How frequency is measured
Direct frequency measurement is carried out by frequency meters, which are based on different measurement methods depending on the range of measured frequencies and the required measurement accuracy. The most common methods of measuring frequency are:
The method of recharging the capacitor for each period of the measured frequency. The average value of the recharge current is proportional to the frequency and is measured with a magnetoelectric ammeter, the scale of which is graduated in frequency units. Capacitor frequency counters are manufactured with a measurement limit of 10 Hz — 1 MHz and a measurement error of ± 2%.
Resonance method based on the phenomenon of electrical resonance in a circuit with adjustable elements in resonance with the measured frequency. The measured frequency is determined by the scale of the tuning mechanism. The method is applied at frequencies above 50 kHz. The measurement error can be reduced to hundredths of a percent.

Discrete counting method is the basis of work electronic counting of digital frequency meters... It is based on counting pulses of the measured frequency for a certain period of time.It provides high measurement accuracy in every frequency range.
The method of comparing the measured frequency with the reference… Electrical vibrations of unknown and sample frequencies are mixed in such a way that shocks of a certain frequency occur. At a beat frequency of zero, the measured frequency is equal to the reference frequency. Frequency mixing is done by heterodyne method (zero beat method) or oscillographic.
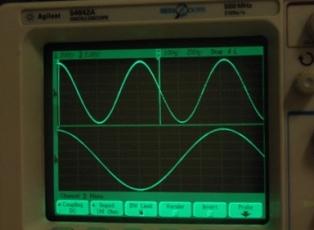
The latter method uses an oscilloscope with the internal generator turned off for cleaning. The voltage of the reference frequency is applied to the input of the horizontal amplifier and the voltage of unknown frequency is applied to the input of the vertical bias amplifier.
By changing the reference frequency, a stationary or slowly changing Lissague figure... The shape of the figure depends on the frequency ratio, amplitudes and phase shift between the voltages applied to the oscilloscope deflection plates.
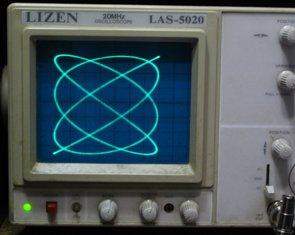
If you mentally cross the figure vertically and horizontally, then the ratio of the number of vertical crossings m to the number of horizontal crossings n is equal to a fixed number to the ratio of the measured fx and the sample freb of the frequencies.
When the frequencies are equal, the figure is a slanted line, ellipse, or circle.
The rotation frequency of the figure will correspond exactly to the difference df between the frequencies fx' and fx, where fx' = frequency (m / n) and therefore fx = fsample (m / n) + de. The accuracy of the method is mainly determined by the error at setting the reference frequency and determining the value de.
Another method of measuring frequency by comparison method — using an oscilloscope with a calibrated sweep duration or a built-in generator of calibrated marks.
Knowing the duration of the oscilloscope reading and calculating how many periods of the measured frequency fit within the selected length of the central part of the oscilloscope screen, which has the most linear sweep, you can easily determine the frequency. If the oscilloscope has calibration marks, then, knowing the time interval between the marks and counting their number for one or more periods of the measured frequency, determine the duration of the period.