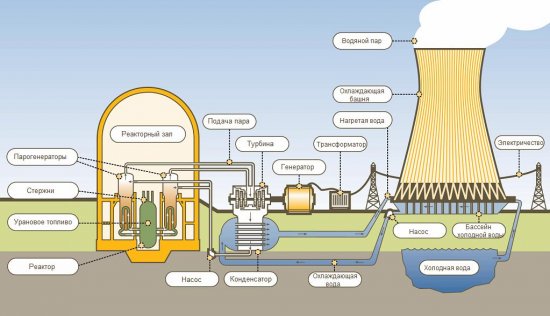
How a nuclear power plant (NPP) works
One of the ways to fight environmental pollution is to switch to cleaner sources of electricity. These sources today rightfully include nuclear power plants (NPP)… In Europe alone, thanks to nuclear power plants, more than half a billion tons of carbon dioxide are NOT released into the atmosphere every year, which would certainly become a serious source of pollution if the energy was obtained by burning hydrocarbons.
Thanks to nuclear power plants that operate 24/7, many homes and businesses around the world are continuously supplied with electricity. Plus, the stations employ many specialists and these are decently paid jobs.
What is a nuclear power plant? Let's find out how it works and how it works.
Nuclear power plants (NPP) are a type thermal power plants.
The source of thermal energy at these stations is the process of nuclear fission of uranium and plutonium atoms, which are the main source of nuclear fuel carried out in nuclear reactors.The coolant used is water or gases pumped through the reactor channels and steam generators. The resulting steam is fed to steam turbines that drive generators, just like in conventional thermal power plants.
The world's first nuclear power plant was built in the USSR in 1954.
Any nuclear power plant is a complex complex of equipment, devices and structures, the purpose of which is to generate electrical energy, and a special substance serves as fuel here — uranium-235… In the process of fission of uranium-235 nuclei, a huge amount of nuclear energy is released, which is easily converted into heat, and heat into electricity.
Nuclear chancellor — the heart of a nuclear power plant, as it is loaded with nuclear fuel and a controlled fission chain reaction of uranium-235 takes place inside the reactor. Neutrons act on unstable uranium-235 nuclei, causing them to decay and release energy.
The conclusion is that in the nucleus of the uranium-235 isotope used in the reactor, three neutrons are not enough for stability, therefore the nucleus of this element is very unstable and easily splits into two parts, it is worth a neutron flying at a certain speed, to hit him.
As soon as such a neutron enters an unstable nucleus, it decays releasing energy, but at the same time 2-3 new neutrons fly out of the already decayed nucleus, they split other nuclei, etc. — this is how the chain reaction of fission from uranium-235 nuclei occurs. And to prevent an explosion, the neutrons acting as a fuse must be controlled—not feeding too many neutrons into the fuel.
In nuclear reactors equipped with operating power plants, energy is generated in fuel elements (fuel rods). In the simplest case, a fuel element can be represented as a rod (core) containing nuclear fuel (for example, uranium dioxide) and enclosed in a cladding of structural materials.
During the fission of uranium nuclei, its fragments fly off at high speed, but practically do not leave the core, as they slow down inside it, transferring their energy to the atoms and heating the core.
The heat released in the core of the fuel cell is the energy that is then converted into electricity in the complex process of its conversion in the heat exchanger-steam-turbine-generator system.
The fission fragments moving in the core of the fuel element "displace" the atoms, disrupt the crystal structure of the materials from which they are made, and lead to a change in their physical properties. The longer the fuel element works in the reactor, the more the properties of the core change, the more radioactive fragments accumulate in it.
The fuel is introduced into the working zone of the reactor in special tubes, which are placed in a moderator capable of converting neutron energy into heat. In the retarder dip rods made of neutron-absorbing material to very precisely control the speed of the reaction... The higher the rods are raised, the more neutrons act on the fuel, respectively, the lower they are lowered into the reactor, the less intensively the reaction proceeds.
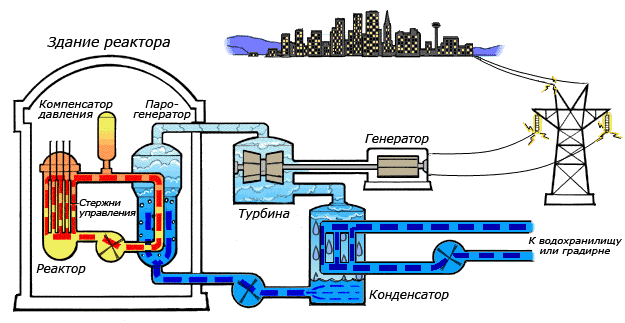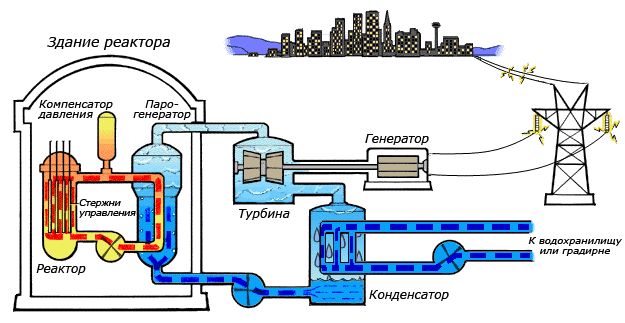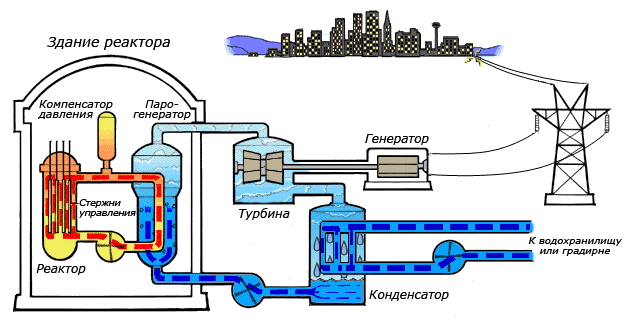
Scheme of operation of a double-loop pressurized water reactor (VVER) nuclear power plant
Geographically, the reactor is located in the reactor hall of the main building of the NPP, there is also a nuclear fuel storage pool as well as a loading machine. The working area where the reaction actually takes place is erected in a special concrete shaft equipped with control system (to select the operating mode) and protection, so that in the event of an emergency the reaction can be quickly stopped.
The heat from the working zone of a nuclear reactor is removed using a liquid or gaseous coolant that passes directly through the reactor working zone. The heat accumulated by the heating medium is then transferred to the water in the steam generator where steam is generated.
Steam under enormous pressure transmits its mechanical energy turbine generatorwhich generates electricity which is then transmitted of power lines (power lines) — to consumers. The turbine together with the steam generator are installed in the turbine hall, from which the electricity is sent by wires to the transformer and then to the power line.
On the territory of the nuclear power plant there is also a building where the spent fuel is stored in the pools. And the large tubes in the form of towers, narrowed at the top, are cooling towers - elements of a circulating cooling system that also includes a cooling pond (natural or artificial reservoir) and spray basins.
By the way, the waste generated after the reaction is partially recycled, and the rest is stored in special containers that protect the contents from entering the environment. Thus, today nuclear energy is environmentally friendly.And nuclear power plants themselves do not produce harmful emissions into the atmosphere, while being quite compact and safe.
See also: