Placing a transformer substation in the power supply design
 The choice of the type, capacity and location of the substation depends on the size and nature of the electrical loads and their location in the workshop or on the general plan of the enterprise. This should take into account architectural, construction, production and operational requirements as well as environmental conditions.
The choice of the type, capacity and location of the substation depends on the size and nature of the electrical loads and their location in the workshop or on the general plan of the enterprise. This should take into account architectural, construction, production and operational requirements as well as environmental conditions.
GPP is placed as close as possible (within the gaps allowed by the PUE) to the centers of electrical loads, taking into account the location of the enterprise and the possibility of passing overhead lines 35 — 110 kV. The TP shops are located as close as possible to the center of the groups of electricity consumers consumed by them with a certain shift towards the energy source.
With a supply voltage of 6-10 kV, the location of transformers is determined depending on the size, characteristics and location of loads with a voltage of up to 1 kV, taking into account the installation of capacitors, as well as the possibility of placing a transformer substation (TP) at the intended location .
The use of complete transformer substations (KTP) is recommended, providing an industrial installation regardless of the construction part, bringing the KTP as close to the load center as possible, which ensures maximum economy of non-ferrous metals and reduction of electricity losses in commercial networks.
The location of the transformer substation must take into account the environmental conditions, the required degree of continuity and the dynamics of the technology. In addition, it should be possible to further increase the power of the single-transformer KTP as the load increases by installing a second transformer.
For ease of use, it is desirable to have a minimum number of standard transformer sizes.
Independent transformer substations at least rationally due to the extension of networks with a voltage of up to 1000 V and an increase in losses in them. They are used as a forced power solution for workshops that are dangerous in terms of fire, explosion or corrosion.
The permissible distance of approach of TP to explosive stores is regulated from 0.8-100 m, depending on the explosive danger of the workshop, open or closed installation of oil transformers.
For powering users of industrial enterprises, it is recommended to use built-in substations, if possible with an external installation of transformers, if this is not hindered by the architectural design of the workshops and the necessary alleys and interruptions are provided between them.
The use of independent transformer substations is permissible in the following exceptional cases:
-
when several shops are fed by one substation, if the center of their loads is outside these shops or the construction of independent substations in each shop is not economically justified;
-
if it is impossible to place the substation on the outer walls of the workshops due to production reasons (lack of free space, explosive environment, etc.).
This type of TP can also be used for small enterprises with small workshops scattered throughout the territory.
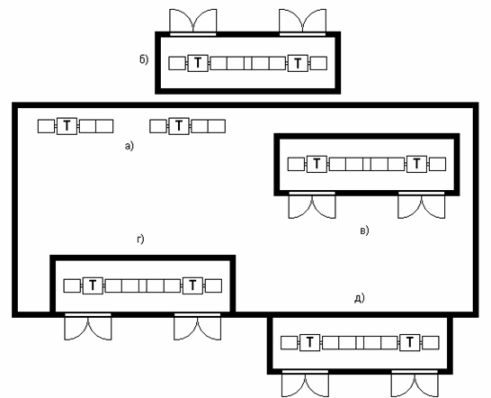
Rice. 1. Installation of a complete transformer substation (KTP) in the shop: a) open, b) free-standing, c) indoor shop, d) attached
Applied TP satisfying the requirements of the economy, they often raise objections from architects and builders, as they deteriorate the appearance of buildings.
Built-in substations make it possible to more successfully solve the architectural design of the workshop wall, however, the location of the substation in the workshop area is not always possible due to the conditions for placing technological equipment.
Built-in substations, such as indoor transformer substations, must be sited carefully, especially in workshops with frequently moved equipment.
In the construction of attached and built-in substations, preference should be given to the external installation of transformers, which reduces the cost of the construction part and improves the cooling conditions of the transformers.
Intrashop TPs should be placed near shop columns, in the dead zone of bridge cranes. The installation of TP on the mezzanine is used, under which there may be conveyor paths or some equipment.
When choosing the location and type of substation, different requirements, often conflicting, must be considered and coordinated.
If the load of the workshop exceeds several thousand kilovolt-amperes and the use of several transformer substations is required, their location should correspond to the approach to the center of the load on the supply side to avoid the opposite direction of the flow of electricity. The location of the TP in the very center of the load is irrational, since there will be a reverse flow of energy to the energy source.
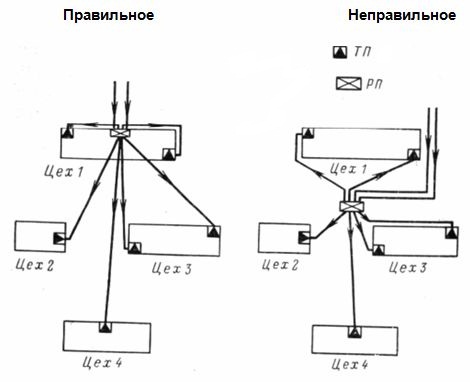
Rice. 2. Placement of KTP
If the load of small stores is only tens or hundreds of kilovolt-amperes, then the question arises: whether to build your own transformer substation in such a store or to feed this store from a neighboring transformer substation. The technical and economic analysis shows that for each load S there is a critical length L at which the transmission of power S over a distance L will be equally economical with a voltage up to 1000 V with a transformer installed in the workshop and a voltage up to 1000 V from a transformer substation, located at a distance L from the central workshop load. This length depends on the cost of energy losses.
It should be borne in mind that on the actual general plan of the enterprise, the cable routes are not located along the shortest distances, but in the direction of the alleys and passages between the workshop buildings.
When choosing a TA location supplying the store, it should be located on the supply side. In an aggressive environment created by workshop production, it is necessary to take into account the wind rose and, if possible, place the TP on the leeward side.
When designing a substation, it is necessary to provide for the use of complete electrical equipment with a voltage of up to 1000 V and more.
