Mechanized fiber optic cable laying: the foreman's story
The brigade's acquaintance with fibers began back in 1996, when specialists from Italy were invited to us for the first installation, who were consultants, curators, installers of connectors, optical measuring devices and at the same time teachers.
First we were told how the cable works.
The light beam travels along the fiber from the source in one direction. Therefore, the exchange of information requires two separate channels. This mode is called duplex.

Light pulses are used to transmit a binary code lasers or LEDs for receiving electronic devices called photodiodes, which convert the received information into voltage pulses.
Light signals are transmitted through optical carriers, which are created by the structure:
1. single-mode;
2. multimode.
Both types have:
-
external polymer coating;
-
glass cover;
-
core.
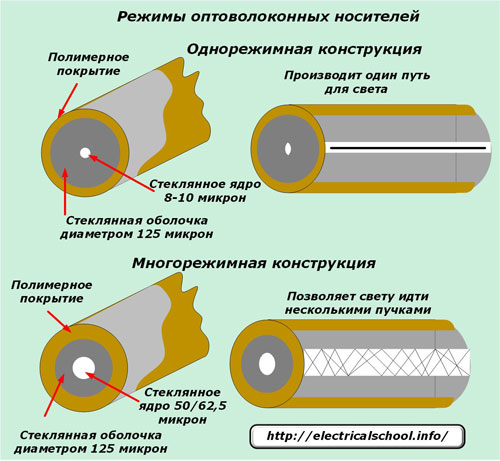
The first type has a smaller core and variation. They use lasers as a light source, transmitting signals several kilometers along highway lines.
Multimode devices have a larger core and increased dispersion, which creates additional signal loss. The light in them is transmitted by LEDs at distances of up to two km. This technology is cheaper.
To protect them from mechanical stress, including tension, special cable inserts are used.
The central support element with a fiberglass rod made of thin cable core modules arranged in a spiral has greater strength. In critical axial loads, the main force is perceived by the central power element — a steel or glass cable. In such a situation, the light modules can be slightly unfolded without breaking their integrity.
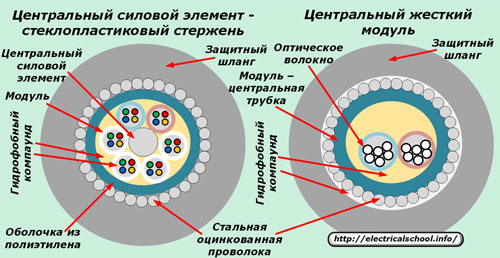
Constructions with a supporting element in the form of a central tube are more economical in production, but delicate in operation. They are able to withstand lower axial loads that only wire armor can handle. Because it is created by coiling, it undergoes unwinding under tension and transfers forces more quickly to the glass fibers of the cable.
Then they explained to us: Rules for working with fiberglass.
All operations must be carried out carefully, carefully, without throws and even more blows, so as not to damage the "fragile glass". A large number of workers are involved in laying out the land. The cable is laid from the drum in large consecutive figure-eights without overlaps, loops and sharp turns.
After a few days of working together, we formed a fully cohesive team, first from the workers, and then from the engineering and technical staff. The reason is the large amount of alcohol distributed in liters to service the clutches. Soon the Italians successfully joined him and quickly found a common language with us...
After a few months of work, we already treated fiber-optic cable in almost the same way as steel cable. And it withstood all the loads, with the exception of two cases of permitted breakage of fiberglass cores during mechanized laying, when it was necessary to replace a two-kilometer section and make additional connectors.
However, this incident made us realize that not all types of fiber optic cables are well protected against stretching and this should be taken into account when working.
How is laying a cutless fiber optic cable in the ground
The main working device that puts the optical fiber in the ground is a layer of cable cable that works on the principle of an old country plow.
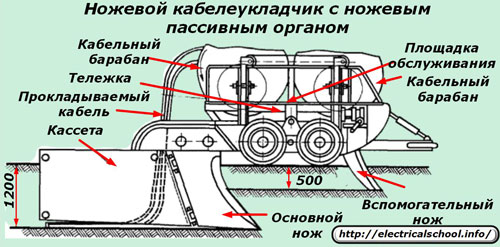
It is designed as a cart with a service platform and wheels on which one or two cable drums are placed. The cart is equipped with a drawbar for connecting to tractors and two knives:
1. auxiliary, penetrating deep into the soil up to 50 cm;
2. the main one, able to sink the cable up to one and a half meters into the ground.
A powerful cassette is attached to the end of the rear end of the main knife, through which the cable runs along the internal channels when transporting the cart with tractors. Cutting the soil with different knives in two successive stages somewhat reduces the load on the cassette, facilitates the paving process. In this case, the soil is moved to the width of the knife up to 10 cm, and a cable from the cassette is inserted into the gap formed at the bottom. The tensile force created on it is controlled and must not exceed critical values.
The photo below shows the basic elements of the cable cutter in action with the blades and optical cartridge.

The insertion of the fiber into the base of the cartridge is shown in the next shot of the service area. Installers are positioned on it, rotating the drum to provide the necessary slack before entering the cartridge.

More details on the stacking mechanism can be found below. Note the thickness and length of the main knife heavy plate, how it is attached to the drawbar. But it is still buried in the ground at least 1.2 meters, with a total height of one and a half.
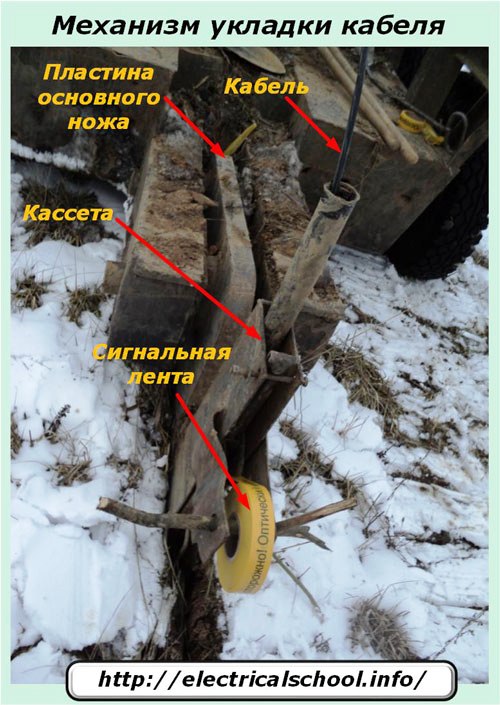
This can only be explained by the fact that such a structure continuously cuts through a large thickness of soil, periodically encountering thick tree roots, rocks, stones, ice and other objects on its way. In this case, the soil must be well spread for reliable laying of the cable at the bottom of the created cut.
The photo shows a roll of yellow non-dissolving signal tape with a warning about the installation of a fiber optic cable. This is done to facilitate the search for service organizations during future excavations and to warn third-party workers of the possibility of damage to the optical fiber during further digging into the soil.
It is clear that to lay the cable in the ground at great depths, it is necessary to create a powerful pulling force. Tractors are used for this.

Depending on the density of the soil and the terrain conditions, their number can vary from three to seven. They are connected in series to the cable layer by a system of cables passed under the frame of each previous tractor, so that the tractive force of each of them is transmitted most efficiently to the working knives.
Actions of tractor drivers during work must be competent and well coordinated. For this, experienced specialists from at least the fifth grade are involved, and all actions are discussed and played with them in advance. All kinds of contingencies are possible on the track, where the overall result depends on the maneuver of each tractor.
During operation, it is necessary to maintain a constant speed in order to exclude the possibility of sharp bends in the cable and its unacceptable stretching. After all, even the slope of the cable layer itself must be maintained at a constant angle to the horizon.
The general management of the movement of the column is carried out by the foreman. With all the contractors, he is constantly in touch with the intercom. The laying route is pre-marked with clearly visible landmarks.
There may be various obstacles on the way of the column:
-
intersections with underground gas pipelines or routes of water supply systems, sewage systems, electrical networks and other devices;
-
streams, rivers, water barriers;
-
asphalt or dirt roads.
In all these situations, their technical solutions specified in the route laying project are applied. For their implementation, the specialists of our organization pre-negotiate the procedure for interaction with the owners of these highways and provide the brigade with executive documentation, the standards of which we must strictly observe.
As an example, the photo below shows the technology of passing a cable under the bed of an asphalt road without destroying its surface, using the technology of "drilling the ground".
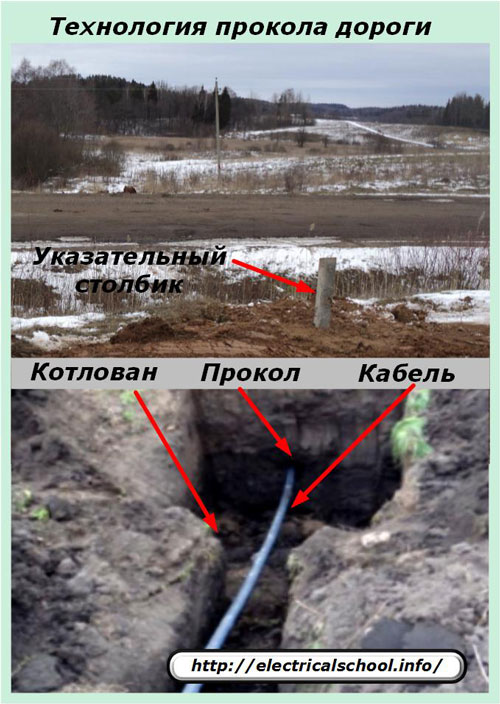
To do this, a pit is dug on both opposite sides of the road to a depth exceeding the level of laying the optical fiber with such a condition that it is convenient to drill a hole under the road. Drilling can be done with a simple pipe with a hammer or special devices.
In critical areas with agricultural land, railway lines, highways, construction complexes, teams are used that carry out horizontal drilling of the soil at a distance of up to 1 kilometer.
After the hole is prepared, one end of the cable is inserted into it and pulled for even distribution in a small trench, which is then covered with earth. The place of drilling the road is marked on both sides with special concrete pillars, as shown in the photo.

The speed of work done by the mechanized cable laying team is quite high. He does not need to be distracted by digging trenches and filling them. Almost all labor-intensive operations are mechanized and thought out in advance.
On average, during a work shift, it turns out that an optical cable is laid at a distance of about two kilometers. When there are no passes or other difficult obstacles on the route, the distance increases.
The presence of overgrown bushes, steep slopes of hilly terrain, marshy areas, dense soils of the third category, water barriers make the work difficult, require more time for its completion.
The route of laying the optical fibers is planned for us mainly along the roads. This allows you to drive to any part of the transport for follow-up service.
The optical fiber design and proven technology allow it to work in winter down to -10 degrees. At lower temperatures, we do not work on the track.
As soon as the cable is laid, the soil at the bottom of the cut trench usually moves and covers it, leaving the knife cut marks above.

We cannot immediately close them, but work for a few days and then start a tractor all over the paved track, which moves these edges with its roller on top. If there are connectors on the route, they are placed in boxes that are convenient for further maintenance.
The leveling of the edges of the soil, cut with a knife, in the period of high groundwater after massive snowmelt is shown in the photo.

The following photo allows you to appreciate the result of such work on the soil covered with a layer of grassy vegetation. Two pictures were taken three days later. The first one still shows snow that has already melted and is not visible on the second one. But the quality of the filling can be assessed visually.

After some time, the layers of soil under the influence of precipitation will finally merge, and the vegetation will hide the traces of our activity. Finding a cable buried in the ground will be difficult. To facilitate this process, technical documentation is served, in which the orientations of the cable and the location of the directional signs on the ground are drawn.
