Voltage conversion using resistors
 The simplest and most convenient voltage conversion circuit is a circuit using a resistor with a movable slider (rheostat) (Fig. 1, a). Each rheostat displays the rated resistance and the highest continuous load current. According to these parameters, a rheostat is selected.
The simplest and most convenient voltage conversion circuit is a circuit using a resistor with a movable slider (rheostat) (Fig. 1, a). Each rheostat displays the rated resistance and the highest continuous load current. According to these parameters, a rheostat is selected.
If the entire resistance of the resistor R is included in the mains voltage Uc, then by moving the slider D of the resistor from point a to point b, you can smoothly change the output voltage U from 0 to Uc Such a voltage converter is very convenient.
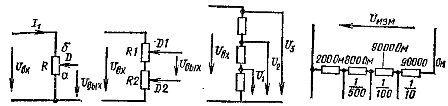
Rice. 1. Schematics of inclusion of resistors for adjustment (a, b, c) and conversion (d) voltage.
The main disadvantage of such converters, limiting their use to low-power circuits, is the presence of a movable contact with its transient resistance.
The second conversion scheme is similar to the first (Fig. 1, b), but has two moving contacts.The circuit allows you to very smoothly change the output voltage from 0 before Uc For this, one resistor is taken with a greater number of turns and a higher resistance than the second. The first allows for coarse adjustment of the output voltage, and the second - smoothly.
It is common to convert a voltage using sample constant resistors connected in series to the input voltage network. Conclusions are made from each resistor, from which the necessary voltage can be removed (Fig. 1, c).
The advantage of such a voltage conversion circuit — there are no transient contacts, and therefore a very accurate voltage conversion is possible. This principle is used by voltage dividers, which are calculated to allow the output to light a value less than the input voltage for a certain number of times. For example, you can get 1/10 of this voltage, 1/100 or 1/500 of its part (Fig. 11, d).
The most widely used voltage dividers are in circuits with potentiometers.

Rice. 3. Voltage divider
The disadvantages of the scheme shown in Figure 1, c, — voltage conversion similar to a jump, the presence of a large number of outputs and the need to switch one of the output wires from contact to contact.
Additional multi-range resistors, commonly installed in combination multi-frequency electrical meters, operate in a similar manner.


