Operating network diagrams up to 1000 V
 The scheme of a workshop for a power supply network up to 1000 V is determined by the technological process of production, power reliability category, the mutual arrangement of the shop's TP or power and electrical receivers, the installed power of the unit and their location on the shop area. The chain must be simple, safe and convenient to work, economical, meet the characteristics of the environment and ensure the use of industrial methods of installation.
The scheme of a workshop for a power supply network up to 1000 V is determined by the technological process of production, power reliability category, the mutual arrangement of the shop's TP or power and electrical receivers, the installed power of the unit and their location on the shop area. The chain must be simple, safe and convenient to work, economical, meet the characteristics of the environment and ensure the use of industrial methods of installation.
The lines of the workshop network starting from the TP of the workshop or from the input device form a supply network, and those supplying energy from bus channels or RP directly to energy consumers form a distribution network.
Network diagrams can be radial, trunk, and mixed-unidirectional or bidirectional.
Radial circuit for powering the workshop network
With a radial scheme, the energy from a separate power supply unit (TP, RP) is supplied to a sufficiently powerful consumer or to a group of electrical consumers.Radial circuits are single-stage when the receivers are fed directly from the transformer, and two-stage when connected to an intermediate RP.
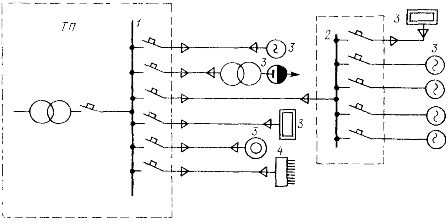
Rice. 1. Radial power circuit: 1 — distribution board TP, 2 — power supply RP, 3 — power supply unit, 4 — lighting board
Radial circuits are used to power concentrated loads with high power, with uneven placement of receivers in a workshop or groups in its separate sections, as well as to power receivers in explosive, fire-hazardous and dusty rooms. In the second case, the control and protection equipment of the electrical receivers installed on the RP is removed outside the adverse environment.
Radial circuits are made with cables or wires in tubes or boxes (trays). The advantages of radial circuits are high reliability (breakdown of one line does not affect the operation of receivers receiving energy from another line) and ease of automation. Increasing the reliability of radial circuits is achieved by connecting the busbars of individual TPs or RPs with redundant jumpers, on the switching devices of which (automatic machines or contactors) an ATS circuit can be carried out - automatic introduction of backup power.
The disadvantages of radial circuits are: low efficiency due to the significant consumption of conductive material, the need for additional areas to accommodate RP powers. Limited flexibility of the network when moving technological mechanisms associated with a change in the technological process.
Main store network power circuit
With trunk circuits, receivers are connected to each point on the line (bus).The electrical network can be connected to the substation switchboards or to the power distribution substation or directly to the transformer according to the block diagram of the transformer line.
Highway circuits with busbars are used when feeding receivers from one process line or with receivers evenly distributed in the workshop area. Such schemes are implemented using buses, cables and wires.
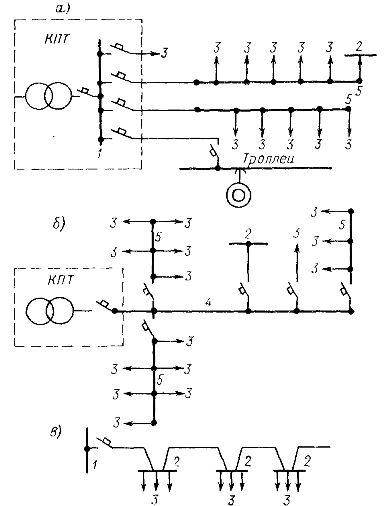
Rice. 2. Bus circuits with unidirectional power supply: a — with channels for distribution bus, b — main block of the transformer, c — circuit, 1 — switchboard TP, 2 — power supply RP, 3 — electrical receiver, 4 — channel of main bus, 5 — distribution bus channel
When installing a technological line of low-power electrical receivers at workplaces, it is recommended to carry out distribution lines with modular wiring. For the backbone of the modular network, insulated wires are used, laid in pipes hidden in the floor, with distribution boxes installed at a certain distance from each other (module), on which floor distribution speakers with plug connectors are placed. The electrical receivers are connected to the speakers by wires in metal hoses. Modular wiring is used for trunk loads up to 150 A,
The advantages of trunk circuits are: simplification of substation panels, high flexibility of the network, which makes it possible to move technological equipment without reworking the network, use of unified elements that allow installation by industrial methods.A trunk circuit is less reliable than a radial circuit, because in the event of a trunk voltage failure, all consumers connected to it lose power. The use of busbars and modular wiring with a constant cross-section leads to some overuse of conductive material.
Mixed power supply scheme
Depending on the nature of production, the location of electrical receivers and environmental conditions, electrical networks can be implemented in a mixed scheme. Some of the electrical receivers are supplied from the mains, some from the power transformer substations, which in turn are supplied either from the transformer substation circuit board or from trunk or distribution channels.
Modular wiring can be fed from busbars or from power distribution devices connected in a radial fashion. This combination allows you to more fully use the advantages of radial and trunk chains.
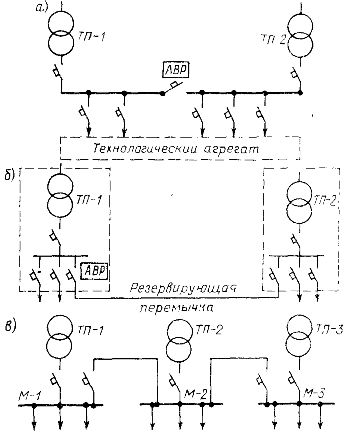
Rice. 3. Two-sided power circuits: a — trunk with distribution bus, b — radial with redundant jumper, c — with mutual shortening of highways
In order to increase the reliability of the power supply of the electrical receivers according to the trunk circuits, bidirectional power supply of the trunk line is used. When laying several highways in large workshops, it is advisable to feed them from separate transformer substations, making jumpers between the highways.Such backbone power supply circuits with mutual redundancy increase the reliability of the power supply, create convenience for repair work in substations, provide the ability to turn off unloaded transformers, as a result of which power losses are reduced.