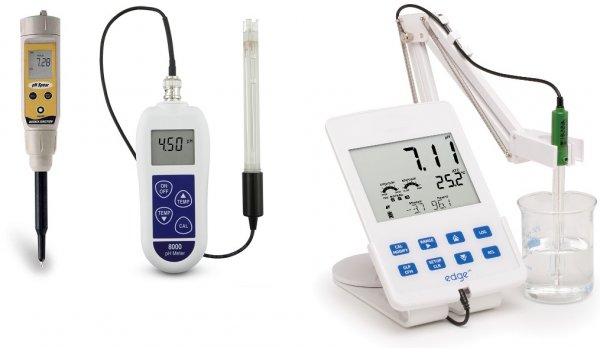
The principle of pH measurement, device and types of pH meters
To quickly determine the pH level (in other words, the acidity level) of various media, pH meters are used. Industrial or drinking water, acid, salt or alkali solution, blood, urine and other body fluids, fruits, vegetables and other foodstuffs, medical drugs, etc. — in principle, everything can become the object of operational research pH value.
Measuring PH is essentially a measurement of the activity of hydrogen ions in a medium. And even the designation pH itself is literally translated from the Latin "pondus Hydrogenii" as "weight of hydrogen".
Today, pH meters are widely used in microbiology and medicine, in water treatment and agrochemistry, in soil science, in hydroponics, in laboratory and field research, in the chemical and food industries, in aquaristics, and in many other places.
The modern pH meter allows you to accurately and quickly determine the pH value.If the pH is 7, the medium is neutral, such as distilled water, in which the positive hydrogen ions H + and the negative hydroxide ions OH- are equally divided. If the acidity is more than 7, then the medium is alkaline. If the pH is less than 7, the medium is acidic.
And although chemists have always been able to determine the acidity of the medium by the classical method, using indicators, for example, phenolphthalein, nevertheless, in some processes it is simply necessary to accurately quantify this indicator, and sometimes it is necessary to constantly monitor it, for arrange to correct it. This is what pH meters were invented for.
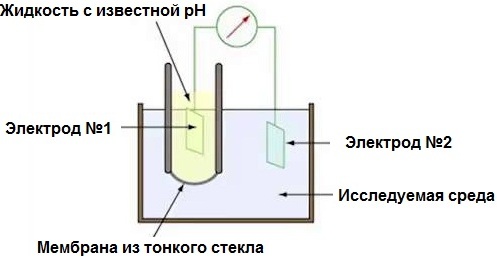
The pH meter is actually an electronic millivoltmeter as it measures the potential difference across the electrochemical system of a pair of electrodes and the test medium in which they are placed. It is true that the scale of the device is graduated here not in millivolts, but in pH, since the measured EMF turns out to be proportional to pH.
Two electrodes: a glass indicator (oxidizers are not afraid of borosilicate glass) and silver chloride — an additional reference electrode. The glass electrode has a very high resistance of tens of megohms, and this is only the basic requirement — the probe resistance should be no less than 0.1 GΩ. The pH meter is calibrated using buffer solutions of known pH.
Due to the fact that the EMF value is affected by temperature, each such measuring device has a temperature compensation for measurements at temperatures other than + 25 ° C.But in order to achieve very high accuracy, it is necessary to measure accurately at a temperature of + 25 ° C, which is why many pH meters are equipped with a built-in thermometer, so you can immediately follow the temperature of the medium in the process of research.
The indicator glass electrode in the form of a tube with a thin-walled ball at the end, made of a special electrically conductive borosilicate glass, is essentially connected to an electrical circuit. The movement of positive H + ions inside such a glass makes it possible to use it (cations inside the glass move relative to the polyanion of silicic acid). A suspension of silver chloride in a solution of hydrochloric acid is poured into the test tube, after which a silver wire is dipped into it - this is how a silver chloride electrode is obtained.
The glass electrode is lowered into the test medium, the electrical circuit is closed by placing an additional reference electrode (mercury-calomel paste in potassium chloride solution) into it (via an electrolytic switch or directly). Potassium chloride creates contact between the mercury-calomel portion of the cell and the test medium. This additional electrode is usually placed in a glass case that is impermeable to H + ions.
The conductive contact of the potassium chloride solution in the reference electrode with the test solution is formed due to a thin thread or capillary in a glass case. In this way, a galvanic cell is obtained from a reference electrode and a silver chloride electrode, and the electrolyte part of the cell includes a conductive glass film and test environment.
The EMF of the electrode system is measured with a millivoltmeter, its scale is graduated in pH.Electrons from the silver chloride electrode are transferred to the reference electrode under the action of the measured EMF, which is always accompanied by the transfer of an equal number of protons from the inside of the glass electrode to the medium.
If in this case we take the concentration of positive hydrogen ions H + in the constant of the glass electrode, then the EMF will be a function of the activity of H +, that is, a function of the pH of the medium under study.
Modern models of pH meters work thanks to microprocessors that perform temperature compensation and solve many related tasks. The more complex the device, the more tasks it can solve. The accuracy class of instruments varies by model, and a suitable pH meter can be selected for different applications.
There are pocket household pH meters, there are professional laboratory, portable and industrial stationary ones. Some pH meters measure the concentration of ions in the medium, the content of nitrates, etc., have a built-in memory to store the results, the ability to communicate with a computer and the function of adjusting parameters through a feedback loop.