Passive and active elements of electrical circuits
 An element of an electric circuit is called an idealized device showing any of the properties of reality electrical circuit.
An element of an electric circuit is called an idealized device showing any of the properties of reality electrical circuit.
Electric circuits in which the parameters of all elements do not depend on the magnitude and direction of currents and voltages, i.e. graphs of current-voltage (VAC) characteristics, the elements are straight lines called linear. Accordingly, such elements are called linear.
When the parameters of the elements of the electric circuit depend significantly on the current or voltage, i.e. I — V characteristics of these elements have a curvilinear nature, then such elements are called non-linear.
If an electrical circuit contains at least one nonlinear element, it is non-linear electric circuit.
In the theory of electrical circuits, there are active and passive elements... The former bring energy into the electrical circuit, while the latter consume it.
Passive elements of electrical circuits
Resistive resistance is an idealized element of an electrical circuit that has the property of irreversible energy dissipation.A graphical representation of this element and its current-voltage characteristic are shown in the figure (a — non-linear resistance, b — linear resistance).
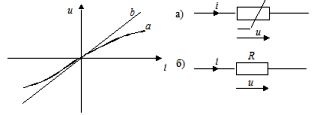
The voltage and current in the resistive resistance are related to each other by dependencies: u = iR, i = Gu. The proportionality factors R and G in these formulas are called resistance and conductivity, respectively, and are measured in ohms [ohms] and siemens [cm]. R = 1/G.
An inductive element is called an idealized element of an electric circuit, which has the property of accumulating the energy of a magnetic field. The graphic representation of this element is shown in the figure (a — non-linear, b — linear).
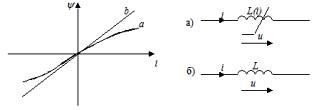
Linear inductance is characterized by a linear relationship between flux linkage ψ and current i, called the Weber-ampere characteristic ψ = Li. Voltage and current are related by u = дψ / dt = L(di / dt)
The proportionality factor L in the formula is called inductance and is measured in henries (Hn).
Capacitive element (capacity) is called an idealized element of an electric circuit, which has the property of accumulating the energy of an electric field. A graphical representation of this element is shown in the figure. (a — non-linear, b — linear).
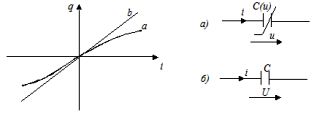
Linear capacitance is characterized by a linear relationship between charge and voltage, the so-called pendant-voltage characteristic q = Cu
Capacitive voltage and current are related by i = dq / dt = ° C(du / dt).
Active elements of electrical circuits
Elements of the circuit are called active, which give energy to the circuit, i.e. energy source. There are independent and dependent sources… Independent sources: voltage source and current source.
Voltage source — an idealized element of an electrical circuit whose terminal voltage does not depend on the current flowing through it.
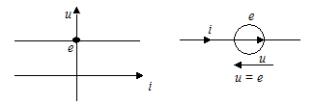
Internal resistance of an ideal source voltage is zero.
Power source It is an idealized element of an electric circuit, the current of which does not depend on the voltage of its terminals.
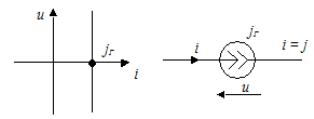
The internal resistance of an ideal current source is equal to infinity.
Sources of voltage (current) are called dependent (controlled), if the value of the voltage (current) of the source depends on the voltage or current of another section of the circuit. Dependent sources simulate vacuum tubes, transistors, amplifiers operating in linear mode.
There are four types of dependent sources.
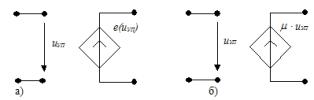
1. INUN — voltage controlled voltage source: a) nonlinear, b) linear, μ — voltage gain
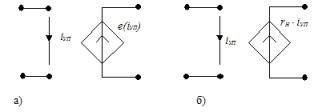
2. INUT — voltage source controlled by current: a) non-linear, b) linear, γn — transfer resistance
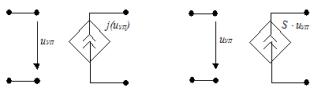
3. ITUT-current current source: a) non-linear, b) linear, β — current amplification factor
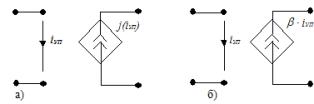
4. ITUN — voltage-controlled current source: a) non-linear, b) linear, S — slope (transfer conductivity)