Protecting the lines from a distance
 Distance protections are used in networks of complex configuration where, for reasons of speed and sensitivity, simpler overcurrent and directional overcurrent protections cannot be used.
Distance protections are used in networks of complex configuration where, for reasons of speed and sensitivity, simpler overcurrent and directional overcurrent protections cannot be used.
The distance protection determines the resistance or the distance (distance) to the short-circuit location and, depending on this, is triggered with a shorter or longer time delay. Distance protection is implemented in multi-level, and in the event of a short circuit in the first zone covering 80-85% of the length of the protected line, the response time of the protection is no more than 0.15 s.
For the second zone, which goes beyond the protected line, the delay is one step higher and varies from 0.4 to 0.6 s. In the event of a short circuit in the third zone, the time delay increases even more and is selected as well for directional overcurrent protections.
Distance protection is a complex protection consisting of a number of elements (organs), each of which performs a certain function.
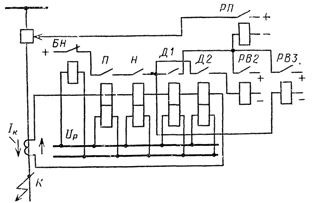
In fig. 1 shows a simplified diagram of distance protection with a step delay characteristic.The chain has an actuation mechanism and remote control, as well as direction and delay controls.
The actuating element P performs the function of setting protection from normal operation and starts it at the moment of short circuit. As such a body, a resistor relay is used in the considered circuit, which responds to the current IP and the voltage UR at the terminals of the relay.
Rice. 1. Simplified distance protection scheme with step delay characteristic
Distance (or measuring) bodies D1 and D2 establish a measure of the distance to the short circuit location. Each of them is made using a resistor relay that is triggered by a short circuit if
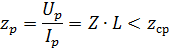
where Zp is the resistance of the relay terminals; Z is the resistance of the protected line with a length of 1 km; L is the length of the linear section to the short circuit point, km; Zcp — relay actuation resistance.
From the above relation it is seen that the resistance across the relay terminals Zp is proportional to the distance L to the short circuit point.
Time delay devices PB2 and RVZ create a time delay with which the protection acts to turn off the line in the event of a short circuit in the second and third zones. The directional element H allows the protection to operate when the short-circuit current is directed from the busbars to the line.
The circuit provides for BN blocking, which removes the protection from action in case of failure of the voltage circuits supplying the protection. The fact is that if with damaged circuits the voltage at the protective terminals is Uр = 0, then Zp = 0. This means that both the trigger and the remote control can be damaged.To prevent line interruption in the event of a fault in the voltage circuits, blocking removes the direct current from the protection. In this case, the service personnel must quickly restore the normal voltage of the protection. If for any reason this fails, the protection must be terminated.
Operation of remote line protection.
In the event of a short circuit along the line, the starting element relay P and the guide element relay H are activated. Through the contacts of these relays, DC plus will go to the contacts of the remote elements and to the coil of the third zone time relay PB3, activating it. If the short circuit is in the first zone, remote control D1 will close its contacts and send a pulse to open the circuit breaker without delay.
In the case of a short circuit in the second zone, D1 will not work because the resistance value at the terminals of its relay will be greater than the response resistance value. In this case, the remote control of the second zone D2 will be triggered, which will start the relay for time PB2. After the second zone delay has elapsed, a line break pulse will be sent from relay PB2.
If a short circuit occurs in the third zone, the remote elements D1 and D2 will not operate because their terminal resistance values are greater than the feedback resistance values. The time relay PB3, started at the moment of the short-circuiting of the contacts of the relay H, will operate and after the third zone delay time has expired, it will send a pulse to open the line breaker. The remote control for the third protection zone is usually not installed.