Electrical circuit structure
 Electric circuits — a set of devices and objects that form a path of electric current, electromagnetic processes in which can be described using the concepts of electromotive force, current and voltage.
Electric circuits — a set of devices and objects that form a path of electric current, electromagnetic processes in which can be described using the concepts of electromotive force, current and voltage.
Electric circuits consist of devices for generating electrical energy, transmitting it over a distance, and converting it into other forms of energy. The former are called sources of electrical energy, the latter are called electrical communication lines, and the third are receivers of electrical energy… It is customary to depict electrical circuits in electrical circuits, in which generating and converting devices, as well as the electrical communication lines connecting them, are represented by conventional graphic symbols.
Sources of electrical energy are energy converters other types in electric. These include: galvanic and storage cells, electromechanical generators, thermocouples, solar cells, magnetohydrodynamic generators, fuel cells and other converters.
These sources perform conversion with an efficiency of less than one and are characterized by electromotive force or EMF. etc. with E, internal resistance Rvn, rated current AzNe. D. d. S. is the cause that excites an electric current in a closed electric circuit. The unit d. etc. v. serves as a volt (V). D. d. S. can be measured with a voltmeter when all receivers are disconnected from the source of electrical energy, that is, when there is no current in it.
Rice. 1. A simple electrical circuit
Electrical communication lines that transmit electrical energy at a distance are power lines, electrical networks and other devices that are characterized by their resistance in a stationary state.
Receivers of electrical energy
Sources of electrical energy as well as receivers with their inherent e. etc. (electric motors, batteries in the process of charging, etc.) are active elements, and electrical communication lines, connecting wires and receivers are without e. etc. (resistors, electric ovens, electric lighting devices, etc.) — passive elements. A resistor, which is a passive element, is designed to use its electrical resistance in various electrical circuits.
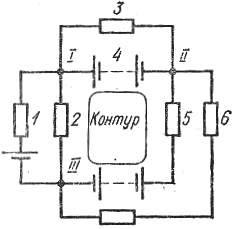
Electric circuits can consist of any number of active and passive elements, which are included in separate branches, interconnected with nodes. Each branch, which is a section of the circuit with the same current, includes one or more elements connected in series, and at least three branches converge at each node - the junction of the branches (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2. Diagram of an electrical circuit with six branches and three nodes
Each closed path along several branches of an electrical circuit is called delineation... Depending on the number of circuits, electrical circuits are classified as single-circuit or multi-circuit, which in turn can be with one or more sources of electrical energy.
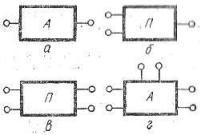
V electric circuits with many circuits, you can select a part of a circuit with active elements - an active circuit, as well as a part of a circuit with passive elements - a passive circuit, which are conveniently depicted as a rectangle with the letter A or P in the middle. Depending on the number of outputs of the rectangle, inside which the selected elements of the considered part of the electric circuit are located, connected to each other according to the accepted electric circuit, it is called active or passive two-, three-, four- or multi-pole, respectively (Fig 2, a, b, c, d).
Rice. 3. Conventional graphic symbols: active two-terminal, b-passive three-terminal, c-passive four-terminal, e-active six-terminal.