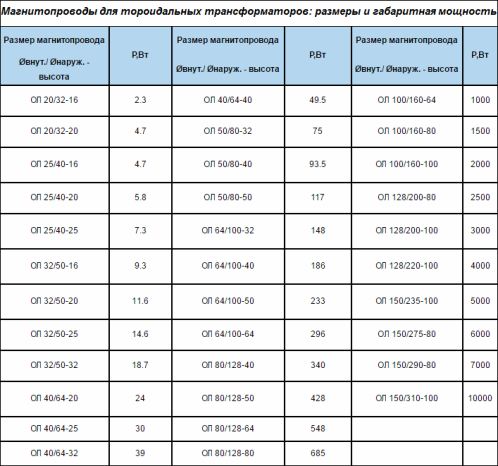
Toroidal transformers — device, application, technical characteristics
 According to the shape of the magnetic circuit, transformers are divided into rod, armored and toroidal. It seems that there is no difference, because the main thing is the power that the transformer can convert. But if you take three transformers with magnetic circuits of different shapes for the same total power, it turns out that the toroidal transformer will show the best performance of all. For this reason, toroidal transformers are most often chosen to power various devices in many industrial areas, of course, due to their high efficiency.
According to the shape of the magnetic circuit, transformers are divided into rod, armored and toroidal. It seems that there is no difference, because the main thing is the power that the transformer can convert. But if you take three transformers with magnetic circuits of different shapes for the same total power, it turns out that the toroidal transformer will show the best performance of all. For this reason, toroidal transformers are most often chosen to power various devices in many industrial areas, of course, due to their high efficiency.
Today, toroidal transformers are used in various industries, and most often toroidal transformers are installed in uninterruptible power supplies, in voltage stabilizers used to power lighting equipment and radio equipment, often toroidal transformers can be seen in medical and diagnostic equipment, in welding equipment etc. …

As you understand, the expression «toroidal transformer» usually means a single-phase mains transformer, supply or measuring, step-up or step-down, in which the toroidal core is equipped with two or more windings.
A toroidal transformer works in the same way as transformers with other basic shapes: lowers or raises voltage, raises or lowers current — converts electricity. But the toroidal transformer differs with the same transmitted power in smaller dimensions and less weight, that is, with better economic indicators.
The main feature of the toroidal transformer is the small total volume of the device, up to half compared to other types of magnetic circuits. Laminated core twice the volume of the toroidal strip core for the same total power. Therefore, toroidal transformers are more convenient to install and connect, and it is no longer so important whether we are talking about indoor or outdoor installation.

Any specialist will say that the toroidal shape of the core is ideal for a transformer for several reasons: firstly, economy of material in production, secondly, the windings evenly fill the entire core, distributed over its entire surface, leaving no unused places, thirdly . Because the windings are shorter, the efficiency of toroidal transformers is higher due to the lower resistance of the winding wires.
Cooling of the coils is another important factor. The coils are cooled efficiently by being arranged in a toroidal shape, therefore the current density can be higher. In this case, the losses in the iron are minimal and the magnetizing current is much smaller.As a result, the thermal load capacity of the toroidal transformer is very high.
Saving energy is another plus in favor of a toroidal transformer. Approximately 30% more energy is retained at full load and approximately 80% at no load, compared to other forms of laminated cores. The dissipation factor of toroidal transformers is 5 times lower than that of armored and rod transformers, so they can be safely used with sensitive electronic equipment.
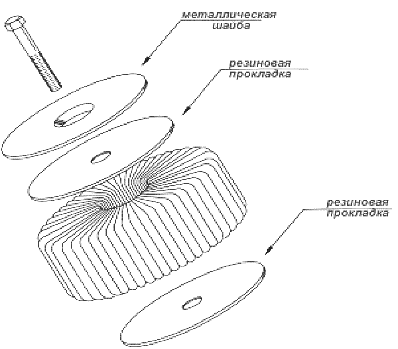
With the power of a toroidal transformer up to a kilowatt, it is so light and compact that it is enough to use a metal washer and bolt for installation. The user must select an appropriate transformer for the load current and for the primary and secondary voltages. When manufacturing a transformer at the factory, the cross-sectional area of the core, the area of the window, the diameters of the windings are calculated and the optimal dimensions of the magnetic circuit are selected, taking into account the permissible induction in it.