Electrotherapy in physiotherapy - types and physical basis
Electrotherapy is a group of physiotherapeutic methods based on a dosed electromagnetic effect on the body. The shock can be delivered through an electric current directly or through a magnetic field, depending on the purpose of the procedure.
Different methods differ in the form and parameters of the applied current: alternating or direct, what current strength, with what voltage, what frequency — the required effect is achieved by a suitable combination of these parameters.
The physical basis of the mechanism of action of electrotherapy lies in the fact that electric currents serve as stimuli for muscle and nerve tissues, as well as for the patient's systems and organs. As a result, the adequate use of electrotherapeutic methods is recommended in cases where the pathology has not yet led to significant changes in one or another part of the body, has not impaired the ability of the organ on which the procedure is performed to function.
Spread through the body electricity, causes the necessary change in certain biological processes, for example: increases blood flow, improves lymph circulation, accelerates tissue recovery, activates enzyme systems, helps remove lactic acid, has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
At the end of the course of electrotherapy, the patient's well-being usually improves, his mood rises, the person's sleep normalizes, the tone of the autonomic nervous system improves, heart rate and blood pressure indicators stabilize. So let's look at a few popular types of electrotherapy.
Transcutaneous Electroneurostimulation
Transcutaneous electroneurostimulation includes a group of methods using weak impulse currents. The key effect of this area is pain relief.
Transcranial electrical stimulation
Transcranial electrical stimulation is a therapeutic effect of impulse currents on the brain system, associated with the ability to non-invasively, selectively and strictly dose to activate the work of structures that produce endogenous opioid peptides.
Myoelectric stimulation
Normally, the processes of excitation and contraction of muscles in a living organism are caused by nerve impulses that come from the nerve centers to the muscle fibers. In the same way, arousal can be induced by an electric current - by means of electromyostimulation.
Bioregulated electrical stimulation
Bioregulated electrical stimulation is the impact of pulsed currents with changing parameters on skin areas.The peculiarity of the method consists in the appearance of biological feedback associated with a change in the electrical conductivity of the skin.
Thus, each subsequent impulse acting on the body differs in parameters from the previous one, since it seems to respond with adequate parameters to the reaction coming from the body. As a result, the corresponding, more effective external influence activates a much larger part of the nerve fibers, covering even thin C-fibers.
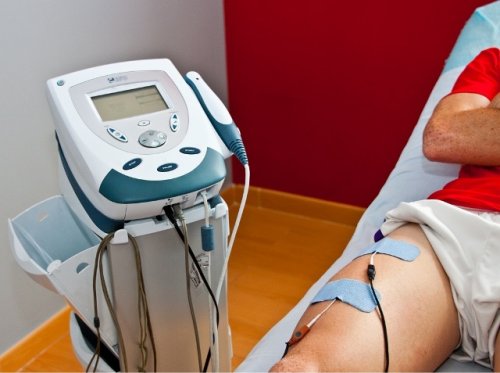
Electrotherapy with direct (continuous) or pulsed electrical current of small magnitude and low voltage is called LF electrotherapy and is divided into two types: direct current electrotherapy and pulsed current electrotherapy.
Galvanotherapy
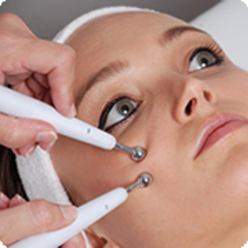
In galvanotherapy, a continuous direct current of up to 50mA and with a voltage of 30 to 80V is used. The method is named after Luigi Galvani, an Italian physician and researcher of electrical phenomena.
Electrodes are applied to the body and during the procedure, a direct current passes through the tissues of the body to cause specific physico-chemical changes in them, related to the presence of salt solutions and colloids (proteins, glycogen and other large molecular substances) in the tissues. .
These substances, which are constituents of muscle and glandular tissues, as well as body fluids, are broken down into ions. The path of current in the body depends on the presence or absence of wires, and fatty tissue conducts current poorly, as a result of which the current does not go in a straight line.
First of all, the irritation falls on the receptors of the skin due to the change in the concentration of ions, so the patient feels tingling and burning under the electrodes.In this case, nerve impulses enter the central nervous system, causing local and general body reactions. Blood vessels expand, blood flow accelerates, and biologically active substances (histamine, serotonin, etc.) are produced at the place of exposure to the current.
As a result, the action of direct current normalizes the functional state of the central nervous system, increases the functionality of the heart, stimulates the endocrine glands and accelerates regeneration processes. At the same time, the protective abilities of the body increase.
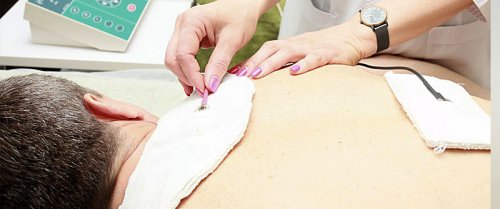
Electrophoresis
Therapeutic electrophoresis allows, when exposed to the body with direct current, to introduce drug particles into the body through the skin or mucous membranes.
During the procedure, the general reactivity of the body changes, the protective function is stimulated, the intensity of metabolic and trophic processes increases. The pharmacological effect of the administered drug is achieved at a small dose, but since it enters the blood slowly, it takes longer.
The drug itself is applied to a disposable filter paper located on the side of the electrode pad, which is applied to the patient's body. Electrophoresis pads are taken individually for each drug. Sometimes, electrophoresis uses baths of a low-concentration drug solution in which carbon electrodes are immersed.
Pulse current treatment
Impulse currents are characterized by a temporary deviation of voltage or current from a constant value. In medical practice, pulsed currents with a low frequency are used for such procedures as: electrical stimulation, electrosleep, diadynamic therapy.Medium frequency currents are used in interference therapy and amplipulse therapy. Next, we will look at these methods in more detail.
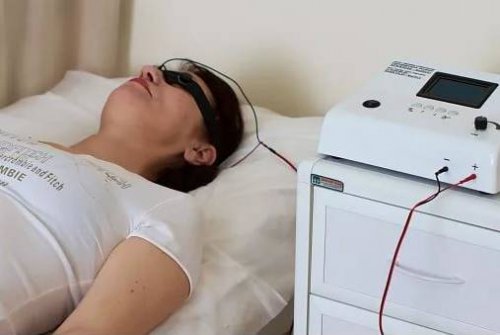
Electrical sleep therapy
During electrosleep, electrical current pulses affect brain structures. The currents pass into the cranial cavity through the orbits, as a result of which the maximum current density falls on the vessels of the skull base, which affects the hypnogenic centers of the brain stem (pituitary gland, hypothalamus, reticular formation, as well as the internal area of the pons varoli) and sensory nuclei of the cranial nerves.
The frequency of the pulses is synchronized with the slow rhythms of the bioelectrical activity of the brain. In this way, the impulse activity of the aminergic neurons of the blue spot and reticular formation is inhibited — the ascending activating effects on the cerebral cortex are reduced, and the internal inhibition is enhanced.
Electrostimulation
Electrical stimulation is an impulse effect on muscles and adjacent tissues with currents close in phase to the current of neuromuscular cell membranes. This procedure is used both in general physiotherapy, in sports and rehabilitation medicine, and in apparatus cosmetology. It is performed using professional equipment. The muscles or the corresponding innervating nerves are irritated by an impulse current, which leads to a change in the bioelectrical activity of the muscle, to peak responses and intense contractions.
Diadynamic therapy
In diadynamic therapy, half-sinusoidal alternating or periodic pulses with a frequency of 50 and 100 Hz are used. It has analgesic, vasoactive, trophic and myostimulating effects.
Capillaries expand, blood circulation improves, the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the relevant tissues increases, and metabolic and decay products are removed from inflammatory foci, due to which the anti-inflammatory effect is realized, swelling decreases.
Post-traumatic hemorrhages are dissolved, metabolism is activated and there is a trophic effect of currents on tissues. Muscles rhythmically contract and relax, their functions are restored. It also has a hypotensive effect on the body.
Interference therapy
In cosmetology, interference therapy is used when two or more medium-frequency currents are fed through two pairs of electrodes so that these currents interact.
Interfering currents pass through the path of least resistance, there is no discomfort, no skin irritation, but the effect is manifested in the depths of the tissues — the low-frequency current obtained as a result of interference rhythmically compresses the smooth muscle fibers of the vessels, which improves blood supply and lymphatic drainage, increases metabolism in the dermis and hypodermis.
Large nodules of adipose tissue are destroyed, subcutaneous fat becomes less. Inflammation decreases due to the shift of tissue pH to alkaline, plus a trophic effect.
Amplipulse therapy
Amplipulse therapy uses modulated sinusoidal currents up to 80mA. The action is analgesic, vascular spasms are alleviated, arterial inflow and venous outflow increase, transport and absorption of nutrients in the affected organs and tissues improves, metabolism is activated, infiltrates are absorbed and healing is accelerated.
The procedure improves the tone of the intestines and bile ducts, the ureter and the bladder. Drainage function and external breathing are improved, ventilation of the lungs is improved, bronchospasms are relieved and the secretory function of the pancreas is stimulated.
In addition, the secretory functions of the stomach are stimulated, metabolic processes in the liver are improved. The functional state of the central nervous system improves, the compensatory and adaptive abilities of the body increase.
Another way to use electricity in medicine: Electroencephalogram of the brain - principle of action and methods of application