Installation and connection of programmable logic controllers (PLC) in automation cabinets and panels
A programmable logic controller (PLC) is a special type of computer used to automate technological processes and objects.
The term PLC (English abbreviation — (PLC) programmable logic controller) was introduced by Odo Joseph Struger, an engineer at Allen -Bradley USA in 1971. He also played a key role in unifying the PLC programming languages.
When applying an algorithm to a control system, logical operations and a special organization of communication with sensors, actuators and human-machine interface are usually required.
An important feature of a PLC is its real-time operation. This is ensured by the use of special microprocessors that guarantee the response of the system to a request within a certain time interval.
PLCs usually operate under adverse external conditions — temperature, humidity, dust, electromagnetic radiation, radiation. Therefore, ordinary home computers were not used as controls.
In Russia since 2007.special programmable controller GOST R IEC 61131-1-2016 is in force.
PLCs are based on microcontrollers — specialized microprocessors with single-chip architecture. Microcontrollers can work without a chipset and motherboard, without an operating system. But this mode is mainly used in simple local automation systems. In complex systems, sufficiently powerful processors are used under the control of special operating systems.
For more information on purpose, device and PLC types, see here: What is Programmable Logic Controllers
The variety of PLCs is very large. There is not a single company in the field of automation and electronics that does not manufacture its own PLCs. Nevertheless, all PLCs are united by their common architecture and standardization of interfaces for connecting external devices.
The world's largest PLC manufacturers today are Siemens AG, Allen-Bradley, Rockwell Automation, Schneider Electric, Omron, Micubichi, Lovato. PLCs are produced by many other manufacturers, including the Russian companies Kontar LLC, Oven, Kontel LLC, Segnetiks, Fastwel Group, Tecon and others.
OWEN Programmable Logic Controllers
Siemens programmable controllers from the SIMATIC S7 series
An example of the appearance of a PLC in a standard monoblock is shown in the figure. These are PLC from OWEN (Russia) and PLC from 9 Siemens (Germany). Connectors for connecting power, sensors and actuators are located on both sides of the box.
Programmable logic controller PLC 63 from OWEN (Russia) and PLC from Siemens (Germany)
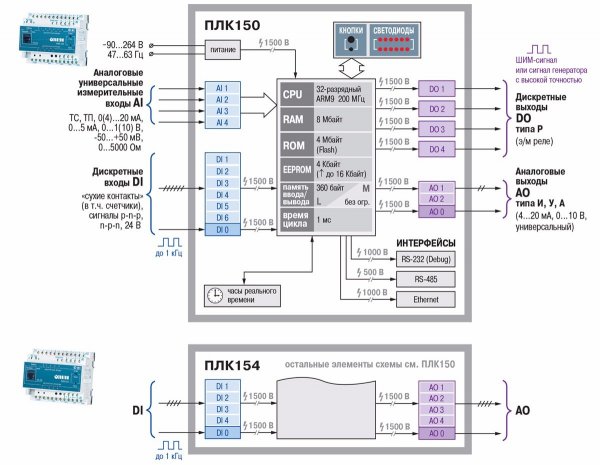
There are the following types of inputs-outputs: discrete, analog, universal, dedicated and interface.
Typically, discrete inputs are used to connect sensors that can be in two states: "active - passive" or "on - off". Using discrete inputs, you can connect buttons, switches, limit switches, thermostats and other equipment.
Discrete inputs of the controllers TAns are usually calculated to accept standard signals with a level of +24 V DC. A typical current value for a single digital input (at +24 V input voltage) is about 10 mA.
PLC discrete outputs are used to generate output signals with electrical parameters as a discrete input. They are generally used to control the switching on or off of drives.
According to GOST IEC 61131-2-2012 (Introduction Date 2014-07-01), an analog input is a device that converts a continuous signal into a discrete binary number for operation in a programmable controller system.
For analog inputs, the most common standard DC voltage ranges are –10… + 10 V and 0… + 10 V. For current inputs, the ranges are 0–20 mA and 4–20 mA.
Analog inputs allow the connection of analog sensors to the PLC.
In accordance with GOST 61131-2-2012 (Introduction date 2014-07-01), an analog output is a device that converts a binary number into an analog signal.
PLCs can be equipped with specialized I/O that enable duration measurement, edge fixation, pulse counting and motor control.
The number of these or these inputs-outputs is the main factor that determines the capabilities of the PLC, when creating an automation system based on it.
PLC outputs and connection of external devices
By design and mounting method, there are four versions of the PLC housing:
- housing for mounting on a DIN rail;
- housing for wall mounting;
- panel version;
- open frame design for embedded modular systems.
The DIN rail mounting housing is designed to mount the PLC on the control cabinet panel and has a special spring lock for fixing on a standard DIN rail.
The wall mount case is usually manufactured to dust and moisture protection standards and has built-in sealed seals for connection of external electrical wires, both power and signal.
The panel version of the PLC is used when the PLC is installed in the entrance door of the automation cabinet. Panel PLCs typically have a touch screen display that shows a mnemonic diagram of an automated process line or local automation system and that is used to input control parameters by the operator.
An open-frame PLC is used to create embedded (on-board) automation systems. In this case, the PLC is a printed circuit board with a set of connectors for connecting external devices and fasteners for connecting to other boards.
The connectors can be made with wires connected to the PLC under the screw clamp or detachable. The latter have a clear advantage in maintenance, for example when replacing a PLC. In this case, it is impossible to confuse the connection of the wires. However, the use of double connectors increases the cost of the PLC, which is why manufacturers more often use screw connections of wires in PLCs rather than detachable ones.
Monoblock PLCs usually have built-in or remote displays installed in the front panels of the control cabinets. They can be graphic, synthesizing or sensory.
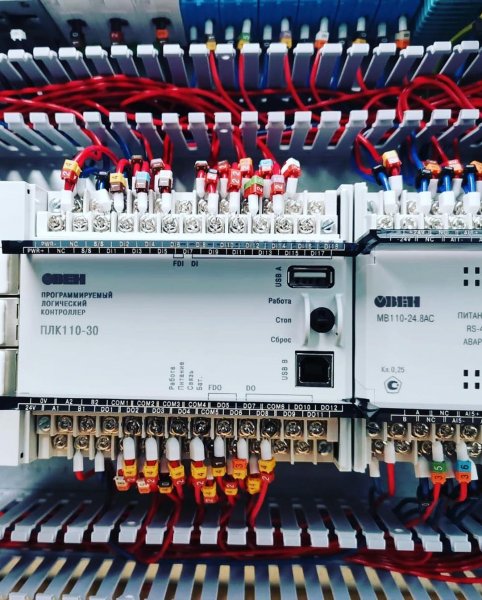
The figure below shows a PLC with a built-in LCD display and a keyboard that is used to set the parameters of the control algorithm locally.
The contacts of the PLC connector provide the PLC user with the ability to connect various types of sensors: analog, discrete, as well as actuators and I/O devices.
In addition, PLCs have a set of standard interfaces for tools for implementing distributed automation systems using different types of communication channels: wire, radio, Internet.
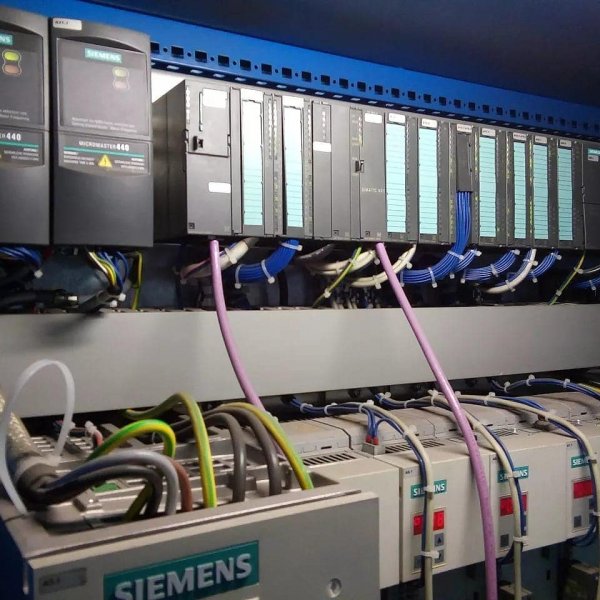
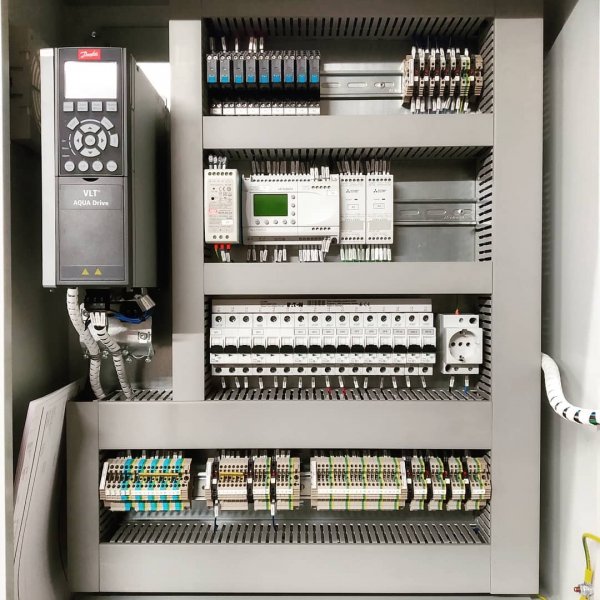
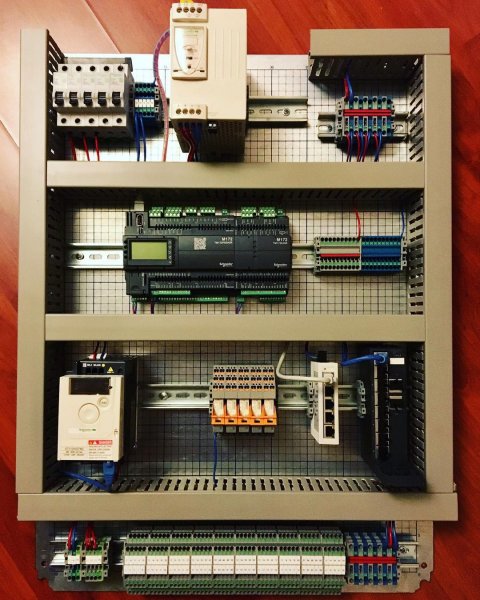
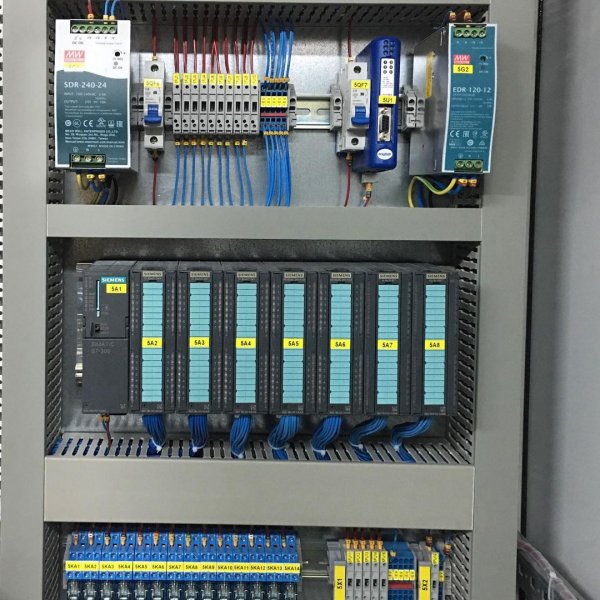
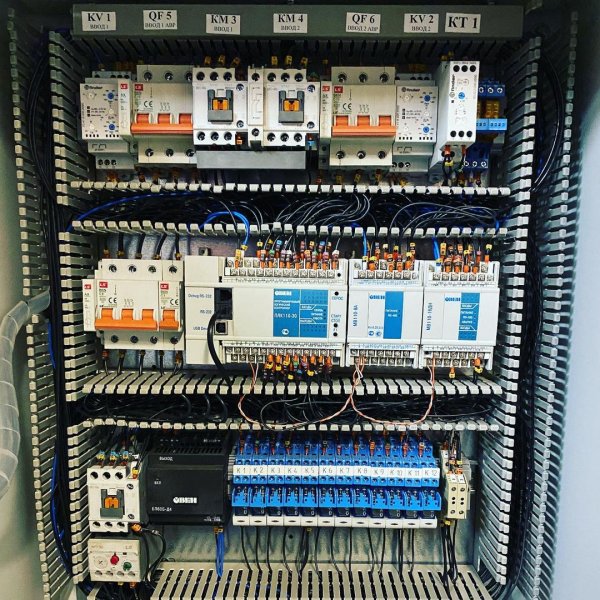
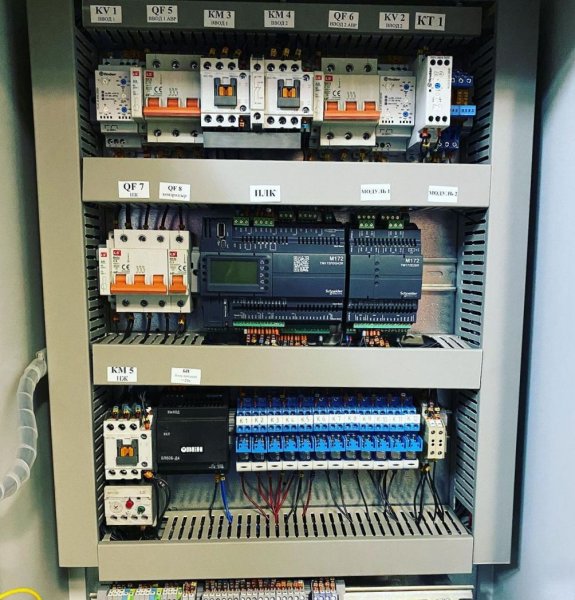
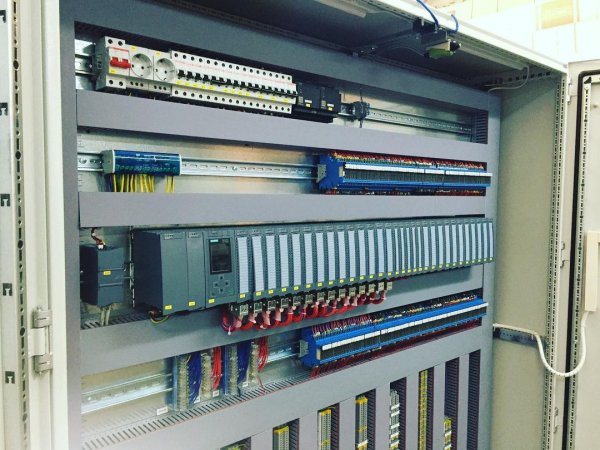
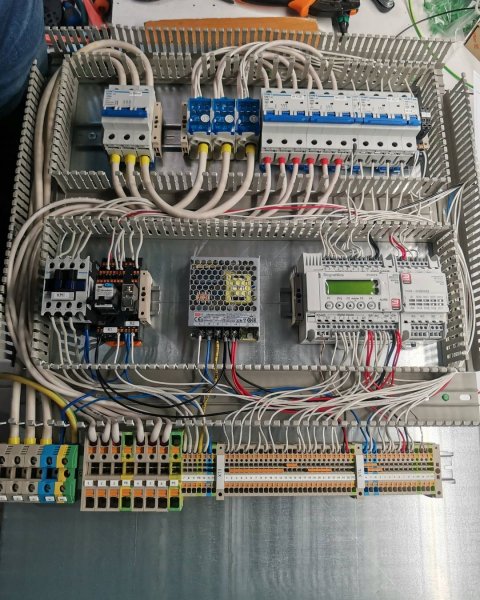
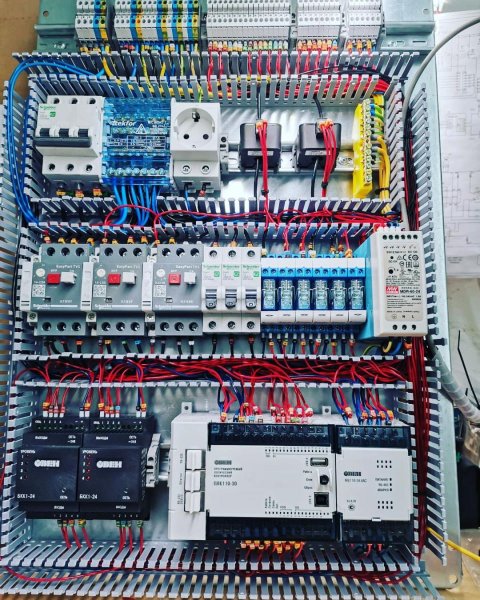
Programmable logic controllers are the basis for the production of automation cabinets (or panels) for various purposes.
The installation of automation elements on the cabinet panel is carried out according to the electrical circuit design, which is developed according to the specifications separately for each system.
The automation cabinet installation technology provides separate routing of power and signal wires in the distribution boxes (for example, power wires — in the right boxes and signal wires — in the left boxes, relative to the mounting panel), mandatory marking of wires, according to the project, and crimping of the ends on the wires with special terminals.
Automation cabinets may have built-in air conditioners or heaters to provide internal temperature control.
PLC based automation cabinet
Almost all modern PLCs have a built-in switching power supply that provides power from an external source in the AC voltage range of 110 to 265 volts (AD-DC voltage converter) or from a DC power supply (DC-DC voltage converter).
Switching power supplies have a number of built-in automatic protections: short circuit, overheating and overload.
A typical PLC power connection requires a surge suppression filter beforehand. The selection of pulsed power supplies is made according to the value of the required energy consumption and the required output values of the nominal powers.
If the main source of input voltage is switched off due to accident or malfunction, then operation or proper shutdown of the device or system can be ensured by an uninterruptible power supply.
The degree of protection of the PLC is encrypted with an IP mark (Ingress Protection Rating). IP literally translates as ingress protection degree. Currently, this is the most common designation system for protecting equipment from the effects of the external environment. It is used to indicate protection against the penetration of various physical particles into the equipment by geometric dimensions, including dust and water.
IP degree of protection — decoding, examples of equipment
PLC enclosures, as well as the cabinets or panels in which they are installed, may have a degree of protection.
The installation and connection of specific programmable logic controllers (PLCs) in automation cabinets and panels must be done in accordance with the manufacturers' instructions.
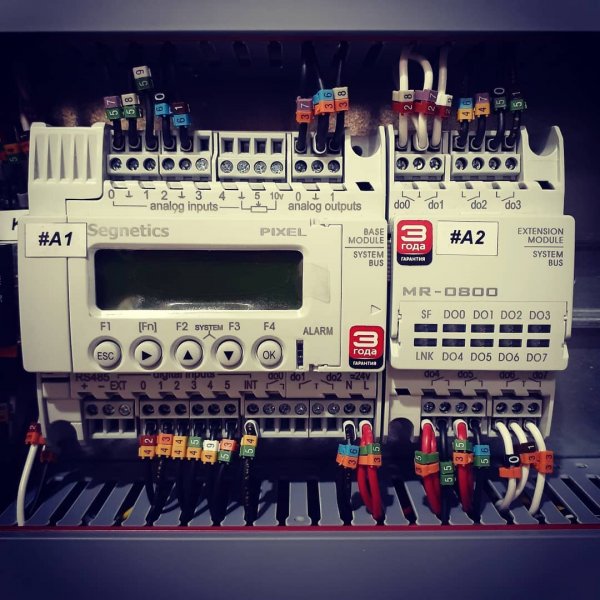
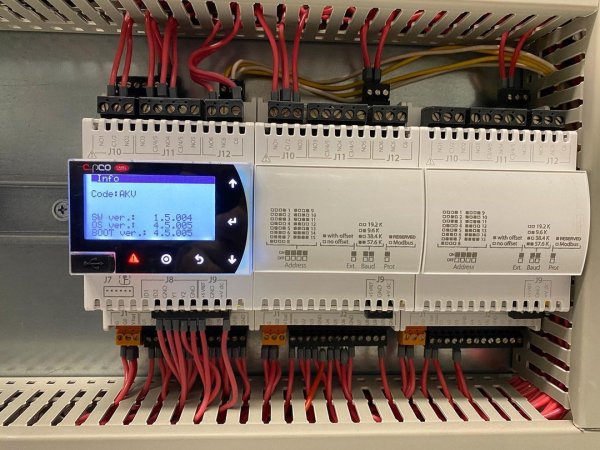
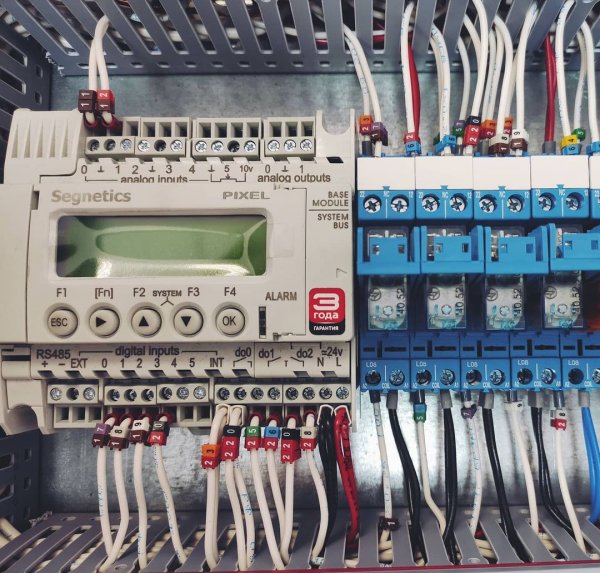
Pictures of automation panels with programmable logic controllers: