How to calculate and select the cross section of the power cable
The choice of the cross-section of the cable lines, as a rule, is made on the basis of economic conditions, which are fulfilled by the method of economic current density.
Selection of cable cross-section by economic current density
The selection of cable cross-sections according to the economic current density is carried out for the normal operating mode of the maximum loads of the electrical network under consideration, for which the calculated current Inb is determined. In addition, based on the proposed brand of cable and the time of use of the maximum loads, we select the value of the economic current density jе.
Cross-section of the conductor, determined by the formula F = Inb / jе
The resulting area is rounded to the nearest standard.
Selection of cables according to the conditions of permissible heating
 The reliability of the operation of electrical networks largely depends on the heating temperature of the cables.The cables must therefore be selected or, if selected for other conditions, checked against the allowable heating conditions: Inb Idop,
The reliability of the operation of electrical networks largely depends on the heating temperature of the cables.The cables must therefore be selected or, if selected for other conditions, checked against the allowable heating conditions: Inb Idop,
where Iadd is the permissible current of the conductor, taking into account the actual conditions of its laying and cooling and emergency overload; Inb — the highest current from normal, after emergency and repair modes.
The permissible current is determined by the expression: Iperm = Iperm.t × kp × kt × kav,
where kn is a correction factor that takes into account the number of working cables laid next to them; kt — correction factor for the ambient temperature, based on the laying conditions; kav — overload factor in emergency mode.
The minimum permissible cross-section of the conductor is determined according to the state of thermal resistance:
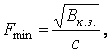
where Vc.z. — thermal pulse; c — coefficient, the value of which for cables depends on the voltage and the material of the conductor.
For cables with a nominal voltage of 10 kV, the coefficient c has the following values: aluminum wires — 98.5; copper wires -141
The thermal impulse from the total short-circuit current is determined by the expression: Vk.z. = Ip.s × Ip.s × (totk + Ta.s),
where Ip.with. Is the effective value of the periodic component of the short-circuit closing of the system; totk — short circuit tripping time; Ta.s is the decay time constant of the aperiodic short-circuit component of the power system: where xS, rS are the resulting inductive and active resistance of the power system, respectively: w = 2pf = 314 is the angular frequency.

