Photodiodes: device, characteristics and principles of operation
 The simplest photodiode is a conventional semiconductor diode that provides the ability to influence optical radiation on the p — n junction.
The simplest photodiode is a conventional semiconductor diode that provides the ability to influence optical radiation on the p — n junction.
In the equilibrium state, when the radiation flux is completely absent, the carrier concentration, potential distribution and energy band diagram of the photodiode fully correspond to the usual pn structure.
When exposed to radiation in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the p-n-junction, as a result of the absorption of photons with energy greater than the band width, electron-hole pairs appear in the n-region. These electrons and holes are called photocarriers.
During photocarrier diffusion deep into the n-region, the main fraction of electrons and holes does not have time to recombine and reaches the p-n junction boundary. Here, the photocarriers are separated by the electric field of the p — n junction and the holes pass into the p region, and the electrons cannot overcome the transition field and accumulate at the boundary of the p — n junction and the n region.
Thus, the current through the p — n junction is due to the drift of minority carriers — holes. The drift current of photocarriers is called photocurrent.

Photodiodes can operate in one of two modes — without an external source of electrical energy (photogenerator mode) or with an external source of electrical energy (photoconverter mode).
Photodiodes operating in photogenerator mode are often used as power sources that convert solar energy into electrical energy. They are called solar cells and are part of solar panels used in spacecraft.
The efficiency of silicon solar cells is around 20%, while for film solar cells it can be much more important. Important technical parameters of solar cells are the ratio of their output power to the mass and the area occupied by the solar cell. These parameters reach values of 200 W / kg and 1 kW / m2, respectively.
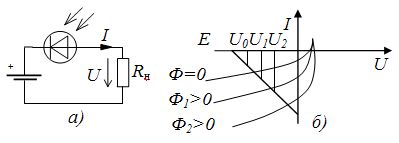
When the photodiode operates in the photoconversion mode, the supply E is connected to the circuit in the blocking direction (Fig. 1, a). The reverse branches of the I — V characteristic of the photodiode are used at different levels of illumination (Fig. 1, b).
Rice. 1. Scheme of switching on the photodiode in photoconversion mode: a — switching circuit, b — I — V characteristic of the photodiode
The current and voltage in the load resistor Rn can be determined graphically from the intersection points of the current-voltage characteristic of the photodiode and the load line corresponding to the resistance of the resistor Rn. In the absence of illumination, the photodiode works in the mode of a conventional diode. The dark current for germanium photodiodes is 10 — 30 μA, for silicon photodiodes 1 — 3 μA.
If a reversible electrical breakdown accompanied by avalanche multiplication of charge carriers is used in photodiodes, as in semiconductor zener diodes, then the photocurrent, and hence the sensitivity, will be greatly increased.
The sensitivity of avalanche photodiodes can be several orders of magnitude higher than that of conventional photodiodes (for germanium — 200 — 300 times, for silicon — 104 — 106 times).
Avalanche photodiodes are high-speed photovoltaic devices with a frequency range of up to 10 GHz. The disadvantage of avalanche photodiodes is the higher noise level compared to conventional photodiodes.
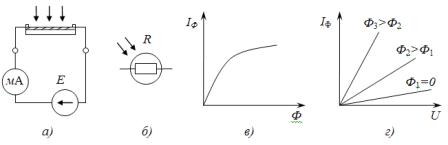
Rice. 2. Circuit diagram of the photoresistor (a), UGO (b), energy (c) and current-voltage characteristics (d) of the photoresistor
In addition to photodiodes, photoresistors (Figure 2), phototransistors and photothyristors are used, which use the internal photoelectric effect. Their characteristic disadvantage is their high inertia (limiting operating frequency fgr <10 — 16 kHz), which limits their use.
The design of the phototransistor is similar to a conventional transistor that has a window in the case through which the base can be illuminated. UGO phototransistor — a transistor with two arrows pointing at it.
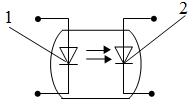
LEDs and photodiodes are often used in pairs.In this case, they are placed in one housing so that the photosensitive area of the photodiode is located opposite the emitting area of the LED. Semiconductor devices using pairs of LED-photodiodes are called optocouplers (Fig. 3).
Rice. 3. Optocoupler: 1 — LED, 2 — photodiode
The input and output circuits in such devices are not electrically connected in any way, since the signal is transmitted by optical radiation.
Potapov L.A.