The selection of an asynchronous electric motor for operation in the mode of dynamic braking by self-excitation
 Asynchronous electric motor with a wound rotor with the simplest control scheme — the inclusion of resistance in the rotor circuit has extremely low control properties. Therefore, before the availability of frequency converters in the market, various schemes were developed to obtain reduced speed in step-down mode.
Asynchronous electric motor with a wound rotor with the simplest control scheme — the inclusion of resistance in the rotor circuit has extremely low control properties. Therefore, before the availability of frequency converters in the market, various schemes were developed to obtain reduced speed in step-down mode.
Actually, there aren't that many of them. Abroad, the use of an additional electric machine—a vortex brake mounted on the same shaft as the main engine—became widespread. The scheme allows you to get sufficiently rigid mechanical characteristics when lowering the load, but such an electric drive has extremely low energy characteristics (braking energy is released in the vortex brake). In addition, the vortex brake has a rather high cost and greatly complicates the layout of the mechanical part.
Therefore, in order to obtain the landing speed in lifting mechanisms based on an asynchronous motor with a phase rotor at the Dynamo plant in the late 1970s, a design team led by E.M. Pevzner introduced self-excited dynamic braking.
Such an electric drive is widely used in domestic cranes (panels of type TSD, TSDI, KSDB for bridge, gantry and gantry cranes, control panels for tower cranes KB-309, KB-403, KB-404, KB-405, KB -406, KB-408, KB-415, KB-415-07, KB-473, KBM-401P.). Thus, we are talking about tens of thousands of cranes in operation.
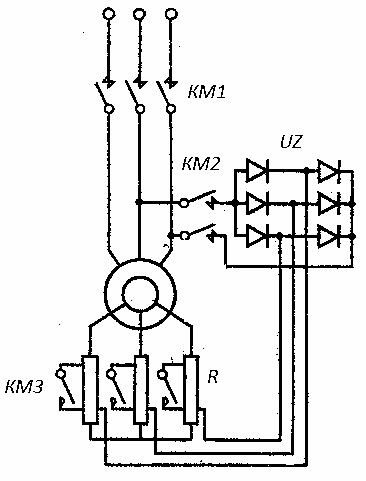
Rice. 1. Scheme of inclusion of an asynchronous motor in dynamic braking mode by self-excitation
The principle of dynamic braking with self-excitation is as follows:
The rotor circuit includes three-phase rectifier UZ (Fig. 1). The electric motor is disconnected from the network via the contactor KM1. The rectified voltage is connected to the stator winding through the contactor KM2. Contactor contacts KM3 are closed. When the brake is released (not shown in the diagram), the motor shaft begins to rotate under the action of the falling weight.
An EMF is induced in the rotor winding, under the influence of which a current begins to flow in the rotor-stator circuit. The motor develops the braking torque, the load is lowered at a constant speed. The speed value is determined by the resistance value of the rotor circuit. The greater the resistance, the faster the rate of descent. To increase the speed, contactor KM3 is turned off.
In self-excitation dynamic braking mode, the electric drive consumes power from the network only to power the brake hydraulic pusher and relay-contactor equipment. As an example, Fig. 7 shows the mechanical characteristics of an electric drive with a TSD panel.
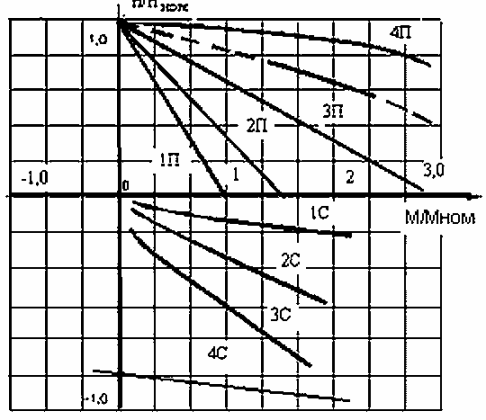
Rice. 2. Mechanical characteristics of the electric drive of the lifting mechanism with the TSD panel
Dynamic braking characteristics are designated as 1C, 2C, 3C. It can be seen that the characteristics have sufficient hardness. The speed adjustment is carried out in the range 1: 8, which in most cases is sufficient for mass faucets.
The condition for self-excitation of the electric motor is:
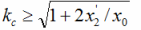
Where x '2- inductive resistance of the rotor winding, Ohm; хо- inductive resistance of the magnetizing circuit. Om
Where ks — coefficient of the scheme
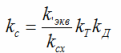
kd — coefficient of reduction of the rotor current to the stator current; kcx — correction circuit coefficient, for a three-phase bridge circuit kx = 0.85; kt is the transformation coefficient of the motor from stator to rotor
Coefficient kd depends on the connection scheme of the stator windings, which are connected to a star in household faucet motors at a mains voltage of 380 V.
Coefficient kt depends on the transformation coefficient, i.e. of the ratio of stator voltage to rotor voltage, which depends on the motor type. For example, for several electric motors of the MT and 4MT series, the value and related parameters are tabulated. 1.
Table 1.
Electric motor type power, kWt Rotor voltage, V kt x x '2 xho √(1 + 2x '2/ho) MTN412-6 30 255 1.5 1.3 0.173 3.74 1.04 4MTN225L6 55 290 1.31 1.31 0.197 3.73 1.05 MTN512-6 55 340 1.11 0.98 0.197 3.8 1.05 4MTN280L10 75 308 1.23 1.06 0.146 2.33 1.06 4MTN280M6 110 420 0. 9 0.7 0.083 2.98 1.02
Condition кс ≥ √(1 + 2х '2/хо) is carried out for engines of type MTN412-6, 4MTN225L6, which can be called "excited". Such electric motors enter the self-excitation mode without making additional circuit decisions. However, in low-voltage complete devices (low-voltage switchgear or control panels) designed to work together with such motors, a small initial excitation is provided for reliable operation.
The initial excitation is carried out by passing a constant, the so-called A small value of "supply current" (usually no more than 10% of the motor's rated current) from a half-wave rectifier. For excited motors, in any case, this is sufficient for a reliable transition to the self-excited dynamic braking mode.
Electric motors MTN512-6, 4MTN280M6, for which the condition кс ≥ √(1 + 2х '2/хо) is not satisfied, are "unexcited". This does not mean that such motors cannot operate in dynamic braking mode with self-excitation, but the value of the additional current required for them reaches 50% of the rated current of the stator.This necessitates the use of special NKU (control panels) for non-excited electric motors. …
Electric motor type 4MTN280L10 with кс = √(1 + 2х '2/хо) is at the limit of self-excitation and any random change in the parameters can violate the self-excitation condition. Therefore, such a motor can also be classified as non-excitable.
The main parameters affecting the ability of the electric motor to self-excite is the rated voltage of the rotor E2nom. The critical value of E2nom, at which self-excitation does not occur without a large supply current, should be taken as 300 V.
This characteristic of the self-excitation dynamic braking mode was taken into account by the Dynamo plant and Sibelektromotor PO when developing a series of 4MT crane electric motors in the early 1980s.
In particular, the E2nom value for some electric motors has been reduced compared to the previous MT series to make the motors excitable.
For example, for the 4MTN225L6 electric motor, widely used in the electric drive of tower cranes, E2nom was reduced compared to the previous MTN512-6 series motor from 340 to 290 V, which made the motor self-excited. Later, OJSC "Sibelectromotor" started the production of electric motor 4MTM225L6 with the same parameters.
Over time, electric motors with a similar purpose began to be produced by other manufacturers.
The Rzhevsky Crane Construction Plant produces the MKAF225L6 electric motor, the Siberian Electrotechnical Company produces the 4MTM225L6 PND electric motor.Despite the appearance different from the prototype related to the technological capabilities of each of the manufacturers, all these electric motors have the same electrical parameters and installation dimensions and are completely interchangeable.
The difference in the names of the engines allows the user to make an informed choice of one or another manufacturer, guided by his own preferences, price, delivery time, etc. And at the same time, be absolutely sure that replacing an electric motor of one faucet manufacturer with an electric motor of another manufacturer will not lead to a malfunction of the faucet or an accident.
However, in the last decade, electric motors from various manufacturers have appeared on the domestic market, the brand of which exactly reproduces the brand of the "original" electric motor produced by JSC "Sibelectromotor". It can be assumed that the origin of electric motors is connected with the big eastern neighbor of our country. Their price is slightly lower than that of traditional manufacturers, so the interest in them from the supplies of enterprises is understandable.
Thus, by ordering an electric motor for installation on a manufactured crane or replacing a damaged electric motor on a crane with a working one, you can get an electric motor of an unknown manufacturer, with an E2nom different from the prototype electric motor.
The situation is somewhat reminiscent of the early 90s, when several pop groups with the same name toured the country at the same time.
Let us recall once again that the ratio E2nom / I2nom is the most important parameter of a motor with a wound rotor, affecting the choice of starting resistors, relay-contactor equipment and, as mentioned above, on the condition of self-excitation of the electric motor.
Often, however, there is no rotor data at all on the nameplates of cloned engines. Here is an example:
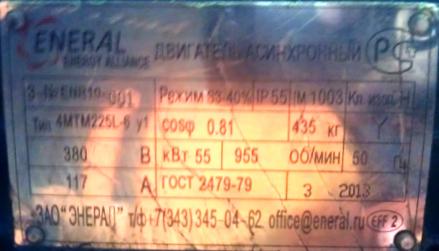
Rice. 3. Rotor crane asynchronous motor nameplate
By the way, this electric motor had the «correct» value E2nom, only now it had to be determined empirically.
In the catalogs of other manufacturers for the 4MTM225L6 electric motor, the value E2nom = 340 V is indicated, i.e. the excited motor became an unexcited one. The consequence of using such an electric motor as part of an electric drive with dynamic braking with self-excitation is a drop in load and separation of the electric motor with mechanical destruction of the rotor and stator windings.
It is exactly this picture that the author observed recently in one of the oldest Russian machine-building enterprises, where a new bridge crane with a cloned electric motor of the type 4MTM225L6 with E2n = 340 V was delivered. Only by luck, people did not suffer. In addition, the owner of the crane restores the engine three (!) times after dodging.
Another manufacturer of clone electric motors, apparently repeatedly experiencing similar accidents, now produces two electric motors under the same brand (!). One with E2nom = 340 V, the other with E2nom = 264 V is given in the catalog with a note: "for type KB taps", i.e. tower cranes.
Such a motor is indeed most widely used on tower cranes, but it is also installed on bridge cranes. So you can hear the dialogue between the Supplier and the Customer: “What crane do you need a motor for? For the flooring. Then take this one (E2nom = 340 V). » And in the drive of the electric hoists there is a control panel with self-excited dynamic braking. The result is described above.
At the same time, no one is saying that these electric motors are defective or unreliable and cannot be used on cranes. The more choices on the market, the better. As they say, there are more good and different engines. It's just that their brand misleads the consumer, which can be fraught with dangerous consequences.
To use an electric motor with rotor parameters other than the prototype, you must:
-
Measure E2nom when the rotor circuit is open and the stator winding is connected to the grid;
-
Based on E2nom measurements, calculate, select and order ballast resistors;
-
Choose a control panel for non-excitation electric motors from the catalog and order it.
Or you can simply ask about the value of E2nom before ordering an engine that attracts with its price and specifically agree on this in the contract. However, this does not preclude the measurement of E2nom during the input control of the ordered motor.
Summarizing the above, we can draw the following conclusions:
-
In the electric drive of household faucets based on phase rotor electric motors, self-excited dynamic braking is widely used. Tens of thousands of such electric drives are in operation. They are still being issued.
-
To operate in self-excited dynamic braking mode, the electric motor must have a certain E2nom / I2nom ratio.
-
The main condition for self-excitation of an electric motor with a wound rotor is the value of E2nom ≤ 300 V.
-
The use of electric motors with E2nom> 300 V with control panels designed for excited electric motors can cause the load to drop and destroy the electric motor.
