How to determine electrical energy savings while increasing power factor
 An important area in saving energy and its rational use is to increase power factor (cos f).
An important area in saving energy and its rational use is to increase power factor (cos f).
Power Factor — A value that indicates how much of the consumed apparent power is active. For the same power being used, a load with a low power factor draws more current, resulting in increased load on power lines and transformers. This leads to a decrease in the working power of the transformer, the generator and increases the losses of electricity in the networks. So, in reduction power factor from one to 0.5, power losses quadruple.
To determine the weighted average power factor for an hour, day, month or year, you can use the formula:
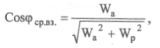
where Wa and Wp are active and reactive power for a certain period of time.
Increasing the power factor in the enterprise is achieved in two ways:
- without installing compensating devices;
- with the installation of compensating devices.
The main consumers of electricity in enterprises are asynchronous electric motors and transformers. The value of the power factor in asynchronous motors and transformers depends on the degree of their loading. At idle, the power factor of the induction motor is 0.1 — 0.25; transformer 0.1 — 0.2. Therefore, to increase the power factor, it is necessary:
- ensure full load of electric motors and transformer;
- elimination of idling; replace underloaded electric motors and transformers, the average load of which does not exceed 30%;
- do high-quality repair of electric motors. It is of great importance to keep the air gap and the calculated data during rewinding in the norm; install synchronous motors whenever possible.
Once you have taken measures to increase the power factor naturally, you can further increase it to the required value with hundredthic capacitors.
Static capacitors can be fitted for individual, group or centralized compensation.
With a sufficiently powerful electrical receiver, you can install static capacitors directly from the user.
In this case, the entire supply and distribution network is completely unloaded from the reactive energy. But in most cases, the enterprise has many low-power users. It is recommended that they establish group or centralized compensation.Centralized compensation makes it possible to make fuller use of the installed capacity of the capacitor, but when they are installed on the low side, only the high-voltage lines and transformers are freed from reactive energy, and the entire network of the plant is not unloaded.
Capacitors are installed in special cabinets or rooms with leakage resistances.
In installations up to 1000 V, it is recommended to install discharge resistors with automatic cut-off when the capacitors are turned off.
The energy consumption of compensating devices is determined by the formula:
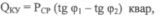
where Psr — average annual active power, kW; tg ф1 — tangent of an angle corresponding to the weighted average Cos ph1 existing in the enterprise; tg ф2 — tangent of the angle corresponding to the weighted average Cos ф2 of the required value.
The value of the discharge resistance is determined by the formula:
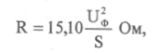
where Uf is the phase voltage of the network, kV; S — capacity battery of capacitors, kvar.
Energy savings from increasing the power factor of the natural in a direct way from Cos f1 to Cos f2 is determined by the formula:
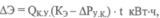
where Wa is the annual active energy consumption, kWh.
When installing compensatory devices, the saving of electrical energy is determined by the formula:

where Qku — reactive compensates for the power of the device, kvar; Ke-economic equivalent equal to 0.1 kW / kvar; Ru.k. — specific consumption of active power for compensation, kW / kvar; t is the number of operating hours of the compensating device per year, h.
Saving electricity when automating the switching on and off of gas discharge lamps, the total power (P2) of the battery of static capacitors of 0.4 kV to eliminate the burning of the lamps when the capacitor battery is turned on is determined by the formula:
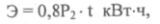 where t is the operating time of the compensating device, h; P2 is the total power of the gas discharge lamps, kW.
where t is the operating time of the compensating device, h; P2 is the total power of the gas discharge lamps, kW.
