Heat shrink for wires - device and principle of operation
For convenient and reliable insulation of wire contacts or simply for marking wires, heat-shrinkable tubes are widely used during electrical work (in common language, heat-shrinkable or heat-shrinkable tubes). In general, you can endlessly list the areas of application of heat shrink, starting with direct use, ending with various crafts. In the meantime, let's take a closer look at the topic.
What is heat shrink, how is it produced?
Many thermoplastic materials are known today: polyethylene, polyester, fluoroelastomer, polyethylene terephthalate, polyvinylidene, polyvinyl chloride, polymers with a polyolefin composition. These materials consist of elongated carbon chains that are usually randomly distributed throughout the bulk of the material.
If such a material is heated, the crystals will dissolve and the material itself will flow, forming an extensible mass, which, if cooled, will then assume the shape it will acquire when it cools.
So if you influence gamma rays on a material of this kind, then the separation of hydrogen atoms from molecules will occur, and in the places where the hydrogen has separated, the carbon chains are stitched together, a polymer with a new structure is formed.
If the cross-linked polymer is now heated above the dissolution temperature of the crystals, it will no longer stretch as before, but will be elastic like rubber. The cross-linked polymer can now be formed into the desired shape and it will retain this shape when cooled (for example, the shape of a wide tube).
If you then reheat such a product above the temperature of dissolution of the crystals, it will quickly return to its original shape (the tube will become narrower). That is, a conventional polymer, after exposure to gamma rays, acquires a new interesting and useful property — shape memory, in terms of the aspect under consideration — heat shrinkability.
For the production of direct heat shrinkable tubes, the polymer is processed in three stages: extrusion, exposure to radiation and the final stage — orientation. In extrusion, the softened material is squeezed through the orifice. The material is then exposed to a stream of electrons or gamma rays.
Electron irradiation produces thin-walled materials, and gamma rays produce materials with strong shrinkage and high elasticity, with a low shrinkage temperature. Orientation consists of heating the workpiece until it melts, stretching it, giving it the required size, shape and fixing it in this state during cooling.
Properties of heat shrink tubing

The main characteristics of heat shrink are: resistance to excessive heat, ability to elongate three times when stretched, slight change in shape, flame resistance, tensile strength of 15 MPa, elasticity, chemical resistance to acids and bases. So ordinary heat-shrinkable tubes can work normally at temperatures up to 120 ° C, and special ones - up to 270 ° C.
How does heat shrink tubing work and what is it for?
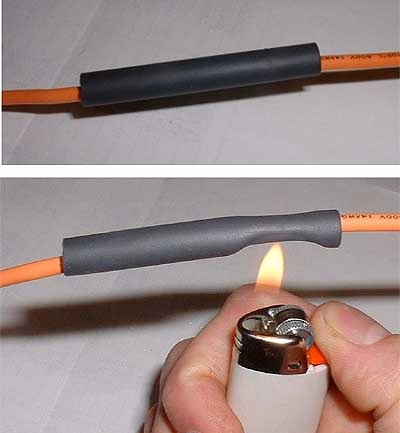

The tube is placed on the object to be insulated, then the tube is heated and it, shrinking, takes the shape of the object, pressing it, forming an insulating layer. So heat shrink tubing is used to insulate open spaces by compressing them with tubing. Isolation band, although it is used for similar purposes, but sometimes it is not as convenient as heat shrink, which is ideal for insulating contacts, terminals and wires.
Let's name just a few areas of application of heat shrink: insulation of wires, repair of cable connections, production of cables, installation of connectors, just like a sealant, for marking with different colors of wires for different purposes, installation of cables, protection of mechanisms from external factors (from acid, bases, high temperature), wiring repair, corrosion protection, etc., it is possible to list all areas for a long time ...
In general, thermal shrinkage:
-
protects objects from harmful temperature, chemical and mechanical influences;
-
helps to make visible markings or imperceptible insulation (the color of the pipe is the same as the color of the device);
-
the pipe is easy to use and reliable during installation;
-
easily fills in irregularities, performing the role of high-quality sealing;
-
natural;
-
and, importantly, with all these advantages, heat shrink tubing has a very low cost.
What are the types of heat shrink, how do they differ from each other
Heat-shrinkable adhesives have an inner adhesive layer, which when shrinking plays the role of an additional reliable sealant - the pipe is tightly pressed to the object, protects it from moisture. The shrinkage here is over 300%. When the object insulated from the pipe is much narrower than the pipe itself, then adhesive heat shrink is just what you need.

Thick-wall polyolefin heat shrinks are more popular than adhesives because they are inexpensive, easier to use, and come in a wide range of colors. They are burning and burning.
The first type of tube is made of components, none of which are combustible, and in the absence of an open flame, the tube will not catch fire, it will quickly go out. If the production is hazardous, for example a military plant or the production of explosives, then polyolefin heat shrink with flame suppression is suitable as an insulator.

In general, there are different types of special heat shrinks. In poorly lit places, fluorescent thermal shrinks are used, which accumulate light energy during the day and glow at night.
Heat shrink for high voltage circuits has increased insulating properties. Teflon shrink sleeves are suitable for high temperature conditions. Grooved heat shrink tubing is ideal for lining the handles of power tools and other electrical appliances.
Handling heat shrink tubing
It is best to use a special tool such as a heat gun or heat gun to properly and securely install heat shrink tubing.
Hot air is supplied through a special nozzle to the pipe, while it is better to adjust the air temperature and the shape of the nozzle can be selected individually. Under normal conditions, if there is no construction hair dryer or heat gun, use the available means: lighter, matches, soldering iron, boiling water, gas burner.
First of all, the surface on which the heat shrink will be installed is prepared: cleaned and degreased. Then select a suitable pipe according to: current environmental conditions, surface material, surface diameter and shrink diameter of the pipe, working surface temperature, moisture resistance, heat resistance, strength.
The thick-walled pipe is first heated, then placed so as not to overheat the surface to be treated, if this is critical, and only then heated to final shrinkage.
When cutting the heat shrink, do it carefully so that there are no burrs that could cause tearing in the future. Do not overheat, as this can unnecessarily deform the surface of the pipe. Properly installed heat shrink material has a flat, smooth surface without waves and bulges.
