How short circuit protection works and works
 The term «short circuit» in electrical engineering refers to the emergency operation of voltage sources. Occurs in the event of violations of the technological processes of energy transmission, when the output terminals are short-circuited (short circuit) of a working generator or chemical element.
The term «short circuit» in electrical engineering refers to the emergency operation of voltage sources. Occurs in the event of violations of the technological processes of energy transmission, when the output terminals are short-circuited (short circuit) of a working generator or chemical element.
In this case, the full power of the source is immediately applied to the short circuit. Huge currents flow through it, which can burn equipment and cause electrical injuries to nearby people. To stop the development of such incidents, special protections are used.
What are the types of short circuits
Natural electrical anomalies
They appear during lightning discharges accompanied by powerful lightning.
The sources of their formation are high potentials of static electricity of different signs and magnitudes, accumulated by clouds when they are moved by the wind over long distances. As a result of natural cooling, as it rises in height, the moisture in the clouds condenses, forming rain.
A humid environment has a low electrical resistance, which creates a breakdown of the air insulation for the passage of current in the form of lightning.
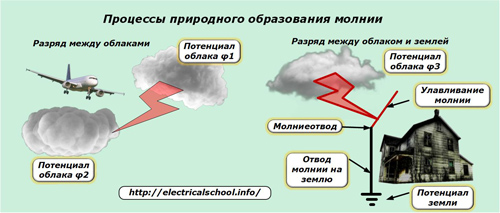
An electric discharge slides between two objects of different potentials:
- on the approaching clouds;
- between a thundercloud and the ground.
The first type of lightning is dangerous for aircraft, and discharge to the ground can destroy trees, buildings, industrial facilities, overhead power lines. To protect against it, lightning rods are installed, which successively perform the following functions:
1. receiving, attracting the lightning potential to a special arrester;
2. passage of the received current through a conduit to the grounding circuit of the building;
3. the discharge of the high voltage discharge from this circuit to ground potential.
Short circuits in direct currents
Galvanic voltage sources or rectifiers create a difference in the positive and negative potentials of the output contacts, which under normal conditions ensures the operation of the circuit, for example, the glow of a light bulb from a battery, as shown in the figure below.
The electrical processes taking place in this case are described by a mathematical expression Ohm's law for a complete circuit.
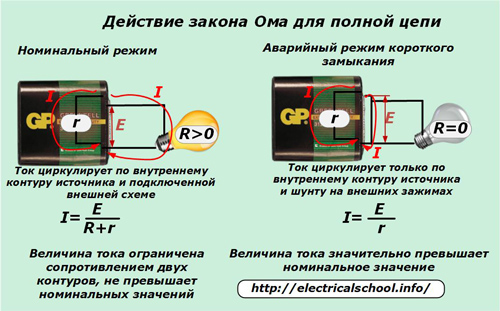
The electromotive force of the source is distributed to create a load in the internal and external circuits by overcoming their resistances «R» and «r».
In emergency mode, a short circuit with very low electrical resistance occurs between the battery terminals «+» and «-», which practically shuts off the flow of current in the external circuit, deactivating this part of the circuit. Therefore, with respect to the nominal mode, we can assume that R = 0.
All the current circulates only in the internal circuit, which has a small resistance and is determined by the formula I = E / r.
Since the magnitude of the electromotive force has not changed, the value of the current increases very sharply. Such a short circuit flows through the shorting wire and the inner loop, causing enormous heat generation in them and subsequent structural damage.
Short circuits in AC circuits
All electrical processes here are also described by the operation of Ohm's law and proceed according to a similar principle. The characteristics of their passage require:
-
the use of single-phase or three-phase networks with different configurations;
-
the presence of a ground loop.
Types of short circuits in AC circuits
Short circuit currents can occur between:
-
phase and ground;
-
two different phases;
-
two different phases and grounding;
-
three phases;
-
three phases and ground.

For the transmission of electricity through overhead power lines, power systems may use a different neutral connection scheme:
1. isolated;
2. deafly grounded.
In each of these cases the short circuit currents will form their own path and have a different value. Therefore, all the above options for assembling an electrical circuit and the possibility of short-circuit currents in them are taken into account when creating a current protection configuration for them.
A short circuit can also occur in consumers of electricity, for example an electric motor. In single-phase structures, the phase potential can break through the insulation layer to the housing or neutral conductor.In three-phase electrical equipment, an additional fault can occur between two or three phases or between their combinations with the frame / ground.
In all these cases, as in the case of a short circuit in DC circuits, a short circuit current of very large magnitude will flow through the short circuit formed and the entire circuit connected to it to the generator, causing an emergency mode.
To prevent this, protections are used that automatically remove voltage from equipment exposed to increased currents.
How to choose the operating limits of short circuit protection
All electrical appliances are designed to consume a certain amount of electricity in their voltage class. It is accepted to evaluate the load not by power, but by current. It is easier to measure, control and create protection against it.
The picture shows graphs of currents that can occur in different modes of operation of the equipment. For them, the parameters for setting and setting protective devices are selected.
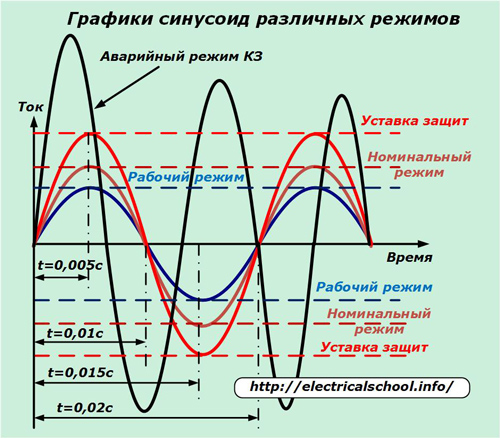
The graph in brown color shows the sine wave of the nominal mode, which is selected as the initial one in the design of the electrical circuit, taking into account the power of the wiring and the selection of current protection devices.
Industrial frequency sine wave 50 hertz in this mode it is always stable, and the period of one complete oscillation occurs in a time of 0.02 seconds.
The sine wave of the operating mode is shown in blue in the picture. It is usually less than the nominal harmonic. People rarely fully use all reserves of their assigned capacity.As an example, if a five-arm chandelier hangs in a room, then one group of bulbs is often included for lighting: two or three, not all five.
In order for electrical appliances to work reliably at rated load, they create a small current reserve for setting protections. The amount of current at which they adjust to trip is called the setpoint. When reached, the switches remove voltage from the equipment.
In the range of sinusoidal amplitudes between the nominal mode and the set point, the circuit operates in a slight overload mode.
A possible time characteristic of the fault current is shown in the graph in black. Its amplitude exceeds the protection setting, and the oscillation frequency has changed dramatically. It is usually aperiodic in nature. Each half-wave changes in magnitude and frequency.
Overcurrent protection algorithm
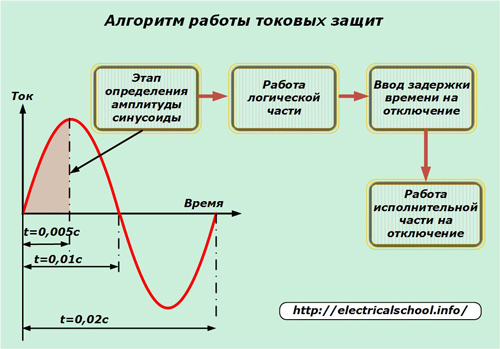
Each short-circuit protection includes three main stages of operation:
1. constant monitoring of the state of the monitored current sinusoid and determination of the moment of the malfunction;
2. analysis of the situation and issuing a command to the executive body from the logical part;
3. release of voltage from the equipment by means of switching devices.
In many devices, another element is used — the introduction of response time delay. It is used to provide the principle of selectivity in complex, branched circuits.
Since the sine wave reaches its amplitude in a time of 0.005 sec, this period is at least necessary for its measurement by the protections. The next two stages of work are also not carried out immediately.
For these reasons, the total operating time of the fastest current protections is slightly less than the period of one harmonic oscillation of 0.02 sec.
Design features of short circuit protection
The electric current flowing through each wire causes:
-
thermal heating of the conductor;
-
directing a magnetic field.
These two actions are taken as the basis for the design of protective devices.
Current protection
The thermal effect of current, described by scientists Joule and Lenz, is used to protect fuses.
Security guard
It is based on the installation of a fuse in the current path, which optimally withstands the nominal load, but burns out when exceeded, interrupting the circuit.
The higher the value of the emergency current, the faster the circuit break is created - removing the voltage. If the current is slightly exceeded, it may turn off after a long period of time.

Fuses successfully work in electronic devices, electrical equipment of cars, household appliances, industrial devices up to 1000 volts. Some of their models are used in high voltage equipment circuits.
Protection based on the principle of electromagnetic influence of the current
The principle of inducing a magnetic field around a current-carrying wire made it possible to create a huge class of electromagnetic relays and switches using a trip coil.
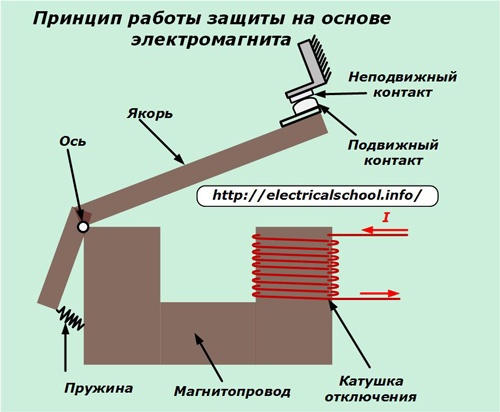
Its coil is located on a core — a magnetic circuit in which magnetic fluxes are added from each turn. The movable contact is mechanically connected to the armature, which is the swinging part of the core. It is pressed against the stationary contact by the force of the spring.
The rated current flowing through the turns of the spiral coil creates a magnetic flux that cannot overcome the force of the spring. Therefore, the contacts are permanently closed.
In case of emergency currents, the armature is attracted to the stationary part of the magnetic circuit and breaks the circuit created by the contacts.
One of the types of circuit breakers operating on the basis of removing electromagnetic voltage from the protected circuit is shown in the photo.
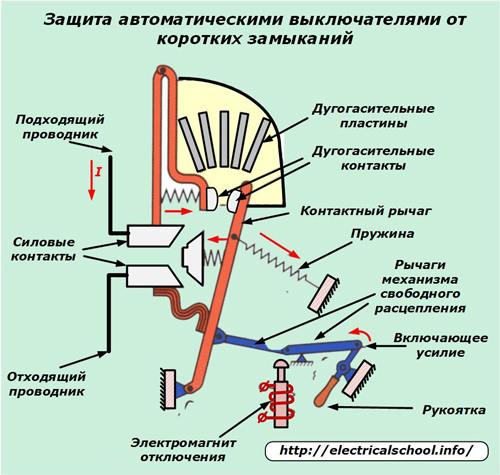
It uses:
-
automatic shutdown of emergency modes;
-
electric arc extinguishing system;
-
manual or automatic start.
Digital short circuit protection
All the protections discussed above work with analog values. In addition to these, recently in industry and especially in the energy sector, digital technologies are actively introduced based on the work microprocessor devices and static relays. The same devices with simplified functions are produced for household needs.
The measurement of the magnitude and direction of the current passing through the protected circuit is carried out by a built-in step-down current transformer with a high degree of accuracy. The signal measured by it is digitized by superposition high frequency rectangular pulses according to the principle of amplitude modulation.
Then it goes to the logical part of the protection of the microprocessor, which works according to a certain, pre-configured algorithm. In case of emergency situations, the device logic issues a command to the shutdown actuator to remove the voltage from the network.
For the protective operation, a power supply unit is used, which takes voltage from the mains or autonomous sources.
Digital short-circuit protection has a large number of functions, settings and capabilities up to registering the emergency state of the network and its shutdown mode.
