Energy characteristics of the drive and methods of increasing them
The operating conditions of electric motors are evaluated by the activation and load operating factors. Shift ratio of the machine
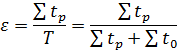
where ∑tр is the total working time of a shift; T is the change time; ∑t0 — total auxiliary time and time of work breaks.
Most modern machines are stopped by disconnecting the electric motor from the mains. Under these conditions, the switching factors of the machine and the electric motor are the same. For machines with friction clutch in the main drive circuit, the electric motor usually rotates continuously. It only turns off during long breaks in work.
If we assume that under different operating conditions of the universal machine ∑tр can take any values (from 0 to T) and that all values of ∑tр within the specified limits are equally likely, then
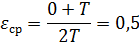
The degree of utilization of machines is characterized by a load factor
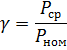
where Psr is the average power of the electric motor shaft; Пн — nominal power of the electric motor.
If all loads of universal machine tools operating under different conditions are equally likely, the average power
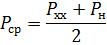
For example, with the common ratio Px.x = 0.2Pn we have γav = 0.6.
The product of the duty factor and the load factor is called the utilization factor of the electric motor:
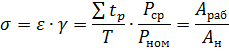
where arab is the mechanical energy actually given by the electric motor to the machine; An is the energy that would be given during continuous operation of the electric motor at rated power.
With the above average values of the inclusion and load factors, we get bsr = 0.3.
The ratio of the energy used to process parts to the energy that the machine could use in the case of continuous operation at rated load is called the utilization rate of the machine:
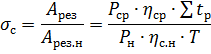
The actual average values of the switching and load factors of electric motors driving metal cutting machines are less than those indicated. This shows the predominance of work with low loads and significant auxiliary time.
The values of work factors close to the real ones can be obtained by analyzing the loads of the power supply network of industrial enterprises. The load of the electrical network supplying a particular workshop is chosen significantly less than the sum of the nominal powers of the electric motors operating in this workshop.
In order to avoid excessive consumption of copper, when determining the cross-section of wires supplying electricity to the workshop, the simultaneous load of consumers, as well as their underload, are taken into account. The analysis of the loads of the power supply network of the factories allows us to find that the average value of the switching factor is ~ 0.3 and the load factor is ~ 0.37. Average machine utilization rate is ~ 12%. All of the above indicates the availability of large resources in the field of using the machine tool park.
The ratio of the energy Ares spent on the cutting process to the energy A consumed by the electric motor during the cycle is called the cyclic efficiency of the system:
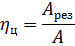
It characterizes not only the structural perfection of the machine tool and the electric motor, but also the rationality of the selected technological process in terms of energy consumption and the use of installed power. Efficiency values of multi-cycle machines operating with long periods of idling and significant underload are small (5-10%).
Underloading of electric motors leads to insufficient recovery of funds invested in electric motors, electric grid and plant substations. Due to the underloading of electric motors, their efficiency and cosφ decrease. A decrease in efficiency leads to a loss of energy. A decrease in cosφ when consuming constant active power leads to an increase in current strength. As the current strength increases, network losses increase and the installed capacity of transformers and generators is not fully utilized.
If the plant has many electric motors operating at part load, the electricity bill increases because a certain fee is charged for each kilovolt-ampere of the transformer capacity installed in the plant, which does not depend on the actual energy consumption. In addition, at low values of cosφ, the cost per unit of consumed energy increases.
The use of equipment and the organization of production can also be assessed by the operational coefficients of switching on and charging electric motors. Knowledge of the coefficients characterizing the operation of the machine helps to identify the unused resources of the machine park and the organization of the rational operation of the metal-cutting machines.
To control the operation of metal-cutting machines, special devices have been developed, some of which are attached to metal-cutting machines, others are used for centralized control of workshops and production in general.
With each change of the processing process in order to increase productivity, the energy indicators of the machine and the electric drive, as a rule, increase. This refers to increasing cutting speeds, increasing feeds, a combination of processing transitions, reducing auxiliary time, etc. An effective means of increasing the energy characteristics of the electric drive of the main movement of the machines is the automation of the approach and withdrawal of the tool , clamping the workpiece, measurements, etc.
However, the possibilities for such rationalization of technological processes are often limited.When processing a part on a machine, the necessary accuracy, cleanliness of processing and high labor productivity must be ensured, which determines the type of processing and cutting modes and forces the roughing and finishing operations from one installation per part.
In machines with a friction clutch in the main drive chain, so-called idle brakes are often used. The idle speed limiter is a switch that shuts off the electric motor when the clutch is disengaged. This switching off of the electric motor results in a saving of active and reactive energy. However, this increases the number of starts of the electric motor, which is associated with some additional energy consumption.
In addition, due to deterioration of engine cooling during breaks, in some cases it may overheat. Finally, when using an idle speed limiter, due to the increase in the number of starts of the electric motor, the wear of the equipment increases. These circumstances can be taken into account by special calculations. Satisfactory results are obtained by automatically switching off the electric motor with pauses longer than a certain set duration.
There are many special technical means to increase the cosφ of electric drives. These include the use of static capacitors connected in parallel with the motor, synchronization of asynchronous motors, replacement of asynchronous motors with synchronous ones. Measures to improve the energy performance of metal cutting machines are not widespread.
Since in most cases the electric drives of general-purpose metalworking machines work with long pauses, the complex and expensive installation will not be used enough, and therefore the funds spent on it will take too long to recover. Most often reactive power compensation on a general store or general scale. Static capacitor banks are used for these purposes.
