How to check motor for overload capacity
Once you have selected a motor of suitable power and required speed from the manufacturer's catalog, ensure that its rated voltage and current values correspond to your network by choosing the type of installation and ventilation conditions specifically for your equipment, ensuring that the construction of the case is suitable for the environmental conditions — the engine must be checked … And they check the engine not only for operability, but for overloading, for heating, for starting conditions in the established form.

Heating test
To check the heating of the motor, the methods of equivalent current, equivalent power, equivalent torque are used.
The equivalent current test is used when there is an accurate, previously obtained graph of the dependence of the current on time during the operation of the motor. Such a graph is obtained experimentally or by calculation. And if the engine, according to the inspection results, meets the condition:
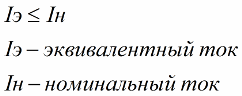
then it passes the heat test.
The equivalent torque test is suitable for DC motors. These motors include: DC motors with independent excitation and induction motors operating at close to rated slip. The engine will pass a warm-up test if the following condition is met:

The equivalent power test is used only for those motors whose operation is assumed not only at constant magnetic flux but also at constant speed. These conditions are met when the motor is operating at a variable load less than rated at nearly constant speed. The verification condition is as follows:

When the engine is running repeatedly for a short time, then the equivalent current, equivalent torque and equivalent power are taken exclusively during the time intervals of operation, pauses are excluded from consideration. If the theoretical duty cycle (DT) values differ from the standard, then the equivalent duty cycle value is reduced to the standard duty value as follows:
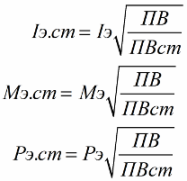
The check is considered successful if the engine meets the conditions for heating at a given PVst:

If the equivalent power, torque or current exceeds the rated value of this motor, overheating will be unacceptable, which means that it will be necessary to select a motor with a higher rated power and then repeat the overheating test, taking given the actual load cycle.
Check for overload
Based on the known load diagram (the dependence of the shaft torque on time), the motor is checked for overload under the following conditions:

The startup check is performed based on the following conditions:

