Wire and cable removal tool
 Electrical cables and wires are designed for reliable transmission of electricity. Their design provides for a strictly limited cross-section of the metal core, which is calculated in terms of thermal load and resistance. In this case, a balance is created between the increase in temperature of the metal when a current passes through it and the environment in which the heat is removed.
Electrical cables and wires are designed for reliable transmission of electricity. Their design provides for a strictly limited cross-section of the metal core, which is calculated in terms of thermal load and resistance. In this case, a balance is created between the increase in temperature of the metal when a current passes through it and the environment in which the heat is removed.
Effect of wire thickness on current flow
When the current through the wire exceeds the calculated nominal values, this balance is disturbed. As a result, the insulating layer overheats or, at critical values, the metal melts. The principle of operation of electric welding machines is based on this phenomenon.

As the thickness of the wire decreases, its electrical resistance increases and the characteristics decrease.Such a wire no longer withstands the declared current loads, although at lower values it can work for a long time and, in addition, further reduces its mechanical properties. This issue is especially relevant for aluminum wires, which are most sensitive to bending and require very careful handling.
The influence of the cross-section of the wire on the value of the current passed through it is demonstrated by Formulas of Ohm's law.
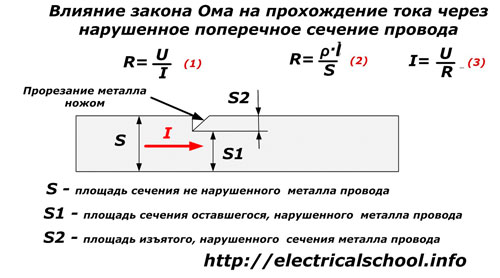
If more force is applied to the knife cutting through the insulation layer, the blade will enter the metal, disrupting its structure and section.

Therefore, removing the insulating layer from the wire, it is impossible to break the mechanical condition of its metal core, make scratches and cuts. Even their small depth can significantly increase over time under the influence of various environmental factors, which will lead to damage and improper operation of the equipment.
Methods for removing insulation
To install electrical circuits, it is necessary to cut the ends of the cable, remove the insulation from the wire. This is done by:
1. the method of burning the surface layer during heating;
2. mechanical cutting.
Thermal impact
The first method is based on the use of temperature:
-
heated tip for a soldering iron (laborious, not very popular method);
-
open flame from matches, lighters or other sources.
These techniques are best suited for thin, low-power wires used in communications devices, electronics, audio equipment with soft stranded wires operating in circuits with voltages on the order of 5 volts.An example of this is the repair work of the headphone wiring.

Mechanical impact
These methods are the most widely available and widely used. They are based on the removal of the insulating layer with the cutting edges of a special tool.
Household knives
Electricians cut the insulation with different tools. The old workers often had a home-made knife, made from a piece of hacksaw blade with a short blade, sharpened on a grinder into a sharp, thin wedge. The handle is made by tightly winding the wire, followed by applying several layers of electrical tape.
The elastic steel of such a blade perfectly cuts the polyvinyl chloride layer, but if the orientation is wrong, it easily damages the nearby aluminum or copper metal. It is necessary to use such home-made products very carefully and carefully, and the plane of sharpening the blade must be directed at a very sharp angle to the cut insulation, so that when it touches the metal core, it does not crash into it, but slides.
Household knives with a razor blade or similar sharpened cutting edge are even more dangerous in this regard.
It is unacceptable to place the blade perpendicular to the wire, and even more so to press it with a finger from the opposite side. Metal scratches and cuts are guaranteed.
A "stationery" knife with a set of interchangeable blades replaced the described self-made design, but in terms of the probability of creating defects on conductive wires, it is not inferior to its predecessor, especially when processing thin threads.

Using the cutting edges of pliers, wire cutters, side cutters and similar tools will also deform the metal layer, although many electricians use this method, referring to their skills and abilities. However, the experience of checking the results shows that in a hundred operations carried out in this way, one or two defects are always found in every self-confident craftsman.
High reliability electrical circuits
In principle, it is impossible to violate the integrity and strength of the wires everywhere. A broken wire will always cause a lot of trouble. However, in schemes where maneuvering of certain areas is used, this issue is given more attention.
As an example, the picture shows a small fragment of a complex, branched secondary circuit of high-voltage circuits of current transformers that are constantly operating in bypass mode. If during the operation of such equipment, a wire break occurs anywhere, then a high potential of several thousand volts occurs on all elements connected to the transformer located at a distance of hundreds of meters.
This is dangerous not only for the life of the workers, but also for the serviceability of the equipment. Therefore, in such circuits, all work is done very carefully, and the installation is checked and checked repeatedly.
Industrial knives for electricians
A distinctive feature of their design is a short thick blade up to 5 cm long and up to 3 mm thick with a sharpening at an angle of about 30 degrees. This is quite enough for cutting plastics and at the same time the possibility of cutting is minimized.
For some models, an additional blade has been created, which is convenient for working in hard-to-reach places, for example, a nest.
Their dielectric handle, made of strong plastic, fits comfortably in the hand, ensuring comfortable operation.

How strippers work
Manufacturers of electrical installation tools have long produced products that allow you to quickly, reliably and conveniently remove wires made according to international standards. Such structures are equipped with two movable semi-knives in the form of cut semicircles of a certain caliber for the diameter of the metal wire. They are integrated into one body. When the plates are separated, an electrical wire is installed in them.
When the handles of the tool are pressed, the half-knives move, cut through the insulation, but do not reach the metal - the mechanical blocking of the device protects it from damage.
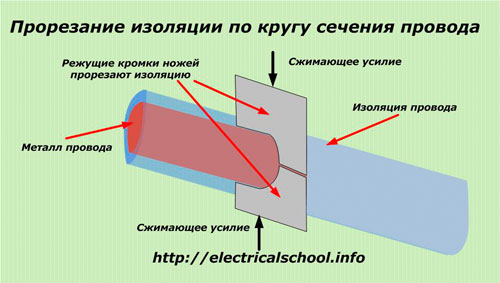
The tool with the offset handles is then moved along the length of the wire. From the applied force, the plates dislodge the insulation, fully exposing the metal without any damage.
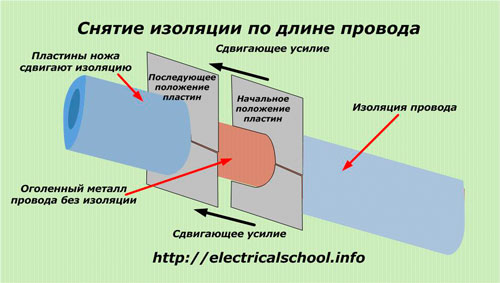
Devices working on this principle are called "strippers". Usually they are made in the form of combined pliers with a different number of functions and a certain set of calibrated holes for the metal of the wire.
In most cases, they are convenient to work with both solid metal wires and stranded braided wires.
Strippers are divided into:
1. guidance;
2. semi-automatic;
3. automatic.
The first designs are the simplest, designed to remove the insulation from a single wire of a certain diameter.
Semi-automatic dressing rooms equipped with a special working adjustable area in which the wire is placed and have blades for cutting the insulation with jaws that slide it from the core. Equipping the work area with an adjusting screw allows you to change the length of the cleaning insulation.
Automatic professional strippers of various companies have the capabilities of a multifunctional tool:
-
automatic adjustment of the knives according to the thickness and length of the removed layer of insulation;
-
pressing of bushings;
-
wire cutting;
-
twisting strands of stranded wires.

In these models, the cutting wire is inserted into the working space next to the limiter, adjustable in depth. It provides the same length of removal of any number of machined cable cores.
Then, when the tool handles are pressed, the jaw blades cut through the insulation and make a translational movement, tearing it away from the rest held by the other jaws and sliding it away from the metal core. The sharp movement of the handles ensures quality rest.
Typically, strippers are designed to work with wires with a cross section of 0.5 to 6 mm square. The cases of the professional models are made of high-quality alloys, covered with dielectric materials and equipped with comfortable handles. The plastic cases of the cheaper models are lighter, but can work for a long time with careful handling.
When working with any tool, it is necessary to study its features and characteristics and make the correct settings.Otherwise, even a professional tool can damage the base metal, as shown in the photo below.

Cable stripping knives
Electrical cables are round or flat. To cut your upper PVC sheath in a longitudinal direction without damaging the insulation of conductive wires, two types of knives are used, made:
-
with a "patch" at the end of the blade;
-
in the form of a hook.
When cutting shells from round profiles, it is convenient to use a slotted blade. It is installed on the edge of the cut end so that the base of the patch penetrates the shell and slides along the outer surface of the veins, and the blade does not reach them and cuts only the outer insulation.
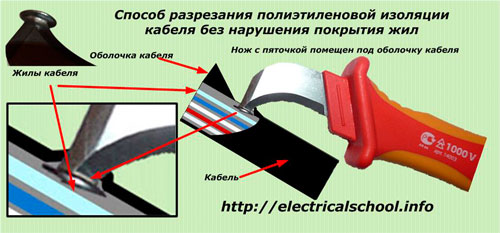
For flat cable profiles, you can use a blade in the form of a hook, which is wound between the cores, rests on them and cannot be damaged.
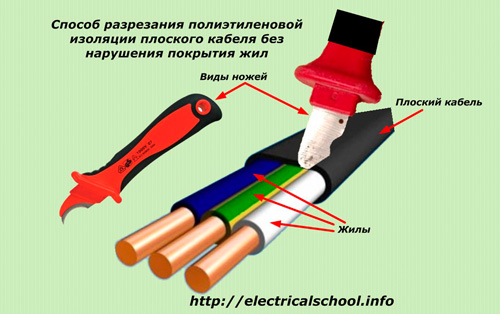
Both methods do not require the kind of "jewelry" skills that are required when using conventional knives with a sharp wedge point.
Machines for cutting cable insulation
If it is necessary to expose a large number of cables, special devices with a massive body are used, on which two blocks with a concave circular profile are mounted between them for placing the cable.

The lower block is made durable, and the upper one is pressed and equipped with a built-in knife that cuts through the outer shell. When the electric motor is turned on, the torque is transferred to the clamping device, which pushes and cuts the cable.
