Electrical equipment of grinding machines
 Grinding machines are mainly used to reduce the roughness of the parts and obtain accurate dimensions. The main grinding tool is the grinding wheel. Grinding machines can process external and internal cylindrical, conical and shaped surfaces and planes, cut details, grind threads and teeth, sharpen cutting tools, etc.
Grinding machines are mainly used to reduce the roughness of the parts and obtain accurate dimensions. The main grinding tool is the grinding wheel. Grinding machines can process external and internal cylindrical, conical and shaped surfaces and planes, cut details, grind threads and teeth, sharpen cutting tools, etc.
Grinding machines, depending on the purpose, are divided into cylindrical grinding, internal grinding, centerless grinding, surface grinding and special.
Metal processing on a cylindrical grinding machine:
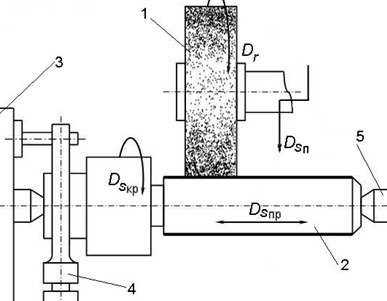
Circular grinding: 1 — grinding disc; 2 — empty; 3 — driving cartridge; 4 — collar; 5 — rear center
Internal grinding:

Electrical equipment for surface grinding machines
Spindle Drive: Squirrel Asynchronous Motor, Pole Change Asynchronous Motor, DC Motor. Stopping: by opposition and by means of an electromagnet.
Table drive: variable hydraulic drive, reversible squirrel-cage induction motor with anti-rotation brake or by means of an electromagnet, EMU drive, squirrel-cage induction motor (with rotating table).
The auxiliary devices are used for: hydraulic pump with transverse periodic feed, transverse feed (asynchronous squirrel motor or DC motor of heavy machinery), vertical movement of the grinding wheel head, cooling pump, lubrication pump, conveyor and washing, magnetic filter.
Special electromechanical devices and interlocks: electromagnetic masses and plates, demagnetizers, magnetic filters for coolant, counting the number of wheel dressing cycles, active control device.
A characteristic feature of the development of grinding machines in recent years is the rapid increase in grinding speeds from 30 — 35 to 80 m / s and higher.
 They usually use asynchronous squirrel-cage motors to drive the grinding disc on surface grinders... They can be embedded and form a single unit with the wheel head.
They usually use asynchronous squirrel-cage motors to drive the grinding disc on surface grinders... They can be embedded and form a single unit with the wheel head.
The grinding spindle is simultaneously the shaft of the electric motor, and only if it is necessary to increase or (less often) reduce the speed of rotation of the abrasive wheel, it is connected to the shaft of the electric motor by a belt drive. Due to the significant inertia of the wheel, the rotation time of the grinding spindle by inertia is 50 — 60 s and more. When it is necessary to reduce this time, they resort to electrical braking.
Normally, the speed of the grinding wheel motor is not controlled.Infinitely variable speed control of the grinding spindle within small limits (1.5:1), in some cases used to maintain a constant peripheral speed of the abrasive wheel as it wears.
The desire to reduce vibration in the operation of drives installed on grinding machines has led to the use of various types of shock absorbers in the installation of electric motors and the widespread use of belt drives, soft clutches and hydraulic systems.
Of particular importance for grinding machines are the thermal deformations that occur during the processing of a part. To prevent the part from heating up, it is abundantly cooled with an emulsion, which is sometimes fed through the full shaft of the wheel, and sometimes through the pores of the grinding disc. Coolant pumps are mounted on emulsion tanks placed separately from the machine to avoid heating of the machine by the cooling emulsion. The electric motors of such pumps are connected to the circuit of the machine by means of plug connections.
The piston masses of small machines are usually moved hydraulically. Speed changes are made by hydraulic seals. A variety of variable speed drives are used on heavy machinery.
A characteristic feature of the periodic transverse feed of grinding machines is the small value of the smallest feed (1 — 5 microns). Such feeding is often done by means of a hydraulic actuator acting on a ratchet mechanism. An electric drive with EMU is often used to drive the rotary tables of surface grinding machines. In some cases, an adjustable hydraulic drive is also used for rotary motion.
 The wheel dressing device for grinders operating on an automatic and sometimes semi-automatic cycle is usually hydraulically driven. Electric drive is less often used. Standing is carried out at regular intervals, reaching 1 hour, and sometimes more. The motor timing relay is used to automate the process. Another solution to this problem is to use a pulse counting relay.
The wheel dressing device for grinders operating on an automatic and sometimes semi-automatic cycle is usually hydraulically driven. Electric drive is less often used. Standing is carried out at regular intervals, reaching 1 hour, and sometimes more. The motor timing relay is used to automate the process. Another solution to this problem is to use a pulse counting relay.
Electromagnetic plates (as well as permanent magnet plates) and electromagnetic rotary tables are widely used on surface grinding machines. On some rotary table surface grinders, small parts are loaded, fixed, removed and demagnetized continuously while the table rotates.
Electrical equipment for machines for cylindrical grinding, internal grinding and centerless grinding.
Spindle drive: asynchronous squirrel-cage motor.
Rotation drive: pole-switch cage induction motor, DC motor (with dynamic braking), G-D system with EMU, electromagnetic clutch cage induction motor, magnetic amplifier drive and DC motor, thyristor DC drive.
Drive: adjustable hydraulic drive, DC motor, G — D system.
Auxiliaries are used for: cooling pump, hydraulic feed pump, lubrication pump, wheel dressing, vacuum cleaner, wheel head movement, tail movement, drive wheel rotation (for centerless machines), parts conveyor, drive feed wheels, oscillator, magazine device, magnetic separator.
Special electromechanical devices and interlocks: electrical measuring devices for active control and automatic adjustment, devices for automatic wheel dressing, electromagnetic chucks, magnetic separators for coolant.
In heavy cylindrical grinders, variable parallel excitation motors are usually used to rotate the abrasive wheel. As the abrasive wheel wears and its diameter decreases, the drive speed changes so that the cutting speed does not change. The control range is 2:1.
 A G-D system drive with an adjustment range of 1:10, as well as thyristor drives, are commonly used to rotate a part of heavy cylindrical grinding machines. The peculiarity of the drive consists in a large torque under load (up to 2 Mn).
A G-D system drive with an adjustment range of 1:10, as well as thyristor drives, are commonly used to rotate a part of heavy cylindrical grinding machines. The peculiarity of the drive consists in a large torque under load (up to 2 Mn).
For the longitudinal feed of heavy longitudinal grinding machines, an EMC drive with a control range of up to 50: 1 is most often used, and in recent years also thyristor drives. Additional mechanical adjustment is usually not performed. The drive with longitudinal feed must guarantee the constancy of the set speed with an error of up to 5%. Stopping should be done with an error of no more than 0.5 mm. To improve reversing accuracy, the speed before reversing is reduced.
For longitudinal feed, multi-speed asynchronous motors with a multi-stage feed box are sometimes used. Such a drive is simpler and more reliable. However, it is used less often, as it does not provide the possibility of smooth adjustment. Installation movements are carried out at a speed of 5 — 7 m / min.
For heavy-duty grinding machines, the use of an electric drive with infinitely variable speed control is of particular importance. Such a drive makes it possible not to operate at a speed at which vibrations appear. In addition, increased productivity is ensured. To control the load as well as the degree of loop dullness, wattmeters are sometimes used which are included in the spindle motor circuit.
In centerless grinding machines, an axial oscillating movement of the wheel (up to 6 mm) is used. This increases the processing frequency. For internal grinding of holes with a small diameter, grinding electric spindles with high-frequency electric motors are used.
For cylindrical grinders, to increase productivity, the abrasive wheel is usually brought to the workpiece at high speed. If at a certain small distance from the circumference of the machined surface the transition to the working feed is automatically made, then the path of further movement before the start of the cutting process will be a variable value. This is due to the inconsistency of the machining allowance of different parts, as well as the wear of the grinding wheel.
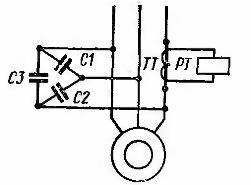
Moving the grinding wheel slowly before cutting takes a long time. To reduce it, an increase in the current of the electric motor at the beginning of the cutting process is used. In this case (Fig. 1), the winding of the current relay RT through the current transformer CT is connected to one phase of the electric motor. When the circle is cut, the motor current increases, the current relay turns on and with its contacts switches to the working power supply.To increase the sensitivity of the device, capacitors CI, C2, C3 are connected in parallel with the motor, selected so that the reactive component of the idle current is compensated.
Rice. 1. Control of the start of cutting of grinding machines
For the same purposes, a power relay is used, as well as photodetectors that give a signal from sparks that occur when cutting the abrasive wheel. The use of active inspection and readjustment is expanding to improve the performance and accuracy of grinding machines.
On some rotary table surface grinding and wheel rim grinding machines, a significant reduction in machine time can be achieved by automatically increasing the table rotation speed as the wheel approaches the table's axis of rotation.
The process of electrochemical diamond grinding has become widespread. In this process, the metal is removed due to the combined action of electrochemical dissolution and abrasive grinding. At the same time, productivity increases 2-3 times compared to abrasive diamond grinding, and the consumption of diamond wheels is reduced three times.
Electro-diamond grinding allows you to process hard alloys and materials in which abrasive diamond grinding is accompanied by cracks, burns and irregularities.In this case, the cleanliness of the surface practically does not depend on the size of the grains of the wheel, since the microbumps are largely eliminated by the anodic dissolution of diamond grains in the gap between the surface of the processed metal part and the grinding wheel. Through this gap, which is several dozen micrometers, an electrolyte is pumped, which is an aqueous solution of salts, for example, sodium and potassium nitrate with a concentration of up to 10-15%.