What is magnetic permeability (mu)
We know from many years of technical practice that the inductance of the coil is highly dependent on the characteristics of the environment in which the coil is located. If a ferromagnetic core is added to a coil of copper wire with a known inductance L0, then under other previous circumstances the self-induction currents (additional closing and opening currents) in this coil will increase many times, the experiment will confirm what will mean several times increase inductancewhich will now be equal to L.

Experimental observation
Let us assume that the medium, the substance filling the space inside and around the coil described, is homogeneous and is generated by the current flowing through its conductor, magnetic field located only in this particular area without going beyond its borders.
If the coil has a toroidal shape, the shape of a closed ring, then this medium, together with the field, will be concentrated only in the volume of the coil, since there is practically no magnetic field outside the toroid.This position is also valid for a long coil - a solenoid, in which all the magnetic lines are also concentrated inside - along the axis.
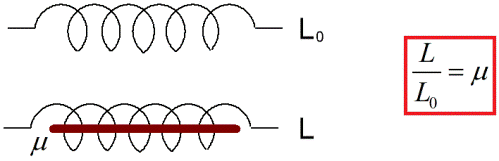
For example, say the inductance of some circuit or coreless coil in vacuum is equal to L0. Then for the same coil, but already in a homogeneous substance that fills the space where the magnetic field lines of a given coil are present, let the inductance be L. In this case, it turns out that the ratio L / L0 is nothing but the relative magnetic permeability of the specified substance (sometimes just called "magnetic permeability").
It becomes obvious: magnetic permeability is a quantity that characterizes the magnetic properties of a given substance. Often this depends on the state of matter (and environmental conditions such as temperature and pressure) and its nature.
Understanding the term

The introduction of the term «magnetic permeability» in relation to a substance in a magnetic field is similar to the introduction of the term «dielectric constant» for a substance in an electric field.
The value of the magnetic permeability, determined by the above formula L / L0, can also be expressed as the ratio of the absolute magnetic permeabilities of a given substance and the absolute void (vacuum).
It's easy to see: relative magnetic permeability (also known as magnetic permeability) is a dimensionless quantity. But the absolute magnetic permeability — has the dimension Hn / m, the same as the magnetic permeability (absolute!) of the vacuum (this is the magnetic constant).
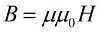
In fact, we see that the environment (magnetic) affects the inductance of the circuit, and this clearly shows that a change in the environment leads to a change in the magnetic flux Φ penetrating the circuit, and therefore to a change in the induction B , applied to each point of the magnetic field.
The physical meaning of this observation is that for the same coil current (at the same magnetic intensity H) the induction of its magnetic field will be a certain number of times greater (in some cases less) in a substance with magnetic permeability mu than in full vacuum.
It is this way because the medium is magnetized, and it itself begins to possess a magnetic field. Substances that can be magnetized in this way are called magnets.
The unit of measurement of the absolute magnetic permeability is 1 H / m (henry per meter or newton per ampere squared), that is, it is the magnetic permeability of such a medium where at a magnetic field voltage H 1 A / m , a magnetic induction of 1 occurs T.
Physical picture of the phenomenon
From the above it is clear that different substances (magnets) are magnetized under the action of the magnetic field of the current loop and as a result a magnetic field is obtained, which is the sum of magnetic fields — the magnetic field of the magnetized medium plus the current loop, which is why it differs in magnitude from current-only field circuits without medium. The reason for the magnetization of magnets lies in the existence of the smallest currents in each of their atoms.
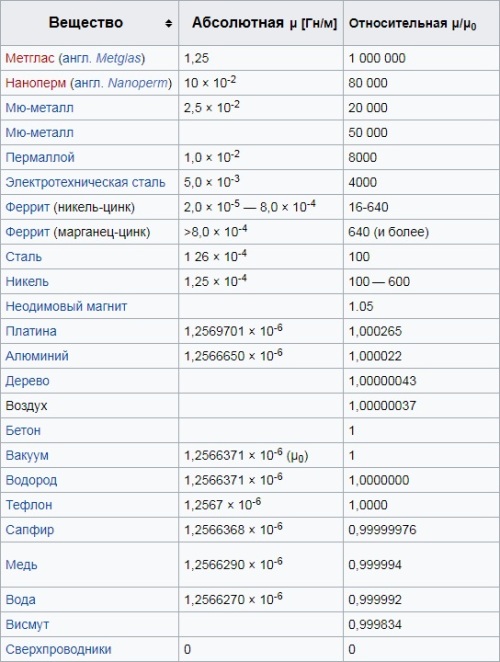
According to the value of the magnetic permeability, substances are classified into diamagnetic (less than one — magnetized with respect to the applied field), paramagnets (more than one — magnetized in the direction of the applied field) and ferromagnets (much more than one — magnetized and have magnetization after deactivation of the applied magnetic field).
Ferromagnets are characterized by hysteresistherefore, the concept of "magnetic permeability" in its pure form is not applicable to ferromagnets, but in a certain range of magnetization, in some approximation, a linear part of the magnetization curve can be distinguished, for which it will be possible to calculate the magnetic permeability.
In superconductors, the magnetic permeability is 0 (since the magnetic field is completely displaced by their volume), and the absolute magnetic permeability of air is almost equal to mu vacuum (read the magnetic constant). For air, mu is slightly more than 1.
