and not at idle.
Read more about this type of engine here: Asynchronous electric motors with a wound rotor
See also: How induction motors differ from synchronous motors

