The magnetic field and its parameters, magnetic circuits

Under the term «magnetic field» it is customary to understand a certain energy space in which the forces of magnetic interaction are manifested. They concern:
-
separate substances: ferrimagnets (metals - mainly cast iron, iron and their alloys) and their class of ferrites, regardless of state;
-
moving charges of electricity.
They are called physical bodies that have a common magnetic moment of electrons or other particles of permanent magnets... Their interaction is shown in the photo. magnetic field lines.
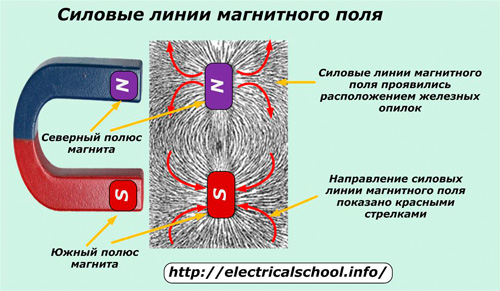
They are formed after bringing a permanent magnet to the back of a cardboard sheet with an even layer of iron filings. The picture shows a clear marking of the North (N) and South (S) Poles with the direction of the field lines relative to their orientation: the exit from the North Pole and the entrance to the South Pole.
How a magnetic field is created
The sources of the magnetic field are:
-
permanent magnets;
-
mobile charges;
-
time-varying electric field.
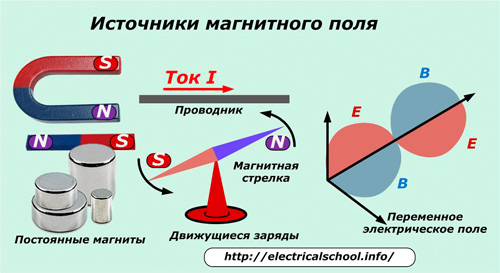
Every child in kindergarten is familiar with the action of permanent magnets.After all, he already had to sculpt pictures-magnets, taken from packets of all kinds of goodies, on the refrigerator.
Electric charges in motion usually have significantly higher magnetic field energy than permanent magnets… It is also denoted by lines of force. Let's analyze the rules for their drawing for a straight wire with current I.
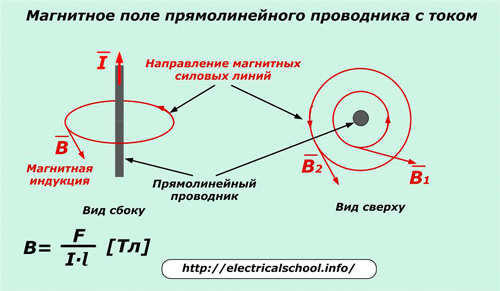
The line of the magnetic field is drawn in a plane perpendicular to the movement of the current, so that at each of its points the force acting on the north pole of the magnetic needle is directed tangentially to this line. This creates concentric circles around the moving charge.
The direction of these forces is determined by the well-known screw or right-hand screw rule.
gimlet rule
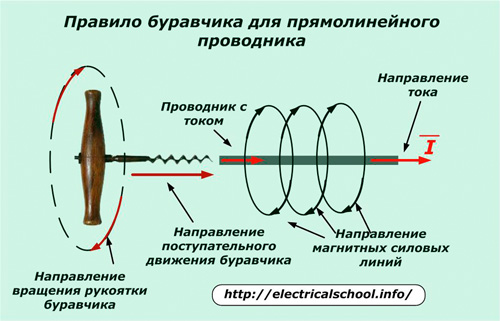
It is necessary to place the gimbal coaxial with the current vector and turn the handle so that the forward movement of the gimbal coincides with its direction. Then the orientation of the magnetic field lines will be indicated by turning the handle.
In a ring conductor, the rotational motion of the handle coincides with the direction of the current, and the translational motion indicates the orientation of the induction.
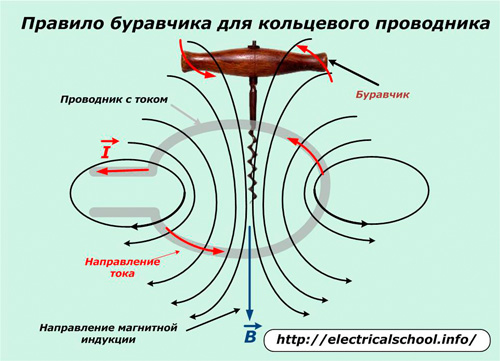
Magnetic field lines always leave the North Pole and enter the South Pole. They continue inside the magnet and are never opened.
See here for more details: How the gimbal rule works in electrical engineering
Rules of interaction of magnetic fields
Magnetic fields from different sources add up to form the resulting field.
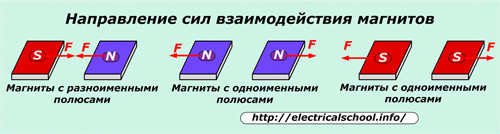
In this case, magnets with opposite poles (N — S) are attracted to each other, and with the same names (N — N, S — S) — they repel each other.The forces of interaction between the poles depend on the distance between them. The closer the poles are shifted, the more force is generated.
Basic characteristics of the magnetic field
They include:
-
magnetic induction vector (V);
-
magnetic flux (F);
-
flux linkage (Ψ).
The intensity or force of the impact of the field is estimated by the value vector of the magnetic induction... It is determined by the value of the force «F» created by the passing current «I» through a wire of length «l». V= F / (I ∙ l)
The unit of measurement of magnetic induction in the SI system is Tesla (in memory of the physicist who studied these phenomena and described them using mathematical methods). In Russian technical literature, it is designated as "T", and in international documentation, the symbol "T" is adopted.
1 T is the induction of such a uniform magnetic flux which acts with a force of 1 newton for every meter of length on a straight wire perpendicular to the direction of the field when a current of 1 ampere passes through that wire.
1T = 1 ∙ N / (A ∙ m)
Vector direction V determined by left hand rule.
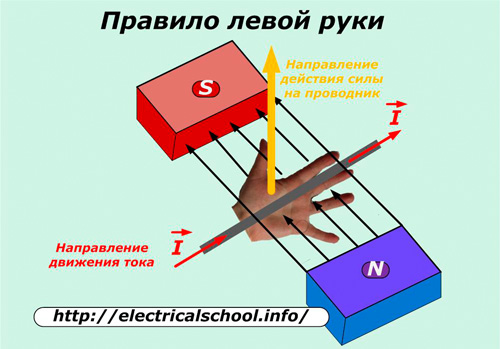
If you place the palm of your left hand in a magnetic field so that the lines of force from the North Pole enter the palm at right angles and place four fingers in the direction of the current in the wire, then the protruding thumb will indicate the direction of the force acting on that wire .
In the event that the conductor with an electric current is not located at right angles to the magnetic field lines, the force acting on it will be proportional to the value of the current flowing and the component of the projection of the length of the conductor with a current on a plane located in a perpendicular direction.
The force acting on an electric current does not depend on the materials from which the conductor is made and its cross-sectional area. Even if this wire does not exist at all and the moving charges start moving in a different environment between the magnetic poles, this force will not change in any way.
If inside the magnetic field at all points the vector V has the same direction and magnitude, then such a field is considered uniform.
Any environment with magnetic properties, affects the value of the induction vector V.
Magnetic flux (F)
If we consider the passage of magnetic induction through a certain region S, then the induction limited to its boundaries will be called magnetic flux.
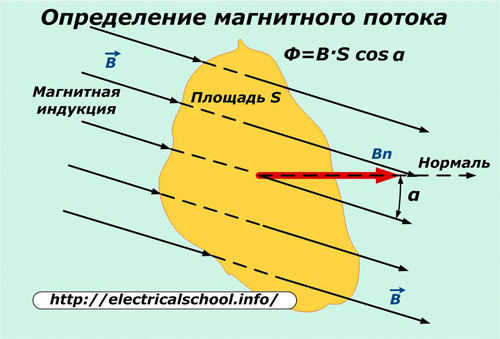
When the region is inclined at some angle α to the direction of magnetic induction, the magnetic flux decreases with the cosine of the angle of inclination of the region. Its maximum value is created when the area is perpendicular to its penetrating induction. Ф = В S
The unit of measurement of magnetic flux is 1 weber, determined by the passage of an induction of 1 tesla through an area of 1 square meter.
Streaming connection
This term is used to obtain the total amount of magnetic flux generated by a certain number of current conductors located between the poles of a magnet.
For the case when the same current I passes through the winding of the coil with the number of turns n, then the total (connected) magnetic flux of all turns is called the flux linkage Ψ.
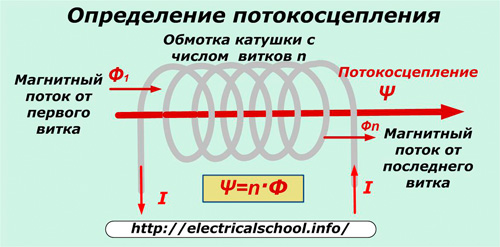
Ψ = n Ф… The unit of flow measurement is 1 weber.
How a magnetic field is formed from an alternating electric
The electromagnetic field interacting with electric charges and bodies with magnetic moments is a combination of two fields:
-
electrical;
-
magnetic.
They are interconnected, they are a combination of each other, and when one changes over time, certain deviations occur in the other. For example, when creating an alternating sinusoidal electric field in a three-phase generator, the same magnetic field is formed simultaneously with the characteristics of similar alternating harmonics.
Magnetic properties of substances
In connection with the interaction with an external magnetic field, substances are divided into:
-
antiferromagnets with balanced magnetic moments, due to which a very small degree of magnetization of the body is created;
-
diamagnets with the property of magnetizing the internal field against the action of the external one. When there is no external field, then their magnetic properties do not manifest;
-
paramagnets with the properties of magnetizing the internal field in the direction of the external action, which have a small degree magnetism;
-
ferromagnetic properties without an applied external field at temperatures below the Curie point;
-
ferrimagnets with unbalanced magnetic moments in magnitude and direction.
All these properties of substances have found various applications in modern technologies.
Magnetic circuits
This term is called a set of different magnetic materials through which a magnetic flux passes. They are analogous to electric circuits and are described by the corresponding mathematical laws (total current, Ohm, Kirchhoff, etc.). Look - Basic laws of electrical engineering.
Based magnetic circuit calculations all transformers, inductors, electrical machines and many other devices are working.
For example, in a working electromagnet, the magnetic flux passes through a magnetic circuit made of ferromagnetic steels and air with pronounced non-ferromagnetic properties. The combination of these elements makes up the magnetic circuit.
Most electrical devices have magnetic circuits in their design. Read more about it in this article — Magnetic circuits of electrical devices
Also read on this topic: Examples of magnetic circuit calculations
