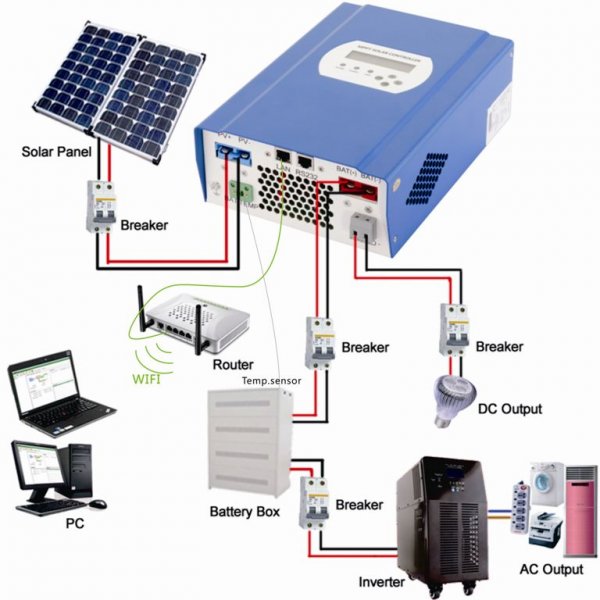
Photovoltaic controllers
Several types of controllers are used in photovoltaic systems to regulate the flow of energy in a battery system. There are three main types of controllers: charge, charge, and drain controllers.
Charge Controllers
Charge controllers are defined as equipment devices that control a constant voltage or constant current, or both, used to charge a battery.
There are four common types of charge controllers:
-
maneuvering,
-
single stage,
-
multistage,
-
pulse.
Shunt controllers drain the excess current through the resistor and generate it as heat. They are usually designed for small systems.
Single stage controllers simply cut the current to the batteries at a certain voltage setting.
Bypass and single-stage controllers are simple and inexpensive, but can reduce flexibility, reduce charge levels, and shorten battery life.
Multi-level controllers have multiple voltage ranges with different current settings, resulting in a higher battery level and longer battery life.
Finally, pulse controllers provide pulsed charges that are reduced when the set voltage value is reached. As batteries are charged and discharged, charge controllers typically regulate current to achieve optimal battery condition.
Charge controllers also provide overcharge and equalization protection, important features to protect battery life.
Equalization restores all the individual cells in the battery to roughly the same state, providing a high voltage.
A number of additional features are often built into the controller, including monitoring functions to indicate system performance, temperature compensation to ensure proper battery charging, LED charge indicators (eg for low battery alarms) and automatic leveling.
Another key feature of charge controllers is sometimes the regulation of the PV array voltage to achieve the maximum power point (MPP). In this case, the controllers are called maximum power tracking controllers or MPPT controllers. MPPT controllers can be significantly more expensive than other controllers, but can pay for themselves by optimizing the power generated by the PV system.

Charge Controllers
Load controllers are generally charge controllers that operate in load control mode. They protect batteries from over-discharge by shutting down loads when the battery voltage gets too low. They can also be used to monitor system performance.
It should be noted that some charge controllers can function as load controllers at the same time. Depending on the level of system monitoring, a separate load controller is often desirable.
Shutdown (Toggle) Controllers
Shutdown controllers are actually specific types of charge controllers and are defined as equipment devices that regulate the battery charging process by diverting power from energy storage to DC or AC loads or to interconnected utilities.
The transmitter controller can be connected to DC loads or, if included in an inverter, to AC circuits.
The backup charge controller is often required to have a backup charge controller to ensure that the batteries are not overcharged. In fact, when the protective devices in the switching circuits are tripped manually or automatically, the switching controllers become inoperative.
Moncef Crarti «Energy efficient electrical systems for buildings»