Determination of engine power in continuous operation
 The mode of operation of the electric drive with such duration, in which the temperature of the electric motor reaches a stationary value, is called long-term. In this case, the nominal power of the electric motor must be equal to the power required to operate the machine. If there is no electric motor with this nominal power in the catalog, the motor with the closest higher power is selected.
The mode of operation of the electric drive with such duration, in which the temperature of the electric motor reaches a stationary value, is called long-term. In this case, the nominal power of the electric motor must be equal to the power required to operate the machine. If there is no electric motor with this nominal power in the catalog, the motor with the closest higher power is selected.
If for a given technological process the cutting force F in N and the cutting speed v in m / min are known, then the cutting power in kW can be determined by the formula:

In order to determine the corresponding shaft power of the driving electric motor, it is necessary to take into account the losses in the mechanical transmissions of the machine and for this it is necessary to know the efficiency of the machine ηc; then:
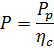
The power losses during engine start-up (on average) exceed the losses at nominal load, but in the considered regime, the starting processes are repeated so rarely that these losses can be neglected.
When determining the driving power of universal (universal) machines, they are considered machines with a continuous mode of operation, since at. the operation of these machines is also possible in such a mode. In this case, the power of the electric motor shaft
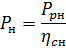
where Prn — the highest possible (nominal) cutting power;
ηcn — efficiency of the main motion circuit of the machine at rated load (value usually close to 0.8).
The efficiency of the machine ηsn at its full load can be defined as the product of the efficiency of the individual gears that form a kinematic chain when operating at a given speed:
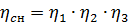
Each speed corresponds to a certain value of the efficiency of the machine, depending on the number of gears and their type.
With a significant increase in rotation speed, the power loss in the machine increases significantly. This is due to the fact that some losses grow faster than the speed of rotation (for example, oil mixing losses in gearboxes).
 The power required to drive power circuits is usually low. When driving the main drive and power circuit together, the motor power should be approximately 5% greater than the power required for the main drive circuit. With a separate power supply, its power must be determined in the same way as it was done for the main drive circuit. In this case, the power of the engine is spent on feeding and overcoming friction in the guides and other transmission connections.
The power required to drive power circuits is usually low. When driving the main drive and power circuit together, the motor power should be approximately 5% greater than the power required for the main drive circuit. With a separate power supply, its power must be determined in the same way as it was done for the main drive circuit. In this case, the power of the engine is spent on feeding and overcoming friction in the guides and other transmission connections.
The effectiveness of a supply chain can be determined by knowing the elements that make up that chain.Typically, the value of this efficiency is in the range of 0.1-0.2.
Universal machines with motors selected based on the highest load conditions are usually under load. With such work, it significantly worsens drive energy performance... The reduction of the nominal power of the electric motor compared to the greatest possible load leads to a limitation of the possibilities of using the machine. Considering this unacceptable, machine tool plants produce universal machines with prime mover electric motors installed on them, selected for the highest power these machines can operate.
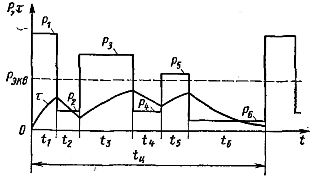
Rice. 1. Schedule of continuous operation with variable load
Under long-term variable load, the operation of the electric drive is characterized by a load schedule similar to that shown in Fig. 1.Each machining transition of a metal cutting machine part corresponds to a certain motor shaft power. Cutting periods are separated by machine idle intervals during which the tool is fed and withdrawn and the workpiece is changed.
The total time to process one part, including all auxiliary operations, is called the cycle time tts. So do machines that process the same type of parts and have a friction clutch in the main drive chain, as do automatic line machines where many electric motors rotate continuously.
When operating with a variable load, the motor must be selected so that it can operate at its highest power according to the schedule (overload selection), so that when operating on a given load schedule, the motor does not overheat above normal (selection by heating). Of the two nominal capacities determined by these conditions, the larger one is selected.
Overload capacity
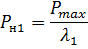
where Pn1 is the rated engine power required under overload conditions; Pmax — the maximum power of the load schedule corresponding to the operation of the engine in an equilibrium state; λ1 — coefficient of permissible overload.
