Electrical equipment of electric arc furnaces
Arc furnace device
 The main purpose of arc furnaces is to melt metals and alloys. There are direct and indirect arc furnaces. In direct firing arc furnaces, the arc burns between the electrodes and the molten metal. In indirect arc furnaces — between two electrodes. The most widespread are the direct-heated arc furnaces used for melting ferrous and refractory metals. Indirect arc furnaces are used to melt non-ferrous metals and sometimes cast iron.
The main purpose of arc furnaces is to melt metals and alloys. There are direct and indirect arc furnaces. In direct firing arc furnaces, the arc burns between the electrodes and the molten metal. In indirect arc furnaces — between two electrodes. The most widespread are the direct-heated arc furnaces used for melting ferrous and refractory metals. Indirect arc furnaces are used to melt non-ferrous metals and sometimes cast iron.
The arc furnace is a lined shell enclosed by a vault, the electrodes are lowered inside through an opening in the vault which engages in electrode holders which are connected to the guides. The melting of the charge and the processing of metal takes place due to the heat of electric arcs burning between the charge and the electrodes.
A voltage of 120 to 600 V and a current of 10-15 kA are applied to maintain the arc. Lower values of voltages and currents apply to furnaces with a capacity of 12 tons and a capacity of 50,000 kVA.
The design of the arc furnace provides drainage of metal through a drainage pump. The slag is pumped through a work window cut in the casing.
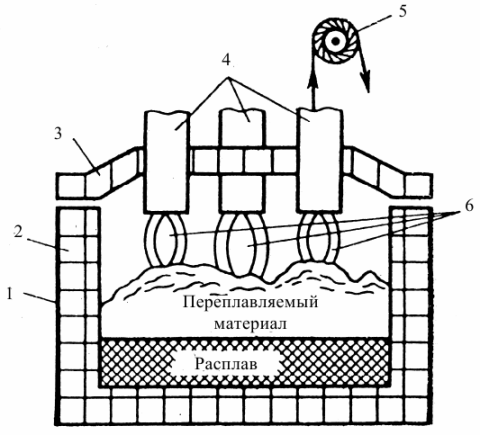
Electric arc furnace: 1 — steel body; 2 — refractory lining; 3 — furnace roof; 4 — electrodes; 5 — mechanism for lifting the electrodes; 6 — rainbow
Technological process of melting metal in an arc furnace
The processing of the solid charge loaded in the arc furnace starts from the melting stage, at this stage the arc is ignited in the furnace and the melting of the charge under the electrodes begins. As the charge melts, the electrode descends, forming acceleration wells. A characteristic feature of the melting stage is the unpleasant burning of an electric arc. The low arc stability is due to the low temperature in the furnace.
The transition of the arc from one charge to another, as well as numerous interruptions of the arc from operational short circuits, which are caused by collapses and movements of conductive pieces of the charge. Other stages of metalworking are in the liquid state and are characterized by quiet burning of arcs. However, a wide range of operational control and high accuracy of maintaining the power input to the furnace is required. Power control ensures the required progress of the metallurgical reaction.
The considered characteristics of the technological process require from the arc furnace:
1) Ability to respond quickly to operational short circuits and arc interruptions, quickly restore normal electrical conditions and limit operating short circuit currents to acceptable limits.
2) Flexibility to control furnace power input.
Electric equipment of arc furnaces
 The installation of an arc furnace includes, in addition to the furnace itself and its mechanisms with electric or hydraulic drive, and additional electrical equipment: a furnace transformer, wires from the transformer to the electrodes of the arc furnace — the so-called network, distribution unit (RU) on the high voltage side of the transformer with oven switches; power regulator; dashboards and consoles, control and signaling; programming device for controlling the furnace operation mode, etc.
The installation of an arc furnace includes, in addition to the furnace itself and its mechanisms with electric or hydraulic drive, and additional electrical equipment: a furnace transformer, wires from the transformer to the electrodes of the arc furnace — the so-called network, distribution unit (RU) on the high voltage side of the transformer with oven switches; power regulator; dashboards and consoles, control and signaling; programming device for controlling the furnace operation mode, etc.
Arc furnace installations are large consumers of electricity, their unit capacities are measured in thousands and tens of thousands of kilowatts. The electricity consumption for melting a ton of solid filling reaches 400-600 kWh-h. Therefore, the furnaces are fed from 6, 10 and 35 kV networks through furnace step-down transformers (the maximum voltage values of the secondary line of the transformers are usually in the range of up to 320 V for furnaces of small and medium capacity and up to 510 V for large furnaces) .
 In this regard, furnace installations are characterized by the presence of a special furnace substation with a transformer and switchgear. In the new installations, cabinets from complete distribution units (KRU) made according to unified schemes are used. Furnace substations are located in close proximity to the furnaces. Panels and control panels for the installation of arc steel furnaces with a capacity of up to 12 tons are placed within the furnace substation with the service control panels from the shop (from the working platform). For larger furnaces, separate control rooms can be provided with a convenient view of the working windows of the furnace.
In this regard, furnace installations are characterized by the presence of a special furnace substation with a transformer and switchgear. In the new installations, cabinets from complete distribution units (KRU) made according to unified schemes are used. Furnace substations are located in close proximity to the furnaces. Panels and control panels for the installation of arc steel furnaces with a capacity of up to 12 tons are placed within the furnace substation with the service control panels from the shop (from the working platform). For larger furnaces, separate control rooms can be provided with a convenient view of the working windows of the furnace.
Electric arc furnaces consume significant currents, measured in thousands and tens of thousands of amperes. Such currents create large voltage drops even with small active and inductive resistances of the electrode supply circuits. As a result, the furnace transformer is placed in close proximity to the furnace in a special furnace substation. The circuits connecting the furnace transformer and the furnace electrodes and having a short length and complex structure are called short network.
 The short network of an arc furnace consists of a busbar in a transformer chamber, a flexible cable string, tube busbars, an electrode holder and an electrode moving along with the carriage. In arc furnaces with a capacity of up to 10 tons, a "star of electrodes" scheme is used, when the secondary windings of the furnace transformer are connected in a delta at the output of the chamber. Other schemes of a short network, allowing to reduce its reactance, are used for more powerful furnaces.
The short network of an arc furnace consists of a busbar in a transformer chamber, a flexible cable string, tube busbars, an electrode holder and an electrode moving along with the carriage. In arc furnaces with a capacity of up to 10 tons, a "star of electrodes" scheme is used, when the secondary windings of the furnace transformer are connected in a delta at the output of the chamber. Other schemes of a short network, allowing to reduce its reactance, are used for more powerful furnaces.
Squirrel cage induction motors rated at 380 V at 1–2 kW in small furnaces up to 20–30 kW in larger furnaces are commonly used in electric drives of furnace mechanisms. Motors of drives for moving electrodes - direct current supplied by an electric machine or magnetic amplifiers, as well as by thyristor converters. These drives are part of an independent unit — a furnace power regulator.
 In furnaces with a capacity of more than 20 tons, in order to increase productivity and facilitate the work of steelmakers, devices are provided for mixing a liquid bath of metal based on the principle of a traveling magnetic field.A stator with two windings is placed under the bottom of the furnace of non-magnetic material, the currents of which are 90 ° out of phase. The traveling field created by the stator windings drives the metal layers. When switching the coils, it is possible to change the direction of movement of the metal. The frequency of the current in the stator of the stirring device is from 0.3 to 1.1 Hz. The device is powered by a frequency converter of an electric machine.
In furnaces with a capacity of more than 20 tons, in order to increase productivity and facilitate the work of steelmakers, devices are provided for mixing a liquid bath of metal based on the principle of a traveling magnetic field.A stator with two windings is placed under the bottom of the furnace of non-magnetic material, the currents of which are 90 ° out of phase. The traveling field created by the stator windings drives the metal layers. When switching the coils, it is possible to change the direction of movement of the metal. The frequency of the current in the stator of the stirring device is from 0.3 to 1.1 Hz. The device is powered by a frequency converter of an electric machine.
Motors serving the mechanisms of arc furnaces work in difficult conditions (dusty environment, close location of highly heated furnace structures), therefore they have a closed design with heat-resistant insulation (crane-metallurgical series).
Furnace transformer units
 Arc furnace installations use specially designed three-phase oil-immersed transformers. The power of the furnace transformer is, after the capacity, the second most important parameter of the arc furnace and determines the duration of metal melting, which significantly affects the performance of the furnace. The total time for melting steel in an arc furnace is up to 1-1.5 hours for furnaces with a capacity of up to 10 tons and up to 2.5 hours for furnaces with a capacity of up to 40 tons.
Arc furnace installations use specially designed three-phase oil-immersed transformers. The power of the furnace transformer is, after the capacity, the second most important parameter of the arc furnace and determines the duration of metal melting, which significantly affects the performance of the furnace. The total time for melting steel in an arc furnace is up to 1-1.5 hours for furnaces with a capacity of up to 10 tons and up to 2.5 hours for furnaces with a capacity of up to 40 tons.
The voltage on the arc furnace during melting must change over a fairly wide range. In the first stage of melting, when the scrap is melted, maximum power must be introduced into the furnace to speed up this process. But with a cold charge, the arc is unstable. Therefore, to increase the power, it is necessary to increase the voltage. The duration of the melting stage is 50% or more of the total melting time, while 60-80% of the electricity is consumed.In the second and third stages - during oxidation and refining of liquid metal (removal of harmful impurities and burning of excess carbon), the arc burns more quietly, the temperature in the furnace is higher and the length of the arc increases.
To avoid premature damage to the furnace lining, the arc is shortened by lowering the voltage. In addition, for furnaces in which different types of metal can be melted, the melting conditions change accordingly, and hence the required voltages.
 In order to provide the ability to regulate the voltage of arc furnaces, the transformers feeding them are made with several stages of low voltage, usually with switching of the taps for the winding of high voltage (12 or more steps). Transformers with a capacity of up to 10,000 kV-A are equipped with a tripping device. More powerful transformers have a load switch. For small furnaces, two to four stages are used, as well as the simplest method of voltage regulation — switching the high voltage (HV) winding from delta to star.
In order to provide the ability to regulate the voltage of arc furnaces, the transformers feeding them are made with several stages of low voltage, usually with switching of the taps for the winding of high voltage (12 or more steps). Transformers with a capacity of up to 10,000 kV-A are equipped with a tripping device. More powerful transformers have a load switch. For small furnaces, two to four stages are used, as well as the simplest method of voltage regulation — switching the high voltage (HV) winding from delta to star.
To ensure stable AC arc burning and limit overvoltages during short-circuiting between the electrode and the charge with 2–3 times the rated electrode current, the total relative reactance of the installation should be 30–40%. Reactance of furnace transformers is 6-10%, short network resistance for small furnaces is 5-10%. Therefore, on the HV side of the transformer for furnaces with a capacity of up to 40 tons, an upstream reactor with a resistance of about 15-25% is provided, which is included in the transformer block kit. The reactor is designed as an unsaturated core choke.
 All arc furnace power transformers are provided with gas protection. Gas protection, as the main protection of the furnace transformer, is carried out in two stages: the first stage affects the signal, the second turns off the installation.
All arc furnace power transformers are provided with gas protection. Gas protection, as the main protection of the furnace transformer, is carried out in two stages: the first stage affects the signal, the second turns off the installation.
Automatic power control of arc furnaces. To ensure normal and high-performance operation, arc furnaces are equipped with automatic power regulators (AR), which maintain the constancy of the given power of the electric arc. The operation of the automatic arc furnace power regulator is based on changing the position of the electrodes relative to the load - in direct heating arc furnaces or relative to each other in indirect heating arc furnaces, i.e. in both cases, arc furnaces use length regulation. The driving devices are most often electric motors.
Regulation of the electrical modes of an electric arc furnace
 Examining the structures allows to show the possible ways to adjust its electrical mode:
Examining the structures allows to show the possible ways to adjust its electrical mode:
1) Changing the supply voltage.
2) Change in arc resistance ie. change in its length.
Both methods are used in modern installations. Rough adjustment of the mode is carried out by switching the stages of the secondary voltage of the transformer, precisely - using the movement mechanism. The mechanisms for moving the electrodes are controlled using automatic power regulators (AWS).
The workplace of arc furnaces must provide:
1) Automatic arc ignition
2) Automatic removal of arc breaks and operational short circuits.
3) The response speed is about 3 seconds when the arc interruptions of the operational short circuit are eliminated
4) The aperiodic nature of the regulation process
5) Ability to smoothly change the input power of the furnace, within 20-125% of the nominal and maintain it with an accuracy of 5%.
6) Stopping the electrodes when the supply voltage disappears.
The aperiodic nature of the control process is necessary to exclude the lowering of the electrodes of the liquid metal, which can carbonize it and spoil the melting, as well as to exclude the breaking of the electrodes when they come into contact with the solid charge. Compliance with this requirement provides protection against the above modes in the event of an emergency or operational shutdown of the furnace.
Electric arc furnaces as consumers of electricity
 Electric arc furnaces are a powerful and unpleasant consumer of the power system. It works with a low power factor = 0.7 — 0.8, the power consumed from the network varies during melting, and the electrical mode is characterized by frequent current surges, up to arc breakage, operational short circuits. Arcs generate high-frequency harmonics that are undesirable for other consumers and cause additional losses in the power network.
Electric arc furnaces are a powerful and unpleasant consumer of the power system. It works with a low power factor = 0.7 — 0.8, the power consumed from the network varies during melting, and the electrical mode is characterized by frequent current surges, up to arc breakage, operational short circuits. Arcs generate high-frequency harmonics that are undesirable for other consumers and cause additional losses in the power network.
To increase the power factor, capacitors can be connected to the busbars of the main power substation, feeding the groups of furnaces, since with current shocks reactive power fluctuates within large limits, it is necessary to ensure the possibility of quickly changing this capacity. For such regulation, you can use high voltage thyristor switchescontrolled by the circuit to keep CM close to 1. To combat higher harmonics, filters tuned to the most intense harmonics are used.
The distribution of furnace substations for independent power supply connected to other consumers for voltages of 110, 220 kV is widely used. In this case, the distortion of the current and voltage curves for other consumers can be kept within acceptable limits.
