What is electric potential
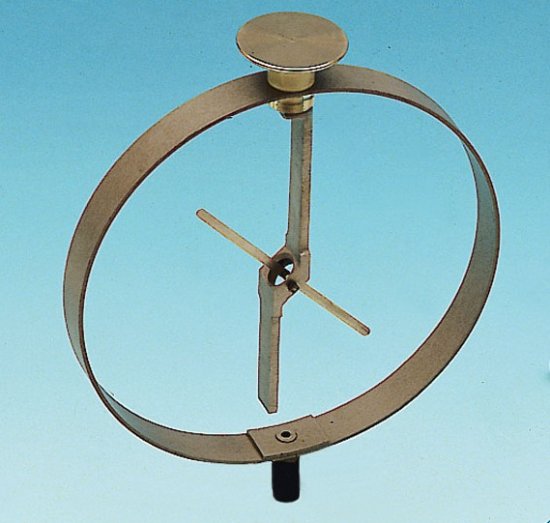
Electric potential is a quantitative characteristic of an electric field based on measuring the work of electric forces that the field does when charges move through it. Special devices are used to measure electric potential — electroscopes and electrometers.
The electric field created by charges has the following important property: the work done by the field forces when the charges move in it depends only on the position of the initial and final points of motion, but does not depend on the path along which motion occurs ( a field with such a property is called a potential).
Therefore, the electric field at any point can be characterized by the work that the field forces do when a certain charge moves from a given point to infinity (practically to such a distant point that the field in it can already be considered equal to zero) .
Such a characteristic is the electric potential at a given point in the field, which is expressed by the work that the field forces do when a positive charge is removed from that point to infinity.
If this motion occurs in the direction of the force acting on the side of the field, then this force does positive work and the potential of the starting point is positive. If the motion is towards the force acting on the side of the field, then the field force does negative work and the potential of the starting point is negative.

Since the work done when a charge moves in an electric field does not depend on the path, but only on the position of the starting and ending points, the work done in moving along each path from point A to point B is equal to the sum of the work done work when going from A to infinity and from infinity to B (since the last two movements also represent movement from A to B, but by a different path).
In other words, the work done by the field forces when a unit positive charge moves from point A to point B is equal to the difference in electric potentials at points A and B.
A free positive charge under the action of the force of the electric field will always move in the direction of the force, which will do positive work, that is, it will always move from points of higher potential to points of lower potential. On the contrary, negative charges will move from a point of lower potential to points of higher potential.
Just as heavy bodies in a gravitational field move from higher to lower potential, positive electric charges move from higher to lower potential.
Just as for the motion of heavy bodies, it is not the absolute level at any point that matters, but the difference in levels of the points between which the bodies move, for the motion of electric charges, it is not the magnitude of the potential itself (measured against infinity) , which is essential, but the potential difference of points between which the movement of electric charges can occur, for example, points connected by a wire.
Therefore, in all electrical problems it is not the potential that plays a role, but the potential difference, and for this last quantity a special name is introduced — voltage (potential difference between two points). The unit of measurement of potential difference (voltage) in the practical system of units is the volt.
There are also concepts in electrical engineering electrode potential and contact potential difference.