Classification of crane electric drives
Electric crane drive control system
Under the management system electric means a complex consisting of an electrical energy converter, control equipment for switching the current in the electric motor circuit, manual control or automatic (programmed) control, high-speed, track or other control, as well as protective elements for electrical equipment and a mechanism affecting disconnecting devices for electrical equipment and mechanism.
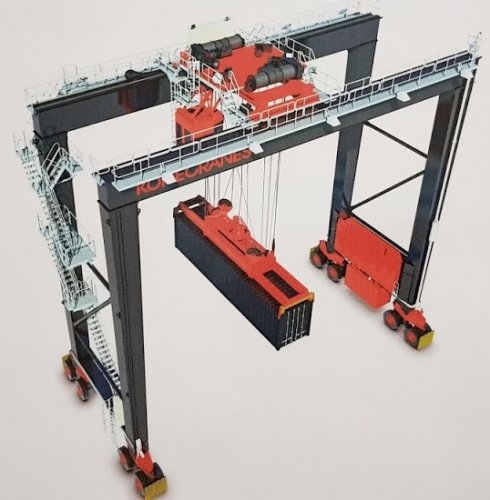
Portal crane:
Bridge crane:
Electric circuits of crane electric drives
Electric circuits of electric drives are divided into the following types.
1. Main circuits through which the main flow of energy of the electric drive passes, as well as the power supply of the lifting magnets.
2. Excitation circuits through which the excitation current of electric machines with direct current, synchronous electric machines with alternating current or electromagnets of braking devices passes, as well as the current of motors of electro-hydraulic thrusters.
3.Control circuits through which commands are sent to the switching devices of the main circuits and the excitation circuits from the controls. In the control circuits, a certain sequence of command execution and switching is also performed according to a predetermined program.
4. Signal circuits that transmit to the operator or control device information about the state of the switching elements of the main circuits and control circuits or about the values of specific parameters of the electric drive and mechanism.
Electric machine and static converters of crane electric drives
 Electric crane drives use electrical and static electrical energy converters.
Electric crane drives use electrical and static electrical energy converters.
In electric machine converters, two (or more) electric machines convert electricityconsumed by the power network in electricity with adjustable parameters (voltage, frequency, current).
In static converters, the conversion of electrical energy is accomplished by contactless switching of DC or AC circuits using controlled and uncontrolled semiconductor devices.
Equipment for controlling electric drives of cranes
Electric drive control equipment is a complex that includes contact and non-contact switching devices in the electric circuits of the motor, energy and control converters, as well as protective elements of the electric circuit.
 Contact equipment in an electric crane drive can be divided into two groups:
Contact equipment in an electric crane drive can be divided into two groups:
1) the control of the contact equipment is carried out directly by the operator using the power controller;
2) with contact drive from an electromagnetic device (contactors and relays).
Classification of crane control system
Crane control systems refer to devices under operator control, i.e. in these systems, the choice of the moment of the start of the operation, the parameters of the speed and the moment of the end of the operation is done by the person who controls the mechanism. In turn, the control system must provide the necessary protection.
The mechanical properties of electric drives are characterized by mechanical characteristics — dependences of the frequency of rotation on the torque on the shaft.
Management systems can be classified according to the method of management and the conditions of regulation.
By way of control of crane control systems there are:
1) is controlled directly by the feed chamber controllers when the control process, including the selection of the necessary accelerations, is performed exclusively by the operator;
2) it is controlled by buttons with buttons when the control options are limited by the design features of the post and by the specified acceleration (deceleration) program;
3) is controlled by a complex overall device (magnetic controller with or without an energy converter.
In this case, the operator selects only the necessary speeds, and the processes of acceleration, deceleration and intermediate switching are carried out automatically.
According to the conditions for regulating the crane control systems, there are:
1) with speed regulation (rotation frequency) below the nominal;
2) with regulation of the speed above the nominal and below the nominal;
3) with adjustment of acceleration and deceleration.
In accordance with the above classification, the following control systems are used in the electric drive of the crane:
-
 K -DP — Direct current electric drive controlled by a power controller;
K -DP — Direct current electric drive controlled by a power controller; -
MK -DP — DC electric drive controlled by a magnetic controller;
-
TP -DP — DC drive with power supply and control through a thyristor converter;
-
GD — DC drive according to the GD (Leonard) system;
-
MP-AD K-electric AC drive with a squirrel-cage motor controlled by a magnetic starter;
-
K-ADK-variable electric drive with a squirrel-cage motor controlled by a power controller;
-
MK-ADD-variable electric drive with a two-speed motor controlled by a magnetic controller;
-
K-ADF-AC electric drive: phase-wound rotor motor controlled by a power regulator;
-
KD-ADF-AC electric drive: phase-wound rotor motor controlled by power controller with dynamic braking by self-excitation method;
-
KI-ADF-AC electric drive: phase-wound rotor motor controlled by power regulator with thyristor pulse switch for speed control;
-
MKP -ADF — AC electric drive: wound rotor motor controlled by a magnetic controller with dynamic opposition braking;
-
MKD-ADF-AC Electric Drive: Phase wound rotor motor controlled by magnetic controller with self-excitation brake;
-
MKB-ADF-AC electric drive: wound-rotor motor controlled by a magnetic controller with arc-free commutation and pulse-switch speed control;
-
TRN -ADF — AC electric drive: rotor wound motor controlled by thyristor voltage regulator;
-
MKI-ADF-AC electric drive: wound rotor motor controlled by magnetic controller with thyristor pulse switch for speed control;
-
PCHN-ADD-AC AC drive: two-speed short-circuit motor controlled by a thyristor frequency converter.
Selecting a crane control system
The selection of a control system for crane mechanisms is made on the basis of the control range, control method, resource (level of wear resistance), the range of possible powers of electric drives, energy and dynamic indicators, as well as additional data that determine operating conditions of electric drives.