Bifilar coil and its use
 A bifilar coil is a coil with two parallel wires placed side by side on a common frame and insulated from each other throughout the coil.
A bifilar coil is a coil with two parallel wires placed side by side on a common frame and insulated from each other throughout the coil.
The same word "bifilar" can be translated from English as two-wire or two-wire, therefore a bifilar wire is usually called a wire made in the form of two wires isolated from each other - ordinary two-wire wires can, in principle, be attributed to bifilar wires . That is, the term «bifilar winding» refers to windings made with bifilar wire.
So, depending on the winding direction of two wires and the type of their connection to each other in a bifilar winding, you can get four possible options for the implementation of such windings:
-
Parallel coil, series connection;
-
Parallel winding, parallel connection;
-
The coil is a counter, the connection is in series;
-
Counter winding, parallel connection.
And no matter how the bifilar winding is wound, when it is connected to the circuit, one of two options for the interaction of the currents of the two wires forming it will be realized.
The first option is when the currents are directed in one direction, in this case the magnetic fields of the currents of the two veins are added, resulting in a total magnetic field that will be greater than the magnetic field of each of the bifilar veins separately.
The second option is when the currents are directed in opposite directions, in this case the magnetic fields of the currents of the two cores will cancel each other, as a result of which the total magnetic field will be zero, i.e. inductance of the coil will be close to zero.
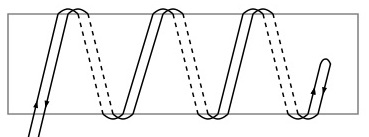
In modern technology, bifilar windings with parallel winding of a series connection (currents are equal and directed in opposite directions) are used to create wire resistors to reduce the parasitic inductance of the element to a minimum (the total magnetic field is close to zero).
In the windings of some transformers and double chokes of switching power supplies, as well as in the windings of some relays, bifilar windings are used to suppress dangerous switching emissions of self-induced EMF.
The two-wire coil has a dual function. The first wire serves as the primary winding of a transformer or inductor, and the second is a protective, limiting winding whose function is to calculate the commutation shock of the EMF. In some relays, the second wire is shorted to itself and dissipates the backwash on itself when the relay opens.
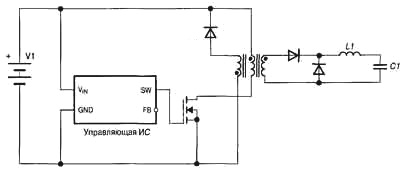
When the power is switched, the protective coil is not short-circuited, it only limits the switching surge of the EMF, directing the energy through the diode back to the power source or to the snubber, and thus the primary winding circuit is protected, the switch voltage does not jump above the safe and the switch (transistor) does not burn.

It deserves special attention Tesla bifilar coil, which the scientist patented in 1894, is US Patent No. 512340. Tesla himself noted in the patent that in order to give the coil a greater self-capacitance, it is necessary to connect two bifilar wires in series so that the currents are directed in one direction, then, although the inductance remains the same, the self-capacitance of such a coil will increase. And the higher the voltage, the stronger will be the effect of this inter-rotating capacitance.
The conclusion is that in a bifilar Tesla coil, the voltage between two adjacent turns is greater than in a conventional single-wire coil with half the voltage applied to the coil.
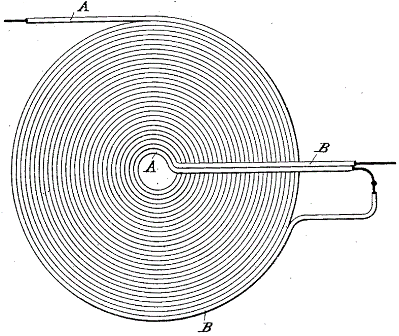
Nikola Tesla uses bifilar windings to give circuits a larger internal capacitance and thus avoids the use of expensive capacitors. In his lectures, the scientist mentions bifilar windings precisely as a tool for increasing the inherent capacity of the charging and working circuits of various high-frequency high-voltage equipment, which he developed both for powering efficient light sources and for transmitting energy over a distance without wires.
