How to calculate the fuse current for a transformer on the HV side
Emergency situations often occur in electrical networks, which can damage expensive equipment, one of the elements of which is a transformer. To protect the transformer from damage, it is necessary to install overcurrent protection.
A high voltage fuse is one of the options to protect a power transformer from damage. It breaks the electrical circuit (fuse blow) when the current exceeds the permissible value (fuse rating).
The high voltage fuse will only protect the transformer winding if it is correctly rated for current. Let's look at how to calculate fuse current for a high voltage (HV) side transformer.
When choosing a fuse, you must first consider the voltage class: the rated voltage of the fuse must be equal to the voltage class of the mains.Installing a high-voltage fuse at a rated voltage lower than the mains voltage will cause the insulation to break or overlap, which in turn will cause a phase-to-phase short circuit. Also, do not install fuses with a voltage lower than the fuse's rating — this can cause overvoltage in the event of a short circuit.
Fuse selection according to rated breaking current
The rated breaking (trip) current of the fuse must not be less than the maximum short-circuit current for the point of the electrical network where the fuse will be installed. For a power transformer, this is the three-phase current at the terminals of the high-voltage winding—where the fuses are mounted.
When calculating the short-circuit current, the most severe mode is taken into account, with minimum resistance to the location of the suspected fault.
Short-circuit currents are calculated individually, taking into account the entire supply circuit.
Transformer protection fuses on the HV side are issued for rated breaking current (maximum breaking current) in the range 2.5-40 kA.
If there is no data on the magnitude of the short-circuit currents in the network section, then it is recommended to select the maximum value of the rated breaking current for the fuse.
Selection of rated fuse current
The high-voltage fuse protects the high-voltage winding of the power transformer not only from short-circuiting, but also from overloading, so the rated operating current must also be considered when choosing a fuse.
There are several factors to consider when selecting a fuse's current rating. First, the power transformer can be subjected to short-term overloads during operation.
Secondly, when the transformer is turned on, magnetizing current surges occur that exceed the rated current of the primary winding.
It is also necessary to ensure the selectivity of operation with protection installed on the low voltage (LV) side and on the consumer's output lines. That is, first of all, the automatic switches (fuses) on the low voltage side of the output lines that go directly to the load to the consumers must be triggered.
If this protection does not work for one reason or another, then the circuit breaker (fuse) at the input of the LV side of the power transformer must be tripped. The fuses on the HV side in this case are backup protection that must be triggered in case of overloading of the low voltage winding and failure of the LV side protections.
Based on the above requirements, the fuse is selected for twice the rated current of the high voltage winding.
Thus, high-voltage fuses installed on the HV side protect the section of the electrical circuit from damage at the input of the transformer, as well as from internal damage to the power transformer itself. And the fuses (circuit breakers) on the LV side of the power transformer protect the transformer itself from overloading beyond the permissible limit, as well as from short-circuiting in the low-voltage network.
The rated current of the windings of the power transformer is indicated in your passport details.
How to calculate fuse current if only power transformer rating is known?
If the type of transformer is known, then the easiest way is to find the current using the power transformer reference data of one of the manufacturers, since all transformers are usually produced according to a standard range of rated powers and, accordingly, with similar characteristics.
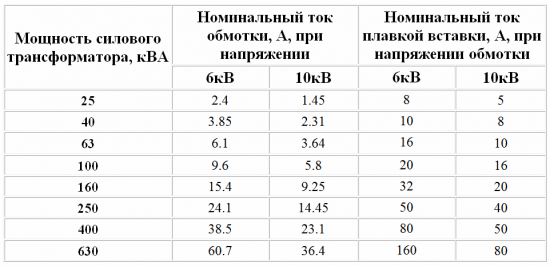
Alternatively, you can use the table below for the recommended values of rated fuse currents for three-phase power transformers 6 / 0.4 and 10 / 0.4 kV:
Fuses to protect the voltage transformer on the HV side
Transformers of voltage 110 kV and above are protected only on the low voltage side by circuit breakers or fuses. For 6, 10 and 35 kV voltage transformers, the fuse current calculation is not performed.
The fuse to protect the voltage transformer on the HV side is selected only according to the voltage class. For each voltage class, special fuses of the PKN (PN) type are produced — 6, 10, 35 (depending on the voltage class), they are used exclusively for protection voltage transformers.