Energy conversion — electrical, thermal, mechanical, light
The concept of energy is used in all sciences. It is also known that energy bodies can do work. Law of conservation of energy states that energy does not disappear and cannot be created from nothing, but appears in its various forms (for example, in the form of thermal, mechanical, light, electrical energy, etc.).
One form of energy can pass into another and at the same time precise quantitative ratios of different types of energy are observed. Generally speaking, the transition from one form of energy to another is never complete, as there are always other (mostly unwanted) types of energy. For example, in the electric motor not all electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy, but part of it is converted into thermal energy (heating of wires by currents, heating as a result of the action of frictional forces).
The fact of incomplete transition of one type of energy to another characterizes the coefficient of efficiency (efficiency).This coefficient is defined as the ratio of useful energy to its total amount or as the ratio of useful power to the total.
Electrical energy it has the advantage that it can be transmitted relatively easily and with low loss over long distances and furthermore has an extremely wide range of applications. The distribution of electrical energy is relatively easy to manage and can be stored and stored in known quantities.
During one working day, a person uses an average of energy equal to 1000 kJ, or 0.3 kW. A person needs approximately 8000 kJ in the form of food and 8000 kJ for heating homes, industrial premises, cooking, etc. kcal, or 60 kWh
Electrical and mechanical energy
Electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy in electric motors and to a lesser extent in electromagnets… In both cases the associated effects with an electromagnetic field… Energy losses, that is, that part of the energy that is not transformed into the desired form, consists mainly of energy costs for heating wires from current and frictional losses.
Large electric motors have an efficiency above 90%, while small electric motors have an efficiency slightly below this level. If, for example, the electric motor has a power of 15 kW and an efficiency equal to 90%, then its mechanical (useful) power is 13.5 kW. If the mechanical power of the electric motor should be equal to 15 kW, then the electrical power consumed at the same efficiency value is 16.67 kWh.
The process of converting electrical energy into mechanical energy is reversible, i.e. mechanical energy can be converted into electrical energy (see — Energy conversion process in electrical machines). For this purpose they are mainly used generatorswhich are similar in design to electric motors and can be driven by steam turbines or hydraulic turbines. These generators also have energy losses.
Electric and thermal energy
If the wire is flowing electricity, then the electrons in their movement collide with the atoms of the material of the conductor and cause them to a more intense thermal movement. In this case, the electrons lose some of their energy. The resulting thermal energy, on the one hand, leads, for example, to an increase in the temperature of the parts and wires of the windings in electrical machines, and on the other hand to an increase in the temperature of the environment. A distinction must be made between useful heat energy and heat losses.
In electric heating devices (electric boilers, irons, heating stoves, etc.) it is advisable to strive to ensure that the electrical energy is converted as completely as possible into thermal energy. This is not the case, for example, in the case of power lines or electric motors, where the heat energy generated is an unwanted side effect and therefore often has to be taken to remove it.
As a result of the subsequent increase in body temperature, thermal energy is transferred to the environment. The process of heat energy transfer takes place in the form heat conduction, convection and heat radiation… In most cases it is very difficult to give an accurate quantitative estimate of the total amount of heat energy released.
If a body is to be heated, the value of its final temperature must be significantly higher than the required heating temperature. This is necessary in order to transmit as little heat energy as possible to the environment.
If, on the contrary, the heating of the body temperature is undesirable, then the value of the final temperature of the system should be small. For this purpose, conditions are created that facilitate the removal of heat energy from the body (large surface of contact of the body with the environment, forced ventilation).
The thermal energy occurring in electrical wires limits the amount of current that is allowed in those wires. The maximum permissible temperature of the conductor is determined by the thermal resistance of its insulation. Why, to ensure the transfer of some specific electric force, you should choose the lowest possible current value and accordingly the high voltage value. Under these conditions, the cost of the wire material will be reduced. Thus, it is economically possible to transmit high power electrical energy at high voltages.
Conversion of thermal energy into electrical energy
Thermal energy is converted directly into electrical energy in the so-called thermoelectric converters… The thermocouple of a thermoelectric converter consists of two metal conductors made of different materials (e.g. copper and constantan) and soldered together at one end.
At a certain temperature difference between the connection point and the other two ends of the two wires, EMF, which in the first approximation is directly proportional to this temperature difference. This thermo-EMF, equal to a few millivolts, can be recorded using highly sensitive voltmeters. If the voltmeter is calibrated in degrees Celsius, then together with the thermoelectric converter the resulting device can be used for direct temperature measurement.
The conversion power is low, so such converters are practically not used as sources of electrical energy. Depending on the materials used to make the thermocouple, it operates in different temperature ranges. For comparison, some characteristics of different thermocouples can be indicated: a copper-constantan thermocouple is applicable up to 600 ° C, the EMF is approximately 4 mV at 100 ° C; an iron-constant thermocouple is applicable up to 800 °C, the EMF is approximately 5 mV at 100 °C.
An example of the practical use of the conversion of thermal energy into electrical energy — Thermoelectric generators
Electric and light energy
In terms of physics, light is electromagnetic radiation, which corresponds to a certain part of the spectrum of electromagnetic waves and which the human eye can perceive. The spectrum of electromagnetic waves also includes radio waves, heat and X-rays. Look - Basic amounts of lighting and their ratios
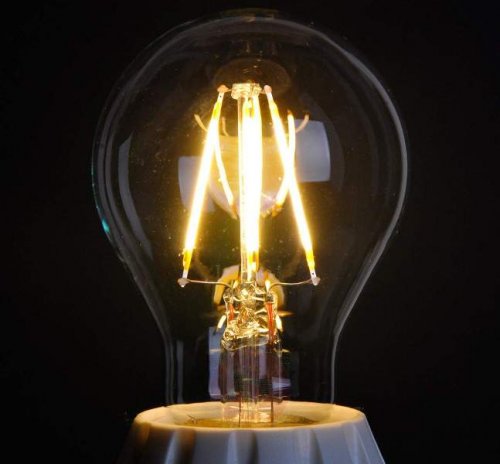
It is possible to obtain light radiation using electrical energy as a result of thermal radiation and by gas discharge.Thermal (temperature) radiation occurs as a result of heating of solid or liquid bodies, which, due to heating, emit electromagnetic waves of different wavelengths. The distribution of the intensity of thermal radiation depends on the temperature.
As the temperature increases, the maximum radiation intensity shifts to electromagnetic oscillations with a shorter wavelength. At a temperature of about 6500 K, the maximum radiation intensity occurs at a wavelength of 0.55 μm, i.e. at the wavelength that corresponds to the maximum sensitivity of the human eye. For lighting purposes, no solid body can be heated to such a temperature, of course.
Tungsten withstands the highest heating temperature. In vacuum glass bottles, it can be heated to a temperature of 2100 ° C, and at higher temperatures it begins to evaporate. The evaporation process can be slowed down by adding some gases (nitrogen, krypton), which makes it possible to increase the heating temperature to 3000 ° C.
In order to reduce losses in incandescent lamps as a result of the resulting convection, the filament is made in the form of a single or double spiral. Despite these measures, however the luminous efficiency of incandescent lamps is 20 lm / W, which is still quite far from the theoretically achievable optimum. Thermal radiation sources have a very low efficiency, because with them most of the electrical energy is converted into heat energy and not into light.
In gas-discharge light sources, electrons collide with gas atoms or molecules and thereby cause them to emit electromagnetic waves of a certain wavelength. The entire volume of gas is involved in the process of emitting electromagnetic waves and, in general, the lines of the spectrum of such radiation do not always lie in the range of visible light. Currently, LED light sources are the most widely used in lighting. Look - The choice of light sources for industrial premises.
Transition of light energy into electrical energy
Light energy can be converted into electrical energy and this transition is possible in two different ways from a physical point of view. This energy conversion can be a result of the photoelectric effect (photoelectric effect). To realize the photoelectric effect, phototransistors, photodiodes and photoresistors are used.
At the interface between some semiconductors (germanium, silicon, etc.) and metals, a boundary zone is formed in which the atoms of the two contacting materials exchange electrons. When light falls on the boundary zone, the electrical equilibrium in it is disturbed, as a result of which an EMF occurs, under the action of which an electric current arises in an external closed circuit. The EMF and therefore the value of the current depends on the incident light flux and the wavelength of the radiation.
Some semiconductor materials are used as photoresistors.As a result of the impact of light on the photoresistor, the number of free carriers of electric charges in it increases, which causes a change in its electrical resistance. If you include a photoresistor in an electrical circuit, the current in this circuit will depend on the energies of the light falling on the photoresistor .
See also — The process of converting solar energy into electricity
Chemical and electrical energy
Aqueous solutions of acids, bases and salts (electrolytes) conduct more or less electric current, which is due to the phenomenon of electrical dissociation of substances… Some of the solute molecules (the size of this part determines the degree of dissociation) is present in the solution in the form of ions.
If there are two electrodes in the solution to which a potential difference is applied, then the ions will begin to move, with the positively charged ions (cations) moving towards the cathode and the negatively charged ions (anions) towards the anode.
Arriving at the corresponding electrode, the ions acquire their missing electrons or, conversely, give up the additional ones and, as a result, become electrically neutral. The mass of material deposited on the electrodes is directly proportional to the charge transferred (Faraday's law).
In the boundary zone between the electrode and the electrolyte, the dissolution elasticity of the metals and the osmotic pressure oppose each other. (Osmotic pressure causes the deposition of metal ions from electrolytes onto the electrodes. This chemical process alone is responsible for the potential difference).
Conversion of electrical energy into chemical energy
In order to achieve the deposition of a substance on the electrodes as a result of the movement of ions, it is necessary to expend electrical energy. This process is called electrolysis. This conversion of electrical energy into chemical energy is used in electrometallurgy to obtain metals (copper, aluminum, zinc, etc.) in a chemically pure form.
In electroplating, actively oxidizing metals are covered with passive metals (gilding, chrome plating, nickel plating, etc.). In electroforming, three-dimensional impressions (clichés) are made of various bodies, and if such a body is made of a non-conductive material, it must be covered with an electrically conductive layer before the impression is made.
Conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy
If two electrodes made of different metals are lowered into the electrolyte, then a potential difference arises between them, due to the difference in the elasticity of dissolution of these metals. If you connect a receiver of electrical energy, for example, a resistor, between the electrodes outside the electrolyte, then a current will flow in the resulting electrical circuit. Here's how they work galvanic cells (primary elements).
The first copper-zinc galvanic cell was invented by Volta. In these elements, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. The operation of galvanic cells can be hindered by the phenomenon of polarization, which occurs as a result of the deposition of a substance on the electrodes.
All galvanic cells have the disadvantage that chemical energy is irreversibly converted into electrical energy in them, that is, galvanic cells cannot be recharged. They are devoid of this drawback accumulators.