Torque of an induction motor
The torque developed on the shaft of an induction motor under conditions of zero rotor speed (when the rotor is still stationary) and the current established in the stator windings is called the starting torque of an induction motor.
The initial moment is sometimes also called the initial moment or initial moment. In this case, it is assumed that the voltage and frequency of the supply voltage are close to the nominal and the windings are connected correctly. In the rated mode of operation, this engine will perform exactly as expected by the developers.

Numerical value of starting torque
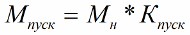
The starting torque is calculated by the above formula. In the passport of the electric motor (the passport is provided by the manufacturer) the multiple of the initial torque is indicated.
Typically, the magnitude of the increase is in the range of 1.5 to 6, depending on the type of engine. And when choosing an electric motor for your needs, it is important to make sure that the starting torque is greater than the static torque of the planned design load on the shaft.If this condition is not met, then the engine simply will not be able to develop the working torque at your load, that is, it will not be able to start normally and accelerate to the rated speed.
Let's look at another formula for finding the starting torque. It will be useful to you for theoretical calculations. Here it is enough to know the power of the shaft in kilowatts and the nominal speed — all these data are indicated on the nameplate (on the nameplate). Rated power P2, rated speed F1. So here is this formula:
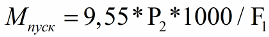
The following formula is used to find P2. Slippage, inrush current and supply voltage must be taken into account here, all of which are listed on the nameplate. As you can see, everything is quite simple. It is obvious from the formula that the starting torque can generally be increased in two ways: by increasing the starting current or by increasing the supply voltage.
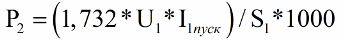
However, let's try to go the simplest way and calculate the starting torque values for three AIR series engines. We will use the parameters of the initial torque set and the nominal torque values, that is, we will use the first formula. The results of the calculations are shown in the table:
engine type Rated torque, Nm Ratio of starting torque to rated torque Starting torque, Nm AIRM132M2 36 2.5 90 AIR180S2 72 2 144 AIR180M2 97 2.4 232.8
The role of induction motor starting torque (starting current)
Often, motors are connected directly to the network, performing switching with a magnetic starter: network voltage is applied to the windings, a rotating magnetic field is created on the stator, and the equipment starts to work.
In this case, the starting current at the time of starting is inevitable and it exceeds the rated current by 5-7 times, and the duration of the excess depends on the motor power and the load power: more powerful motors start longer, their stator windings take longer current overload.
Low-power motors (up to 3 kW) easily withstand these surges, and the grid can easily withstand these minor short-term surges, since the grid always has some power reserve. Therefore, small pumps and fans, metal cutting machines and household electrical appliances are usually switched on directly, without worrying about overcurrent loads. As a rule, the stator windings of motors of this type of equipment are connected according to the "star" scheme based on three-phase voltage from 380 volts or «triangle» — for 220 volts.

If you are dealing with a powerful motor with 10 kW or more, then you cannot directly connect such a motor to the network. The inrush current at the time of start-up must be limited, otherwise the network will experience significant overload, which can lead to a dangerous "abnormal voltage drop".
Break the current limiting paths
The easiest way to limit the starting current is to start at a reduced voltage. The windings simply switch from delta to star at start-up, then back to delta when the motor picks up some speed.The switching takes place a few seconds after the start, using, for example, a time relay.
With such a solution, the initial torque also decreases, and the dependence is quadratic: with a decrease in voltage, it will be 1.72 times, the torque will decrease by 3 times. For this reason, reduced voltage starting is suitable for applications where starting is possible with a minimum load on the induction motor shaft (for example, starting a saw).
Heavy loads, such as a conveyor belt, need a different way to limit the inrush current. Here the rheostat method is more suitable, which allows you to reduce the inrush current without reducing the torque.
This method is very suitable for asynchronous motors with a wound rotor, where the rheostat is conveniently included in the rotor winding circuit, and the operating current is adjusted in stages, a very smooth start is obtained. With the help of a rheostat, you can immediately adjust the operating speed of the motor (not only at the time of starting).
But the most effective way to safely start asynchronous motors is still beginning frequency converter… Voltage and frequency are automatically adjusted by the converter itself, creating optimal conditions for the motor. Turns are obtained stable, while electric shocks are fundamentally excluded.
