What is a load chain
A load circuit is a part of an electrical circuit that consumes useful energy. The equivalent resistance of the load circuit can be: active (the circuit is practically an active resistance, the current in the circuit is in phase with the voltage), capacitive (the effect of capacitance prevails over the effect of inductance, the current leads the voltage) and inductive (the effect of inductance prevails over the capacitance effect, the current lags the voltage).
An electrical device, relative to which the load circuit is considered, is conveniently represented as an energy source with an equivalent internal resistance Zn (Fig., A) or a four-pole (active or passive) with an equivalent input resistance (Fig. , B), where EI is an electric device.
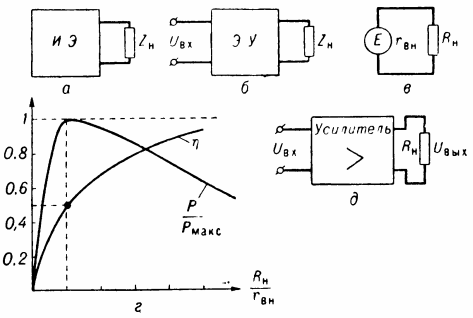
Consider the case of charging a conventional voltage source E with an internal resistance rhn and a load circuit of an active nature (Fig. 1, c).For such a circuit, the condition for the maximum output power of the source to the load circuit is Rn = rvn (Rn is the load resistance) and the source efficiency (the ratio of the power distributed to the load circuit to the total power generated by the source):
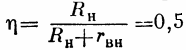
As efficiency increases, the output power in the circuit decreases.
A ratio of Rn and rhn must be chosen depending on the requirements for the operation of the source (fig.1, d), where P is the power distributed to the load circuit, Pmax is the maximum value of P.
When we consider the amplifier of the load circuit as a power amplifier, it is convenient to represent it in the form of an active four-port network (Fig., E), having an active input impedance Rc. For such a circuit, the following ratios are known:
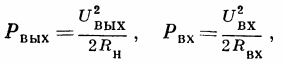
where Pvx is the power distributed to the input circuit of the amplifier, Pvx is the power distributed in the circuit (Rn).
