Grounding devices
 If the insulation is damaged, metal parts of electrical installations and equipment that are not normally energized may be under full operating voltage. If a person touches them, there is a risk of electric shock.
If the insulation is damaged, metal parts of electrical installations and equipment that are not normally energized may be under full operating voltage. If a person touches them, there is a risk of electric shock.
One of the measures to protect people in these cases is to intentionally connect to the ground (through grounding conductors and grounding conductors, for example, pipes driven into the ground) metal parts of electrical equipment and electrical installations that may be under voltage due to insulation failure. The essence of this protection measure is as follows.
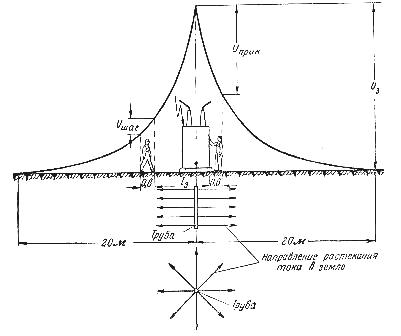
If the insulation is damaged, the current flows through the grounding point. Along the path of the current flow, a voltage drop is created between the energized metal part and the ground, the largest value being «voltage to ground», that is, the voltage between the body of the electrical receiver and the grounding points located outside the area of current distribution in the ground. In practice, such points are located at a distance of 20 m or more from the concentrated earth electrode system (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1.Voltage distribution curve relative to ground
The voltage between two points in the current path that a person can touch at the same time (for example, between the body of an electrical receiver and where a person stands, or between the legs of a person walking or standing in the area of current flow) is called "Touch Voltage" ("Step"). This voltage will always be less than the «voltage with respect to earth».
In networks with low earth fault currents, i.e. where generators and transformers operation with isolated neutral or neutral earthed by compensating resistance, the safety of personnel from touching live metal parts can be achieved by selecting an earthing resistance at which the touch voltage will be within the permissible range.
In networks with high earth fault currents, i.e. where the neutral of transformers or generators is earthed solidly or by a small resistance, safety can only be ensured by the fastest possible automatic tripping of the faulted section. Such disconnection must be done either by relay protection or protective devices (circuit breakers or fuses)… By appropriate positioning of earthing switches to equalize the potentials, further reduction of touch and step voltages can be achieved.
Earthing devices built primarily to ensure the safety of personnel must also meet the requirements due to mains modes and surge protection.
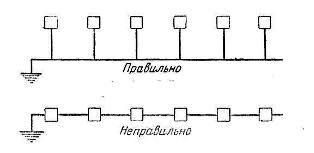
It is not allowed to connect in series to the grounding wire of the grounded installation elements., because when any element of the installation is removed for repair, replacement, etc., there will be a break in the grounding circuit with all the consequent consequences.
When connected in parallel (that is, by means of separate branches) in this case, the continuity of the grounding circuit (grounding line) is maintained. The grounding of the associated mounting elements is not disturbed (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2. Schemes for connecting grounded electrical receivers to the grounding line
Methods of connecting grounding conductors to grounded structures, device housings, machines, to grounding electrodes, etc., as well as connecting grounding conductors to each other must ensure reliable contact. Inadequate connection may impair the function of the grounding device.
Welding ensures the greatest reliability of the connection. The bolted connection is used only in those places of the grounding wiring where it is necessary to disconnect it from the common grounding network, for example, during repairs or tests. If in this case there is any shock or vibration, measures must be taken against loosening of the contact (lock nuts, lock washers, etc.).
To ensure a reliable connection, the bolt surfaces are carefully cleaned.
The welding of grounding wires is carried out with an overlap with a seam length equal to twice the width with a rectangular cross-section or six times the diameter — with a round cross-section of wires.
According to Rules for electrical installation if it is impossible to connect grounding wires to the pipeline (extended grounding electrode) by welding, it is allowed to do it with the help of clamps, the contact surface of which must be tinned. The pipes in the places where the clamps are placed must be cleaned.
Electrical installation regulations also require this equipment grounding, subject to private disassembly or mounted on moving parts, were carried out using flexible wires.