Regulation of the angular speed of the induction motor by changing the number of pole pairs of the stator
 As the number of pole pairs increases, the angular velocity of the field decreases, hence the rotor speed of the induction motor also decreases. Special edition two-speed asynchronous motors, the stator windings of which consist of separate parts. They can be connected again in two different ways: a star and a double star (Fig. 1, a, b) or a triangle and a double star (Fig. 1, b, d).
As the number of pole pairs increases, the angular velocity of the field decreases, hence the rotor speed of the induction motor also decreases. Special edition two-speed asynchronous motors, the stator windings of which consist of separate parts. They can be connected again in two different ways: a star and a double star (Fig. 1, a, b) or a triangle and a double star (Fig. 1, b, d).
In a double star, the field speed is always twice that of a star or triangle. However, these switches are not equal. The fact is that the maximum permissible torque during continuous operation is determined by the maximum permissible phase current according to the heating conditions of the windings and depends on the stator flux proportional to the square of the phase voltage. The long-term permissible power also depends on the same values.
If you switch the windings of the motor from star to double star, the phase voltage will not change, and when switching from delta to double star, it decreases by √3 times. But with double star, the current in each phase can be twice as much as in star or delta, because each phase consists of two parallel branches. We then find that when going from a star to a double star, the speed and power double, therefore the critical moment remains constant (M = P /ω= const).
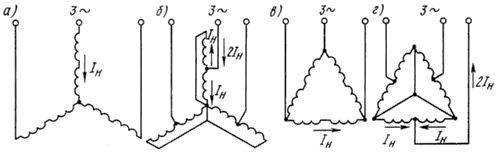
Rice. 1. Schemes for connecting the stator windings of an asynchronous motor in star (a) and double star (b), in deltas (c) and double star (d)
If you go from delta to double star, the phase voltage decreases by √3 times. Then, even with two-phase current, the power will increase only by 2 /√3 = l, 18 times and can be considered unchanged. In this case, as the angular velocity increases by a factor of two, the power almost changes, and the moment decreases approximately by a factor of two. Thus, it is recommended to use motors for driving lifting devices whose windings are connected in star, and for driving metal cutting machines, motors whose stator windings are connected in delta.

Rice. 2. Passport data of a multi-speed motor
There are asynchronous electric motors with two stator windings isolated from each other, one of them without switching, and the second with switching poles. After that, three-speed engines are obtained. If both windings are pole-changed, then the motors are four-stage. In some cases, two insulated windings with different numbers of pole pairs are used. pp without switching.For example, in elevator motors p1 = 3 and p2 = 12, which corresponds to the synchronous speed of rotation of 1000 and 250 rpm.
In fig. 3a shows the mechanical characteristics for a two-speed star-to-double-star motor, and FIG. 3, b — when changing from a triangle to a double star.
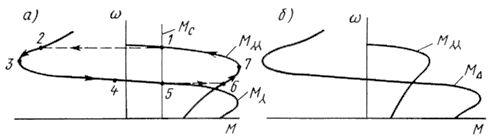
Rice. 3... Mechanical characteristics of asynchronous electric motors when switching from star to double star (a) and from delta to double star (b)
In the case of a quick change from a higher speed to a lower speed, the engine runs for a while. suspension mode… In fact, if the speed of the field decreases, then at the first moment the rotor continues to rotate at the same speed.
The engine instantly switches from one characteristic to another, i.e. from point 1 to point 2 (Fig. 3, a). Regenerative braking follows (points 2, 3, 4), at point 5 it starts operating in a steady state. If you switch from a lower speed to a higher one, the motor instantly moves from point 5 to point b, then acceleration follows (points 6 and 7) and at point 1 an equilibrium state appears again.
