Transformer oil — purpose, application, characteristics
Transformer oil is a refined oil fraction, that is, mineral oil. It is obtained by distillation of oil, where this fraction boils at 300 — 400 ° C. Depending on the grade of the raw material, the properties of transformer oils are different. The oil has a complex hydrocarbon composition where the average molecular weight ranges from 220 to 340 amu. The table shows the main components and their percentage in the composition of transformer oil.
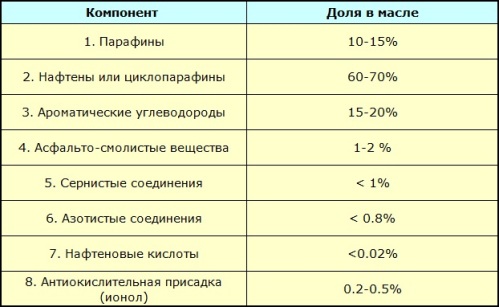
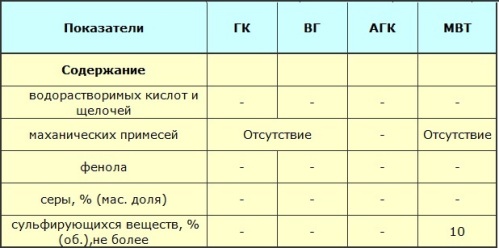
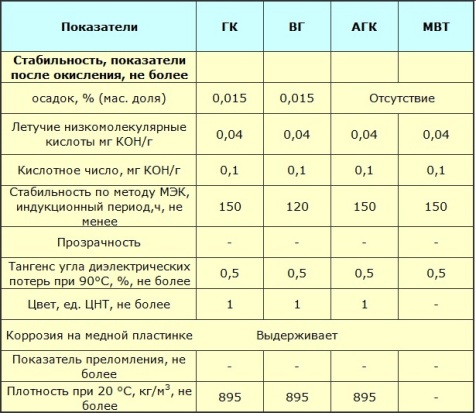
The properties of transformer oil as an electrical insulator are mainly determined by the value dielectric loss tangent… Therefore, the presence of water and fibers in the oil is completely excluded, since any mechanical impurities worsen this indicator.
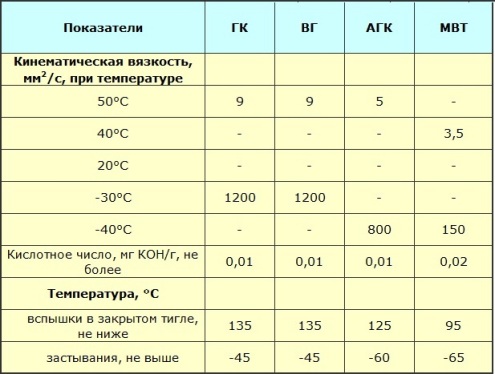
The outflow temperature of the transformer oil is from -45 ° C and lower, this is important to ensure its mobility in low temperature operating conditions. The lowest viscosity of the oil contributes to effective heat dissipation, even at temperatures from 90 to 150 ° C in case of outbreaks.For different brands of oils, this temperature can be 150 ° C, 135 ° C, 125 ° C, 90 ° C, not lower.
An extremely important property of transformer oils is their stability under oxidizing conditions; the transformer oil must maintain the required parameters for a long period of operation.
Regarding RF in particular, all brands of transformer oils used in industrial equipment are necessarily inhibited by the antioxidant additive ionol (2,6-di-tert-butylparacresol, also known as agidol-1). The additive interacts with active peroxide radicals occurring in the hydrocarbon oxidation reaction chain. Thus, inhibited transformer oils have a pronounced induction period during oxidation.
Additive-susceptible oils oxidize slowly at first because the resulting oxidation chains are broken by the inhibitor. When the additive is used up, the oil oxidizes at the normal rate as without the additive. The longer the induction period of oil oxidation, the higher the effectiveness of the additive.
Much of the effectiveness of the additive is related to the hydrocarbon composition of the oil and the presence of non-hydrocarbon impurities that promote oxidation, which can be nitrogen bases, petroleum acids, and oxygen-containing products of oil oxidation.
When the petroleum distillate is refined, the aromatic content is reduced, the non-hydrocarbon inclusions are removed, and ultimately the stability of the ionol-inhibited transformer oil is improved. Meanwhile, there is an international standard "Specification for fresh petroleum insulating oils for transformers and circuit breakers".
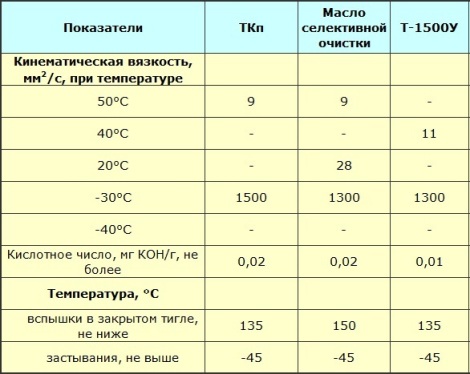
Transformer oil is flammable, biodegradable, almost non-toxic and does not deplete the ozone layer. The density of transformer oil varies from 840 to 890 kilograms per cubic meter. One of the most important properties is viscosity. The higher the viscosity, the higher the dielectric strength. However, for normal operation in power transformers and in circuit breakers, the oil must not be very viscous, otherwise the cooling of the transformers will not be effective and the circuit breaker will not be able to break the arc quickly.
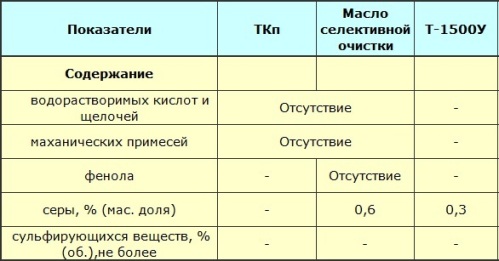
A trade-off is necessary here in terms of viscosity. Typically kinematic viscosity at 20 °C, most transformer oils are in the range of 28 to 30 mm2/s.
Before filling the device with oil, the oil is purified by deep thermal vacuum treatment. According to this guidance document "Scope and Standards for Testing of Electrical Equipment" (RD 34.45-51.300-97), the concentration of air in transformer oil poured into nitrogen or film shielded transformers, in sealed measuring transformers and in sealed bushings must not to be higher than 0.5 (determined by gas chromatography), and the maximum water content is 0.001% by weight.
For power transformers without film protection and for permeable bushings, a water content of not more than 0.0025% by mass is permissible. As for the content of mechanical impurities, which determines the oil purity class, it should not be worse than the 11th for equipment with a voltage of up to 220 kV and not worse than the 9th for equipment with a voltage of -higher than 220 kV. The breakdown voltage, depending on the operating voltage, is shown in the table.
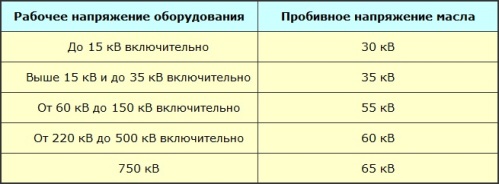
When the oil is filled, the breakdown voltage is 5 kV lower than that of the oil before filling in the equipment. It is allowed to reduce the purity class by 1 and increase the percentage of air by 0.5%.
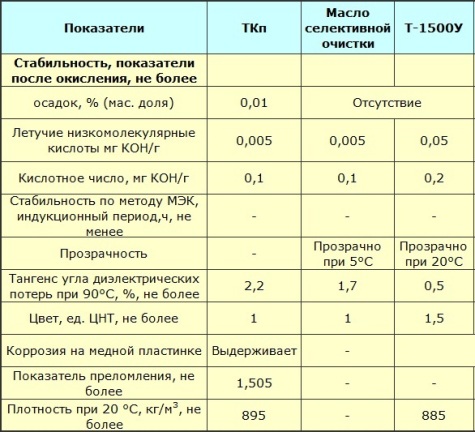
Oxidation conditions (method for determining stability — according to GOST 981-75)
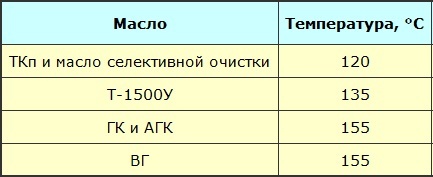
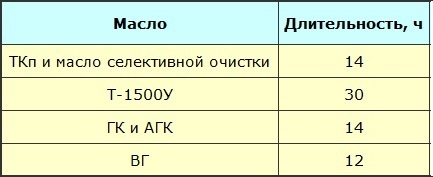
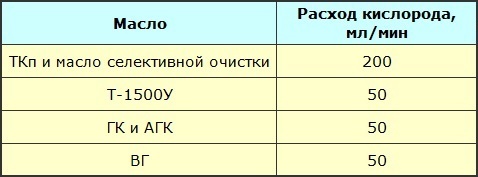
The leakage point of the oil is determined by a test in which a pipe with sealed oil is tilted at 45 ° and the oil remains at the same level for one minute. For fresh oils, this temperature should not be lower than -45 °C.
This parameter is key to oil switches… However, different climate zones have different pour point requirements. For example, in the southern regions it is allowed to use transformer oil with a pouring temperature of -35 ° C.
Depending on the operating conditions of the equipment, the standards may vary, there may be some deviations. For example, arctic varieties of transformer oil should not solidify at temperatures above -60 ° C, and the flash point drops to -100 ° C (the flash point is the temperature at which heated oil produces vapors that become flammable when mixed with air ).
In principle, the ignition temperature should not be lower than 135 ° C. Such characteristics as the ignition temperature (the oil ignites and burns with it for 5 or more seconds) and the self-ignition temperature (at a temperature of 350-400 ° C, the oil ignites even in a closed crucible in the presence of air).

Transformer oil has a thermal conductivity of 0.09 to 0.14 W / (mx K) and decreases with increasing temperature.Heat capacity increases with increasing temperature and can be from 1.5 kJ / (kg x K) to 2.5 kJ / (kg x K).
The coefficient of thermal expansion is related to the standards for the size of the expansion tank, and this coefficient is in the region of 0.00065 1 / K. The resistance of the transformer oil at 90 ° C and under conditions of electric field stress of 0.5 MV / m in in no case should it be higher than 50 Ghm * m.
In addition to viscosity, oil resistance decreases with increasing temperature. Dielectric constant — in the range of 2.1 to 2.4. The tangent of the angle of dielectric losses, as mentioned above, is related to the presence of impurities, so for pure oil it does not exceed 0.02 at 90 ° C under conditions of field frequency 50 Hz, and in oxidized oil it can exceed 0.2.
The dielectric strength of the oil was measured during a 2.5 mm breakdown test with a 25.4 mm electrode diameter. The result should not be lower than 70 kV and then the dielectric strength will be at least 280 kV / cm.

Despite the measures taken, transformer oil can absorb gases and dissolve a significant amount of them. Under normal conditions, 0.16 milliliters of oxygen, 0.086 milliliters of nitrogen, and 1.2 milliliters of carbon dioxide readily dissolve in one cubic centimeter of oil. Obviously the oxygen will start to oxidize a bit. On the contrary, if gases are released, this is a sign of a coil defect. So, due to the presence of gases dissolved in transformer oil, defects in transformers are revealed by chromatographic analysis.
The service life of transformers and oil is not directly related. If the transformer can work reliably for 15 years, it is recommended that the oil be cleaned every year and regenerated after 5 years. In order to prevent the rapid depletion of the oil resource, certain measures are provided, the adoption of which will significantly extend the service life of the transformer oil:
-
Installation of expanders with filters for absorbing water and oxygen, as well as gases separated from oil;
-
Avoiding overheating of the working oil;
-
Periodic cleaning;
-
Continuous oil filtration;
-
Introduction of antioxidants.
High temperatures, the reaction of oil with wires and dielectrics all promote oxidation, which the antioxidant supplement mentioned at the beginning is intended to prevent. But regular cleaning is still required. High-quality oil cleaning returns it to usable condition.
What could be the reason for withdrawing the transformer oil from service? These can be contamination of the oil with permanent substances, the presence of which did not lead to deep changes in the oil, and then it is enough to carry out mechanical cleaning. In general, there are several cleaning methods: mechanical, thermophysical (distillation) and physico-chemical (adsorption, coagulation).
If an accident has occurred, the breakdown voltage has dropped sharply, carbon deposits have appeared, or chromatographic analysis revealed a problem, the transformer oil is cleaned directly in the transformer or in the switch, simply by disconnecting the device from the network.
The service life of oil in transformers can be extended by using antioxidant additives, thermosiphon filters, etc. However, all this does not exclude the need to regenerate used oils.
Therefore, the task of waste oil regeneration is to obtain a well-purified regenerate that meets all fresh oil standards. Stabilizing unstable regenerating substances by adding fresh oil or antioxidant additives makes it possible to use the simplest and most affordable methods for regenerating used transformer oils.
When regenerating transformer oil, it is important to obtain well-purified regenerants, regardless of the regeneration method and the degree of aging of the oil, and stabilization, if the oil is of low stability, must be done artificially - by adding fresh oil or adding with a high stabilizing effect, effective for regenerated oils.
When regenerating used transformer oil, up to 3 fractions of base oils are obtained for the preparation of other commercial oils, such as motor, hydraulic, transmission oils, cutting fluids and grease.
On average, after regeneration, 70-85% of the oil is obtained, depending on the applied technological method. Chemical regeneration is more expensive. When regenerating transformer oil, it is possible to obtain up to 90% of the base oil with the same quality as fresh.
Additionally
A question
Is it possible to dry oil in a working transformer by lifting its cover in dry weather? Will the water evaporate from the oil or, on the contrary, will the oil become moist?
Answer
Dry oil with a breakdown voltage of 40-50 kV contains thousandths of a percent of moisture. To moisten the oil, characterized by a decrease in the breakdown strength of the oil to 15 - 20 kV, hundredths of a percent of moisture is required.
In transformers that have free communication with atmospheric air through an expander (or under a cover), there is a continuous exchange of moisture with air. If the temperature of the oil decreases and the moisture content in it is less than in the air, the oil absorbs moisture from the air according to the law of partial pressures of moisture vapor. In this way, the breakdown voltage of the oil is reduced.
Moisture exchange also takes place between the oil and the transformer insulation (cotton, bakelite) placed in the oil. Moisture moves in insulation from hot parts to cold parts. If the transformer heats up, then moisture passes from the insulation to the oil, and if it cools down, then vice versa.
Since the air humidity is high during the summer months, the breakdown voltage of the oil decreases with free exchange of moisture compared to the winter months.
In winter, when the air humidity is the lowest and the temperature difference between the air and the oil is the greatest, the oil dries out somewhat. In summer, when lightning surges are more likely to affect transformer insulation, the breakdown strength of transformer oil is at its lowest when it should be at its highest.
To eliminate the free exchange of moisture between air and oil, air dryers with an oil seal are used.
Thus, when the transformer cover is open, drying or wetting of the oil may occur.
The oil will dry better in freezing weather when the air contains the least amount of moisture and there is the greatest temperature difference between the oil and the air. But such drying is inefficient and ineffective, so it is not used in practice.
