Ohm's law for a complete circuit
 In electrical engineering there are terms: section and full circuit.
In electrical engineering there are terms: section and full circuit.
The site is called:
-
part of an electrical circuit inside a source of current or voltage;
-
the entire external or internal circuit of electrical elements connected to the source or part of it.
The term «complete circuit» is used to refer to a circuit with all circuits assembled, including:
-
sources;
-
users;
-
connecting wires.
Such definitions help to better navigate the circuits, understand their characteristics, analyze the work, search for damages and malfunctions. They are embedded in Ohm's law, which allows you to solve the same questions to optimize electrical processes for human needs.
Georg Simon Ohm's fundamental research applies to virtually every section of the circuit or the full schematic.
How Ohm's Law works for a complete DC circuit
For example, let us take a galvanic cell, which is popularly called a battery, with a potential difference U between anode and cathode. We connect a light bulb with a filament to its terminals, which has a simple resistive resistance R.
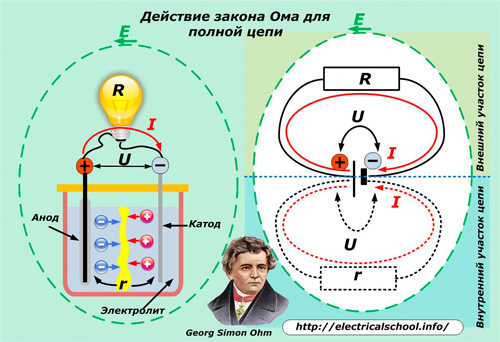
A current I = U / R created by the movement of electrons in the metal will flow through the filament. The circuit formed by the battery wires, connecting wires and the bulb refers to the external part of the circuit.
Current will also flow in the internal section between the battery electrodes. Its carriers will be positively and negatively charged ions. Electrons will be attracted to the cathode and positive ions will be repelled from it to the anode.
In this way, positive and negative charges accumulate on the cathode and anode, and a potential difference is created between them.
The complete movement of ions in the electrolyte is hindered internal resistance of the batterymarked with «r». It limits the current output to the external circuit and reduces its power to a certain value.
In the complete circuit of the circuit, the current flows through the inner and outer circuits, overcoming the total resistance R + r of the two sections in series. Its value is influenced by the force applied to the electrodes, which is called electromotive or EMF for short and is denoted by the index «E».
Its value can be measured with a voltmeter at the terminals of the battery without load (no external circuit). With a load connected in the same place, the voltmeter shows the voltage U. In other words: with no load on the battery terminals, U and E match in magnitude, and when the current flows through the external circuit, U < E.
Force E forms the movement of electric charges in a complete circuit and determines its value I = E / (R + r).
This mathematical expression defines Ohm's law for a complete DC circuit. Its action is illustrated in more detail on the right side of the picture.It shows that the entire complete circuit consists of two separate current circuits.
It can also be seen that inside the battery, even when the external circuit load is switched off, the charged particles move (self-discharge current) and therefore unnecessary consumption of metal occurs at the cathode. Battery energy, due to internal resistance, is spent heating and dissipating into the environment, and over time it simply disappears.
Practice shows that reducing the internal resistance r by constructive methods is not economically justified due to the sharply increasing costs of the final product and its rather high self-discharge.
conclusions
To maintain the efficiency of the battery, it should be used only for its intended purpose, connecting the external circuit exclusively for the period of operation.
The higher the resistance of the connected load, the longer the battery life. Therefore, xenon lamps with an incandescent filament with lower current consumption than nitrogen-filled ones with the same luminous flux ensure a longer service life of energy sources.
When storing galvanic elements, the passage of current between the contacts of the external circuit must be excluded by reliable isolation.
In the event that the external circuit resistance R of the battery significantly exceeds the internal value r, it is considered a voltage source, and when the reverse relationship is fulfilled, it is a current source.
How Ohm's Law is used for a complete AC circuit
AC electrical systems are the most common in the electrical industry.In this industry, they reach enormous lengths by transporting electricity over power lines.
As the length of the transmission line increases, its electrical resistance increases, which creates heating of the wires and increases the loss of energy for transmission.
Knowledge of Ohm's law helped power engineers to reduce unnecessary costs of transporting electricity. To do this, they used the calculation of the component of the power loss in the wires.
The calculation is based on the value of the produced active power P = E ∙ I, which must be transferred qualitatively to remote consumers and overcome the total resistance:
-
internal r at generator;
-
outer R of wires.
The magnitude of the EMF at the generator terminals is determined as E = I ∙ (r + R).
The power loss Pp to overcome the resistance of the complete circuit will be expressed by the formula shown in the picture.

It can be seen from it that the power consumption increases in proportion to the length / resistance of the wires and it is possible to reduce them during the transport of power by increasing the EMF of the generator or the line voltage. This method is used by including step-up transformers in the circuit at the generator end of the power line and step-down transformers at the receiving point of electrical substations.
However, this method is limited:
-
the complexity of technical devices to counteract the occurrence of coronary discharges;
-
the need to distance and isolate power lines from the earth's surface;
-
increase in the energy of air line radiation in space (the appearance of the antenna effect).
Characteristics of Ohm's law operation in sinusoidal alternating current circuits
Modern users of industrial high voltage and domestic three-phase / single-phase electric power create not only active, but also reactive loads with pronounced inductive or capacitive characteristics. They lead to a phase shift between the vectors of the applied voltages and the currents flowing in the circuit.
In this case, for the mathematical notation of the time fluctuations of the harmonics, use complex formand vector graphics are used for spatial representation. The current transmitted through the power line is recorded by the formula: I = U / Z.
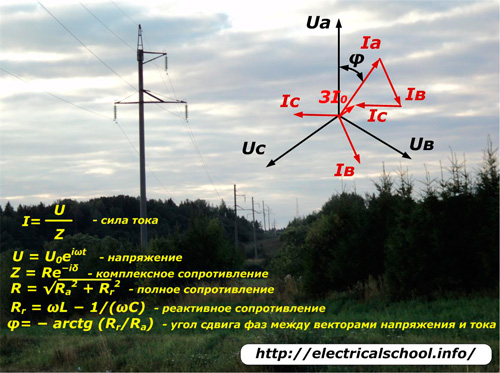
The mathematical notation of the main components of Ohm's law with complex numbers allows programming the algorithms of electronic devices used to control and manage complex technological processes constantly occurring in the power system.
Along with complex numbers, the differential form of writing all ratios is used. It is convenient for analyzing the conductive properties of materials.
Some technical factors can violate Ohm's law for a complete circuit. They include:
-
high vibrational frequencies when the momentum of the charge carriers begins to influence. They do not have time to move with the pace of changes in the electromagnetic field;
-
states of superconductivity of a certain class of substances at low temperatures;
-
increased heating of current wires by electric current. when the current-voltage characteristic loses its linear character;
-
destruction of the insulation layer by high voltage discharge;
-
medium of gas or vacuum electron tubes;
-
semiconductor devices and elements.
