Supercapacitors — device, practical application, advantages and disadvantages
What is a supercapacitor
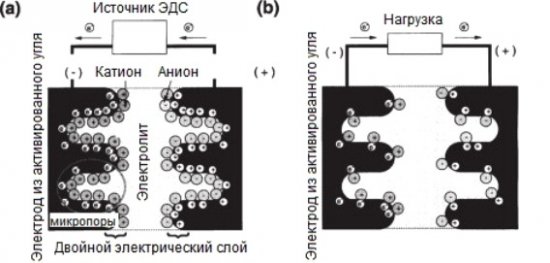
Supercapacitors or supercapacitors resemble ordinary electrolytic capacitors, although they differ from the latter in a much higher electrical capacity (extremely large capacitors). In terms of its properties, an ionistor is a cross between a battery and a capacitor. His device can be described as a capacitor with an electric double layer, it is not for nothing that supercapacitors are called EDLC — Electric Double Layer Capacitor in English resources.

Such a capacitor works thanks to the electrochemical processes taking place in it, and not simply due to the electric field stored in the dielectric between the plates, as in a conventional capacitor. There is no classical dielectric layer between the plates, and the plates themselves are made of substances different in charge carriers of the opposite type.
To the extent that capacitance of the capacitor is directly proportional to the area of its plates; in order to obtain a large capacity, it is necessary to have an extensive area of the plates. It is for this reason that the electrodes of the supercapacitor are usually made of foamed carbon, which gives a very significant area of «plates».
The electrodes are separated by a separator and are in a solid acid or alkaline electrolyte. The separator eliminates a short circuit between the electrodes. The crystalline electrolyte of rubidium, silver and iodine makes it possible to create high-capacity, low-self-discharge ionistors, resistant to low temperatures.
Supercapacitors with low internal resistance are obtained, for example, on the basis of sulfuric acid solution, but the operating voltage of such supercapacitors is limited to 1 volt, in addition, such solutions are toxic, so they are rarely used.
An electrochemical reaction in the supercapacitor causes some of the electrons to leave the electrodes, which charges the electrodes positively. Negative ions are attracted by the electrolyte to the positively charged electrodes. This forms an electrical layer.
As a result, the charge of the supercapacitor is stored at the interface between carbon and electrolyte, and the thickness of the electrical layer formed by cations and anions is only 1-5 nm, which is equivalent to a very small distance between the capacitor plates. This results in significant capacitance measured in farads. The supercapacitor is polar, therefore, when connected to the circuit, it is necessary to observe the correct polarity.
Application of supercapacitors
Today, supercapacitors are often found in digital technology as backup power supplies for microcontrollers, memory circuits, CMOS chips, electronic clocks, and more.

When used in conjunction with batteries, supercapacitors can also increase efficiency and enable reductions in the weight and size of batteries, providing additional power during peak loads.
Being in an intermediate position between capacitors and batteries, supercapacitors are applicable in various fields: energy storage in regenerative braking systems, low power applications and fast charging applications (lightning, player, memory, etc.).
The future is likely to include portable electronic devices, electric cars and anything that runs on batteries today, with the advantage that they can be charged in minutes. Supercapacitors are also indispensable when a large number of charge-discharge cycles are required under conditions of short-term power consumption.
We list only some of the areas of successful application of supercapacitors today:
- wind energy,
- medical equipment,
- redundant power supply,
- energy reserve,
- braking energy regeneration,
- food for consumer electronics and kitchen appliances,
- powering LEDs and sensors,
- backup memory,
- maintaining the power supply of electronic locks,
- voltage stabilization.
Advantages and disadvantages
The disadvantages of supercapacitors include a low operating voltage (up to 2.7 volts per cell, which leads to the need to collect supercapacitors in batteries) and a rather high price compared to batteries and capacitors.
Positive characteristics of supercapacitors: charging and discharging speed, resource of hundreds of thousands of cycles, maintenance-free, small size and weight, ease of use, wide range of operating temperatures, long service life.
See also: What is the difference between batteries and capacitors