Auxiliary power supplies for powering relay protection devices
 For all relay protection devices, in addition to the direct acting relay, an auxiliary current source is required. Sources of operating current are subdivided into:
For all relay protection devices, in addition to the direct acting relay, an auxiliary current source is required. Sources of operating current are subdivided into:
- DC power supplies.
- AC power supplies.
Auxiliary DC Power Supplies
Accumulator batteries are an independent source of operating current.
Advantages of DC power supplies:
- Power is provided for all circuits of connected devices at all times with the required voltage and current level, regardless of the state of the main network.
- Simplicity and reliability of relay protection circuits.
Disadvantages:
- High cost (economically justified for using direct current sources at substations 110 kV and above with several overhead lines);
- The need for a heated and ventilated room;
- The need to use a charger;
- Difficulty at work.
To increase reliability, the auxiliary power network is divided so that the shutdown of one or several sections does not lead to damage to the most critical users of the operating current, which include relay protection, automation and control devices.
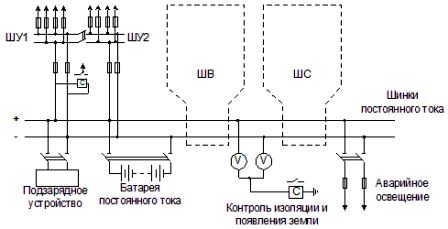
Rice. 1. Connection diagram of a direct current source (accumulator battery) in a switchgear
The accumulator battery works on DC buses, from which the lines feed the auxiliary current sections for each group of users. ХУ — power supply buses for the relay protection, the automation and control device (usually a separate bus for each section of the bus), ШС — signal buses and ШВ — power supply buses for the electromagnets for switching on the switches. The battery is also a source of emergency lighting for the substation.
The storage battery is usually made of lead-acid batteries, which have a sufficiently high durability, efficiency and withstand short-term overloads, for example, when powering electromagnets for turning on powerful switches (electromagnet current can reach several hundred amperes).
The battery room must be heated and ventilated to remove sulfuric acid fumes. To ensure the longevity of the battery, the optimal mode of recharging, charging and discharging must be observed. Automatic regulated rectifiers (rechargers) are used for this purpose.
Protection of the DC network is achieved by means of fuses and circuit breakers providing selectivity and sensitivity. The most common type of fault is a short circuit of one of the poles to ground.
This does not lead to destruction, but the occurrence of a second short circuit can lead to false operation of the protective device or closing of electromagnets. Insulation monitoring is therefore used, for example by installing two voltmeters. In the absence of a short circuit, the bus to ground voltage is the same, otherwise the voltmeter readings differ.
AC power sources
Sources of alternating operating current - use the energy of the protected object. When performing alternating auxiliary power supply, the sources are current transformers and voltage transformers.
Advantages of alternating current sources:
- Lower price.
- Lack of branched working current network.
Disadvantages:
- Fluctuations in the output voltage are higher than with DC sources, especially at the short-circuit current... For electromechanical relays this is not essential, but for analog and microelectronic relays it can lead to incorrect operation.
- A sharp decrease in the auxiliary voltage when the switch is turned on near a short circuit.
There are various options for implementing AC operating current relay protection devices. The simplest schemes that use the installation current.
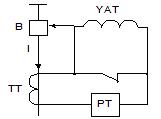
1) Scheme with disposal of the cut-off electromagnet.
YAT — breaker trip coil. In normal mode, the closing coil is bridged by the PT current relay contact. When there is a short circuit RT is triggered, the contact opens and the secondary current transformer energizes YAT, causing the circuit breaker to open.
The circuit is used for overcurrent protection if the inclusion of tripping electromagnets does not lead to unacceptable errors in current transformers, and the maximum short-circuit current does not exceed the current limit that the relay contacts can switch.
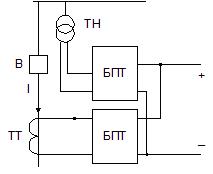
2) Rectified circuits of operating current.
It is recommended to use schemes based on corrected operating current on connections equipped with switches with electromagnetic or pneumatic drives, the electromagnets of which have high energy consumption, as well as in the presence of complex protective devices.
In normal mode, the rectified output voltage provides bnavoltage loc (BPN) and in short circuit — either current supply block (BPT) or both blocks together.
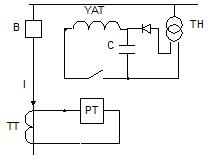
3) Circuits using capacitor banks.
In normal mode, the contact of the PT relay is open and the capacitor C is charged through the diode by the voltage from VT. When there is a short circuit, the current relay PT is activated, its contact closes and the pre-charged capacitor C begins to discharge to the breaker YAT, causing the breaker to open.
This scheme is used if the power supplied to the current transformer is insufficient to use the two previous schemes.