Protection by means of fuses in electrical networks 6 — 10 kV
 In electrical installations with a voltage of 6-10 kV, in order to reduce their cost and increase reliability, instead of switches and relay protection, fuses are used when they can be selected with the necessary parameters, provide selectivity and sensitivity, and do not interfere with the use of the necessary automation.
In electrical installations with a voltage of 6-10 kV, in order to reduce their cost and increase reliability, instead of switches and relay protection, fuses are used when they can be selected with the necessary parameters, provide selectivity and sensitivity, and do not interfere with the use of the necessary automation.
The main parameters for selecting fuses: the rated voltage of the fuse must match the rated voltage of the network, the rated current must match the corresponding load, the maximum breaking current of the fuse must be less than the short-circuit currents in the network, the selected fuse must match the environment in which it will be installed (indoor or outdoor installation).
High voltage fuses computer type complete with load switches can be used: in the circuit of power transformers with a capacity of up to 1600 kV-A at a voltage of 6-10 kV, in dead-end lines with an operating current of up to 100 A at a voltage of 10 kV, up to 200 A — at a voltage of 6 kV, in a circuit of static capacitors with a capacity of up to 400 kvar, in a circuit of short-circuited asynchronous and synchronous electric motors with direct start at a voltage of 6 kV with a capacity of up to 600 kW, provided that the fuses are disconnected from the starting current and simplified management.

Rice. 1. Computer type fuses
Protection of power transformers by means of fuses is widely used in power supply schemes of 6-10 kV according to the main circuit (loop), an example of which is shown in fig. 2.
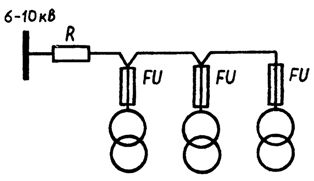
Rice. 2. The main circuit for turning on transformers
An example fuse protection scheme with load breakers is shown in fig. 3.
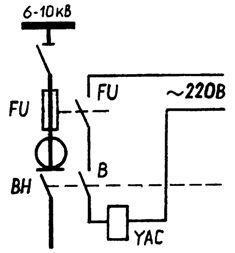
Rice. 3. Fuse protection circuit with load switch
Since fuse protection of power transformers is widely used in enterprise power systems, consideration should be given to:
-
The 6-10 kV fuses are designed to protect against short circuits on the 6-10 kV side and against damage inside the transformers,
-
in the presence of fuses on both sides of the transformer, it is desirable to have a multiple of the rated current of the fuse on the 6-10 kV side relative to the rated current of the fuse on the low voltage side (currents are reduced to the voltage on the same side of the transformer) approximately equal to two or more
-
selectivity must be ensured between the protection of the line feeding the transformer and the fuses on the high voltage side in the event of a short circuit on the high voltage side of the transformer — the total operating time of the fuse must be shorter than the operating time of the protection on the line
-
when operating the high and low sides of the transformer by one organization it is allowed to install fuses only on the high voltage side, in this case it is advisable to observe selectivity between the protection of the line feeding the transformers according to the main circuit and the fuses on the high side voltage in the event of a short circuit of the low voltage installation of one of the transformers,
-
in case of frequent fuse burning due to overloading of the transformer, it is strictly forbidden to replace them with fuses for a larger current, in this case either unload the transformer or replace it with a higher power with simultaneous replacement of the fuse corresponding to the power on the transformer,
-
if a fuse (or circuit breaker) is installed on the low voltage side of the transformer in its circuit, it must be selected according to the rated current of the transformer.
See also: Protective relays and switching circuits in electrical networks 6 — 10 kV
