Purpose of neutral conductor in three-phase systems
One of the most important economic problems of the power supply is to reduce the weight of the wires of the electrical network for a given transmitted power and a certain percentage of losses in the network. It can be achieved not only by increasing the voltage in the network, but also by combining several independent networks, and in some of the wires it is possible to create currents that compensate each other. This makes it possible to reduce either the number of wires or their cross-section.
Already in the first years of the development of electrical engineering, when the transmission of energy was carried out at constant voltage, this idea was used in the so-called. three wire system, proposed by Dolivo-Dobrovolski.
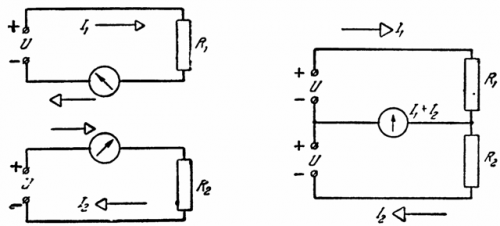
Let there be two identical (in terms of voltage and power) sources of constant voltage U, each of which serves its users.
The network consists of four wires.If you combine two wires in the so-called equalization (neutral) wire, then the oppositely directed currents will be summed in it, so the cross-section of the wire can be significantly reduced.
Three-wire system
With a symmetrical load (I1 = I2), the equalizing wire is unnecessary, and the savings in wires reach 50 °. When the loads change (without equalizing wire), the voltage will be redistributed between them, which is undesirable.
The equalizing conductor significantly reduces the asymmetric voltage distribution. If it is possible to ignore the internal resistance of the sources and the resistance of the line, the asymmetry is almost completely eliminated. A similar idea underlies the construction of multiphase alternating current systems.
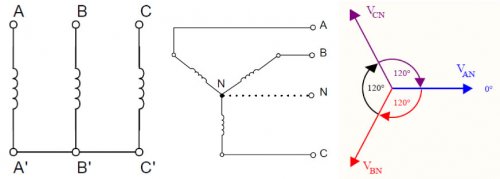
A polyphase symmetrical system is a set of several alternating voltages of equal amplitude and frequency, symmetrically out of phase with time. A three-phase system has gained practical prevalence (see — Three-phase EMF system).
A three-phase (and any polyphase) system has a number of advantages compared to a single-phase system: it allows you to add weight to the wires of the electrical network, provides a more even load on the motor, rotating electric three-phase voltage generator, and finally allows you to create a wide rotating magnetic field used in electric motors.
If a single-phase system (with the same power and the same voltage) is used instead of a three-phase system, then only two wires will be needed, but their cross-section will have to rely on three times the current.Compared to a single-phase system, a three-phase system saves 30-40% in wire weight.
See also here: Three phase current is better than single phase
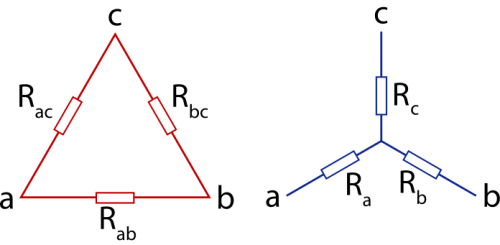
Regardless of the switching circuit of the generator (usually unknown to the user), the load of a three-phase system can also be connected in two ways - delta or star.
In the first case, the voltage at each of the users is equal to the line voltage and does not change when the symmetry of the loads is broken. The current in the user (phase) differs from the current in the line.
When consumers are star-connected, the current in each load is equal to the corresponding line current, but the voltage at each load (phase) is different from the line.
See also —Voltage, current and power values for star and delta connections
When the loads change, the currents are automatically redistributed and their sum (obtained at the common point of the loads) always disappears. At the same time, there is a corresponding redistribution of stresses between the uneven loads.
This disadvantage is eliminated if there is a neutral conductor (connected to the common point of the loads), as it allows the sum of the three phase currents to remain non-zero, i.e. in an unbalanced load, the neutral conductor of the three-phase system helps to maintain a constant load voltage.